Last Updated: 18 Dec, 2020
Find nth elements of spiral matrix
Easy
Asked in company

Given a matrix with ‘N’ rows and ‘M’ columns and an integer ‘K’. Your task is to find the “Kth” element which is obtained while traversing the matrix in spiral form.
Spiral Traversing in the matrix:
The below picture can clearly show how to traverse a matrix in spiral form.
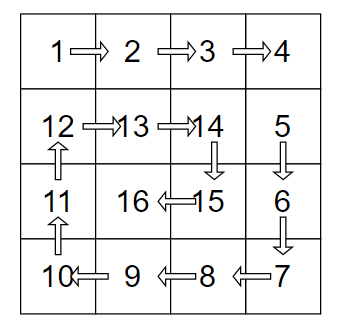
Input format:
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains three space-separated integers ‘N’, ’M’ and ‘K’, where ‘N’ denotes the number of rows in the matrix, ‘M’ denotes the number of columns in the matrix and ‘K’ denotes the position of an element in spiral form matrix.
The next ‘N’ lines for each test case contain the ‘M’ space-separated integer of the “Nth” row of the matrix.
Output Format
For each test case, return an integer that is present at the “kth” position while traversing the matrix in spiral form.
Note:
You do not need to print anything; it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given functions.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 100
1 <= N * M <= 5 * 10^3
1 <= K <= N * M
-10^9 <= mat[i][j] <= 10^9
Time limit: 1 second
Approaches
The basic idea is to start traversing the matrix in spiral form and find the “k’th” element in the traversal.
- We traverse the matrix in spiral form.
- Keep two variables ‘startRow = 0’, ‘startCol = 0’, n and m are already ending indices of row and column.
- Keep a variable ‘count = 0’, if find ‘k == count’ we return.
- Start iterating ‘i’ from ‘startCol’ to ‘m - 1’. For the first row
- For any ‘i’ if ‘count == k’, return ‘matrix[startRow][i]’.
- Update ‘startRow = startRow + 1’.
- Then iterate ‘i’ from ‘startRow’ to ‘n - 1’. For the last column
- For any ‘i’ if ‘count == k’, return ‘matrix[i][m - 1]’.
- Update ‘m = m - 1’.
- Then iterate ‘i’ from ‘m - 1’ to ‘startCol’ with ‘-1’ jumps. We are iterating the last row from right to left.
- For any ‘i’ if ‘count == k’, return ‘matrix[n - 1][i]’.
- Update ‘n = n - 1’
- Then iterate ‘i’ from ‘n - 1’ to ‘startRow’ with ‘-1’ jumps. We are iterating the first column for a bottom to up
- For any ‘i’ if ‘count == k’, return ‘matrix[i][startCol]’.
- Update ‘startCol = startCol + 1’.
- Increase ‘count’ by ‘1’ in every iteration.
- Repeat the same step until ‘count’ does not equal the ‘k’.
If the size of the matrix is ‘n*m’ then the first cycle will contain the first ‘2 * n + 2 * m - 2 * 2’ element because the first row contains ‘m’ element, the last column contains ‘n - 1’, the last row contains 'm - 1’ and the first column contains ‘n - 2’.
- Use two variables ‘startRow =1’ and ‘startCol=1’.
- Iterate a loop ‘level’ from ‘0’ to ‘max(n,m)’
- There can be four cases.
- If ‘ startRow <= k <= m’
- Means k’th element in ‘level’th’ row.
- Then we can find the ‘kth’ element in constant time in this row.
- If ‘ m-level <= k <= n’
- Means k’th element in ‘m-level’th’ column.
- Then we can find the ‘kth’ element in constant time in this column.
- If ‘ (n - 1) * m + 1 <= k <= n * m’
- Means k’th element in ‘n’ row.
- Then we can find the ‘kth’ element in constant time in this row.
- If ‘ startCol - level <= k <= n - 1’
- Means k’th element in ‘startCol - level’ column.
- Then we can find the ‘kth’ element in constant time in this column.
- If any condition is true then find respective ‘k’th element and return else update ‘startCol = startCol + 1’, ‘startRow = startRow + 1’, ‘n = n - 1’ and ‘m = m - 1’.
- Iterate for the next ‘level’.

