Last Updated: 17 Mar, 2021
Insertion in AVL Tree
Moderate
Asked in companies



Ninja has to implement an ‘AVL_TREE’ from scratch.
He is given ‘N’ values, representing the values of nodes to be inserted. Ninja has to insert these values into the ‘AVL_TREE’ and return its root after inserting all the nodes.
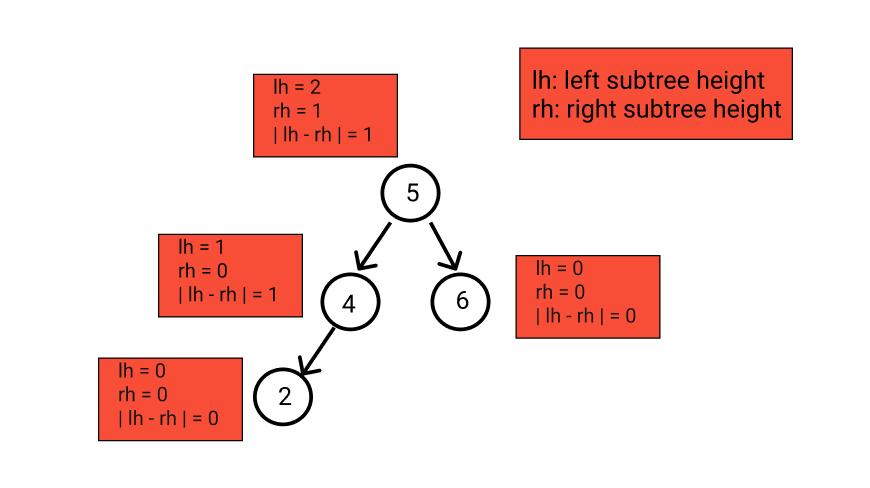
Note: An ‘AVL_TREE’ is a self-balancing Binary Search Tree (BST) where the difference between heights of left and right subtrees cannot be more than one for all nodes.
For example:
Input Format
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ which denotes the number of test cases or queries to be run. Then the test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains an integer ‘N’ which represents the number of nodes in the tree.
The next line of each test case contains ‘N’ single space-separated integers, representing the value of each node.
Output Format :
For each test case, print the ‘AVL_TREE’ after inserting all the nodes in level order.
Print the output of each test case in a separate line.
Note:
You do not need to print anything; it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints :
1 <= ‘T’ <= 10
1 <= ‘N’ <= 10^4
1 <= ‘DATA’ <= 10^5
Time Limit: 1 second
Approaches
We have to implement ‘AVL_TREE’ from scratch and we know ‘AVL_TREE’ follows the ‘BST’ properties. So first, we insert a new node into ‘AVL_TREE’ according to the ‘BST’ properties.
‘BST’ property:
DATA(left) < DATA(root) < DATA(right) for every node.
And the difference between heights of left and right subtrees cannot be more than one for all nodes.
After inserting the new node in our tree according to the ‘BST’ properties our tree may be unbalanced (i.e the difference between the height of left and right subtree more than one for a node).
So for making this tree balance we have to perform some operations:
- Left Rotation.
- Right Rotation.
Here, T1, T2, and T3 are the subtrees of the trees.
For re-balancing the tree by performing appropriate rotations we have 4 possible cases that need to be handled.
- Left Left case
- Left Right case
- Right Right case
- Right Left case
Left-Left case:
Left-Right case:
Right-Right case:
Right-Left case:
Here is the algorithm:
- First, we insert a new node into our tree according to the standard ‘BST’ insertion.
- Starting from the root, we traverse the whole tree and find the unbalanced node.
- Then we re-balance the tree by performing appropriate rotations. We have 4 possible cases as discussed above that need to be handled.

