Last Updated: 12 Jun, 2021
Circle of Words
Ninja
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list of words, your task is to check whether the individual words can be rearranged to form a circle.
Two words, ‘X’ and ‘Y’, can be put together in a circle if the last character of ‘X’ is the same as the first character of ‘Y’ or vice versa.
For Example:
For the array [ “TUNA”, “TIGER”, “RABBIT”, “RAT”, “ANTEATER” ],
A possible circle can be:
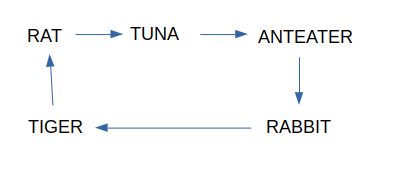
Input Format:
The first line contains a single integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases to be run. Then the test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer ‘N’, representing the size of the array.
The second line of each test case contains ‘N’ space-separated strings representing the words of the given array.
Output Format:
For each test case print ‘true’ if you can make a circle by rearranging the given words, else print ‘false’.
Output for each test case will be printed in a separate line.
Note
You are not required to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 100
1 <= N <= 10^5
1 <= L <= 20
Where L is the length of each word in the given array.
It is guaranteed that the sum of N over all test cases doesn’t exceed 10^5.
Time Limit: 1 sec.
Approaches
We will build a directed graph and for each word, we will add an edge from the first character to the last character in the graph. Now we just have to check whether the graph contains an Eulerian cycle or not. If it contains an Eulerian cycle, then we can form a circle.
The conditions for the existence of an Eulerian cycle in a directed graph are:
- Every node should have in - degree == out-degree.
- All the nodes belong to a single strongly connected component.
Eulerian Cycle: An Eulerian Cycle is a trail that starts and ends at the same graph vertex. In other words, it is a graph cycle that uses each graph edge exactly once.
You can learn more about Eulerian Cycle at the given link:
https://mathworld.wolfram.com/EulerianCycle.html
Algorithm:
- dfs function:
- Create a ‘DFS’ function to traverse the graph.
- It will take the graph, current node, and a ‘VIS’ vector as arguments.
- It will traverse the tree recursively by calling the ‘DFS’ function for the child nodes which are not visited.
- check function:
- It will check whether the graph is fully traversed or not.
- It will take the graph and ‘VIS’ vector as arguments and check whether every existing node is visited or not.
- transpose function:
- It will transpose a given graph.
- It will take the graph and size of the graph as arguments and will reverse each edge and return the transposed graph.
- isStronglyConnected function:
- It will check whether all the nodes of the graph form a single strongly connected component or not.
- We will create a ‘VIS’ vector to store the information whether a node is already visited or not.
- Then we will call the ‘DFS’ function on the graph with an existing node.
- Then we will check whether the graph is fully traversed or not.
- If not, then we will return false.
- Now we will reinitialize the ‘VIS’ vector to false and make a transpose of the graph.
- Then again we will call the ‘DFS’ function on the transposed graph.
- And finally, we will check whether all the nodes are visited or not.
- Given function:
- We will create a vector of vectors to store the adjacency list and two vectors to store the in-degree and out-degree of each node.
- Then we will iterate over the words and for each word add an edge from the first character to the last character of the word.
- We will also count the in-degree and the out-degree of each node.
- Then we will check whether every node has the same in-degree and out-degree or not.
- And finally, we will check whether all the nodes form a single strongly connected component or not.

