Last Updated: 9 Nov, 2020
Day 7 : Langford Pairing
Easy
Asked in companies


You are given a positive integer N. Return a list of integers of size 2N containing all the integers from 1 to N (both inclusive) twice arranged according to Langford pairing. If no such pairing exists return -1 is the only list element.
Note:
There may be more than one Langford pair possible, you need to return anyone permutation.
For example:
For N = 4, one possible Langford pairing will be:-
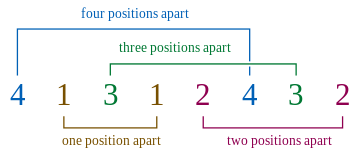
Input format:
The first line contains an integer 'T' which denotes the number of test cases or queries to be run. Then, the T test cases follow.
The first and only line of each test case or query contains the integer N.
Output format:
The only line of output contains “Valid” if the answer is correct and “Invalid” if it’s not, without quotes.
Note:
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 5
0 <= N <= 32
Time Limit: 1 sec
Approaches
It can be observed with some examples that for any number N, the permutation following Langford pairing is possible only if either N mod 4 is 0 or 3. Thus, Langford pairing is possible for 3, 4, 7, 8, etc, and not possible for 1, 2, 5, 6, etc. Now to find the sequence,
- If N mod 4 is 1 or 2, return -1.
- Otherwise, we will use recursion to generate the sequence.
- Create an array of size 2*N and initialize all its elements with 0.
- Now, we will fill the elements in the array keeping in mind the following things:
- We will start filling the array from the maximum number i.e N.
- Once we fill an integer A at the position i, we will also fill integer A at position i+A+1.
- Thus we will call langfordPairing(result, N) to find the sequence where the result is the list in which we will save one required permutation
Algorithm:
bool langfordPairing(result, N):
- If N is 0, there is no element left to put in the sequence, return true.
- For i = 0 to result.size() - N - 1:
- If (i)th and (i+N+1)th position i.e the first and second possible positions for placing N are vacant and also within range of the array result.
- Then add N to the sequence, arr[i] = N, arr[i + N + 1] = N.
- Recursively fill the rest of the elements and find whether it is possible to make the sequence or not, isExists = langfordPairing(arr, N-1, result).
- If isExists is true, then we have found the sequence. Thus return true.
- Otherwise, we need to remove N from the slots, arr[i] = 0, arr[i + N + 1] = 0.
- If (i)th and (i+N+1)th position i.e the first and second possible positions for placing N are vacant and also within range of the array result.
- No such sequence exists, return false.

