int idx;
void inorder(BinaryTreeNode<int> *root, vector<int> &ans, int type){
if(!root) return;
inorder(root->left, ans, type);
if(type==1) root->data = ans[idx++];
else ans.push_back(root->data);
inorder(root->right, ans, type);
}
BinaryTreeNode<int>* binaryTreeToBst(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root){
vector<int> ans;
inorder(root, ans, 0);
sort(begin(ans), end(ans));
idx=0;
inorder(root, ans, 1);
return root;
}Problem of the day
Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Binary Tree To BST
Easy
0/40
Average time to solve is 15m
Problem statement
You have been given a binary tree consisting of ‘N’ nodes where nodes have distinct integer values. Your task is to convert the given Binary Tree to a Binary Search Tree(BST).
Note: The conversion must be done in such a way that keeps the original structure of the Binary Tree.
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure which has the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
For Example:
For the given binary tree :
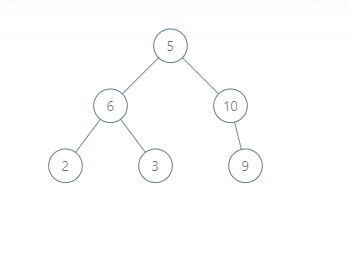
The BST will be:
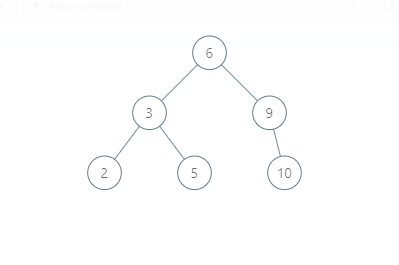
Note: Each node is associated with a unique integer value.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line contains an integer 'T' which denotes the number of test cases or queries to be run. Then the test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains the elements of the tree in the level order form separated by a single space.
If any node does not have a left or right child, take -1 in its place. Refer to the example for further clarification.
Example:
Elements are in the level order form. The input consists of values of nodes separated by a single space in a single line. In case a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image would be :
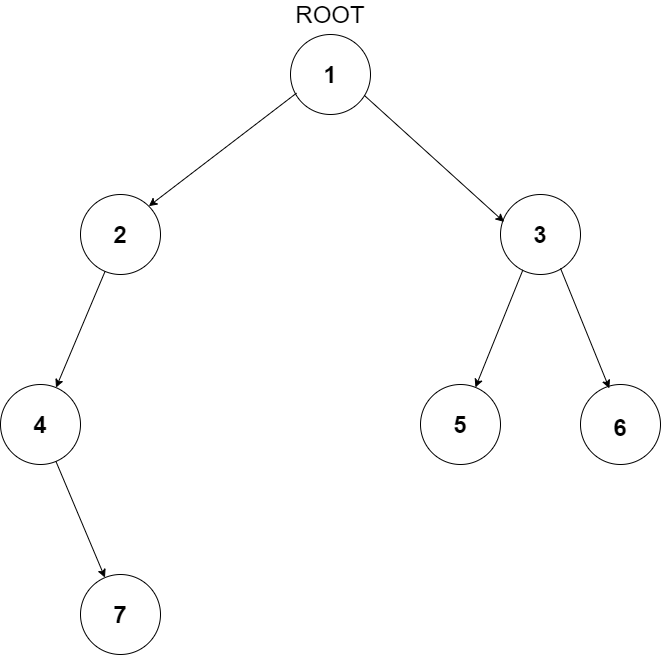
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
Note :
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
For each test case, print a single line containing the level order traversal of the modified binary tree.
The output of each test case will be printed in a separate line.
Note:
You do not need to print anything, It has already been taken care of. Just implement the function.
1 <= T <= 10 ^ 2
1 <= N <= 5 * 10 ^ 3
0 <= data <= 10 ^ 5 and data != -1
Where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the tree, ‘T’ represents the number of test cases and ‘data' denotes data contained in the node of the binary tree.
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1:
1
10 30 15 20 -1 -1 5 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample output 1:
15 10 20 5 30
Explanation of Sample output 1:
The binary tree is represented as follows:
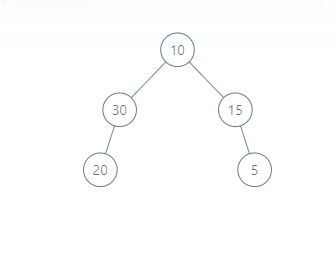
The inorder traversal of this tree will be 20 30 10 15 5.
After converting this tree to BST. It will look like this:

The inorder traversal of the modified tree will be 5 10 15 20 30. Since the inorder is sorted. Hence, it is a valid BST.
Sample Input 2:
2
10 5 -1 -1 -1 -1
20 -1 -1
Sample output 2:
10 5
20
Hint
Hint 1
Use the inorder traversal of the BST.
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Inorder Traversal
We will use the fact that the inorder traversal of BST is sorted.
Here is the algorithm:
- We will traverse the given tree and store the data value of nodes in the array/list.
- Now, sort the array in increasing order.
- Traverse the tree again, but now in an inorder fashion, and put back the values present in the array(in sorted order) to their correct position in the required BST.
Time Complexity
O(N logN), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the Binary Tree.
Since we are storing the node’s values in the array and then sorting it in increasing order, the time complexity is O(N logN).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the Binary Tree.
In the worst case(skewed trees), we will have all the nodes of the Binary Tree in the recursion stack as well as in the array/list. Hence, the space complexity is linear.
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Binary Tree To BST
Interview problems
Single Inorder
139 views
0 replies
1 upvote
Interview problems
C++ Solution
void rec(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root,vector<int>&ans)
{
if (root==NULL) return;
ans.push_back(root->data);
rec(root->left,ans);
rec(root->right,ans);
}
void inorder(BinaryTreeNode<int>* &root,vector<int>&ans,int &ind)
{
if (!root) return ;
inorder(root->left,ans,ind);
root->data=ans[ind++];
inorder(root->right,ans,ind);
}
BinaryTreeNode<int>* binaryTreeToBst(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root)
{
vector<int>ans;
rec(root,ans);
sort(ans.begin(),ans.end());
int ind=0;
inorder(root,ans,ind);
return root;
} 415 views
0 replies
3 upvotes
Interview problems
Java code
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
static void inorder(BinaryTreeNode<Integer> root, List<Integer> ans) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left, ans);
ans.add(root.data);
inorder(root.right, ans);
}
static void solve(BinaryTreeNode<Integer> root, List<Integer> ans, int[] index) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
solve(root.left, ans, index);
root.data = ans.get(index[0]++);
solve(root.right, ans, index);
}
static BinaryTreeNode<Integer> binaryTreeToBst(BinaryTreeNode<Integer> root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, ans);
Collections.sort(ans);
int[] index = {0};
solve(root, ans, index);
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTreeNode<Integer> root = new BinaryTreeNode<>(4);
root.left = new BinaryTreeNode<>(2);
root.right = new BinaryTreeNode<>(7);
root.left.left = new BinaryTreeNode<>(1);
root.left.right = new BinaryTreeNode<>(3);
BinaryTreeNode<Integer> bstRoot = binaryTreeToBst(root);
// Printing the elements of the BST in inorder traversal
printInorder(bstRoot);
}
static void printInorder(BinaryTreeNode<Integer> root) {
if (root != null) {
printInorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
printInorder(root.right);
}
}
}
132 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
c++ sol(performed better than 99.8%)
void helper(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root,vector<int> &ans){
if(!root){
return;
}
helper(root->left,ans);
ans.push_back(root->data);
helper(root->right,ans);
}
void bst(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root,vector<int> &ans,int &idx){
if(!root){
return;
}
bst(root->left,ans,idx);
root->data=ans[idx++];
bst(root->right,ans,idx);
}
BinaryTreeNode<int>* binaryTreeToBst(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root)
{
vector<int> ans;
helper(root,ans);
sort(ans.begin(),ans.end());
int idx=0;
bst(root,ans,idx);
return root;
}
197 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
C++ Easy Using Inorder ✅
void inorder(BinaryTreeNode<int> *root, vector<int> &ans)
{
// base case
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
inorder(root->left, ans);
ans.push_back(root->data);
inorder(root->right, ans);
}
void solve(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root, vector<int> &ans, int &index)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
solve(root->left, ans, index);
root->data=ans[index++];
solve(root->right, ans, index);
}
BinaryTreeNode<int>* binaryTreeToBst(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root)
{
// Write your code here
vector<int> ans;
inorder(root, ans);
sort(ans.begin(), ans.end());
int index=0;
solve(root, ans, index);
return root;
} 182 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
Binary Tree To BST
// Time Complexity:- O(N)
// Space Complexity:- O(N)
// Store All Elements
void inorder1(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root,vector<int>& arr){
if(!root)return;
inorder1(root->left,arr);
arr.push_back(root->data);
inorder1(root->right,arr);
}
// Traverse changing values
void inorder2(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root,int &i,vector<int>& arr){
if(!root)return;
inorder2(root->left,i,arr);
root->data=arr[i++];
inorder2(root->right,i,arr);
}
BinaryTreeNode<int>* binaryTreeToBst(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root)
{
if(!root)return NULL;
vector<int> arr;
inorder1(root,arr);
sort(arr.begin(),arr.end());
int ind=0;
inorder2(root,ind,arr);
return root;
}
235 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
Discussion thread on Interview Problem | Binary Tree To BST
Hey everyone, creating this thread to discuss the interview problem - Binary Tree To BST.
Practise this interview question on Coding Ninjas Studio (hyperlinked with the following link): Binary Tree To BST
312 views
5 replies
0 upvotes
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console


