Last Updated: 18 Nov, 2020
Word Search - l
Moderate
Asked in companies



You are given a 2D board('N' rows and 'M' columns) of characters and a string 'word'.
Your task is to return true if the given word exists in the grid, else return false. The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring.
Note:
The same letter cell should not be used more than once.
For Example:
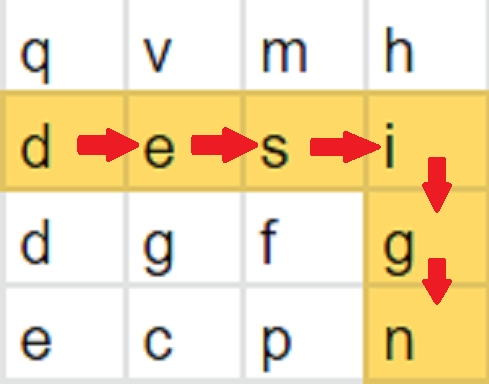
For a given word “design” and the given 2D board
[[q’, ‘v’, ‘m’, ‘h’],
[‘d’, ‘e’, ‘s’, ‘i’],
[‘d’, ‘g’, ‘f’, ‘g’],
[‘e’, ‘c’, ‘p’, ‘n’]]
The word design can be formed by sequentially adjacent cells as shown by the highlighted color in the 2nd row and last column.
Input Format:
The first line contains a string 'word'.
The second line of input contains two single space-separated integers 'N' and 'M' representing the number of rows and columns of the grid respectively.
The next 'N' lines contain 'M' single space-separated characters each representing the elements in a row of the matrix.
Output Format:
The only line contains either “true” or “false”.
Note:
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the function.
Approaches
Approach:
To efficiently find a word on a board using a DFS approach, we can explore the board starting from each cell as the initial position for the first letter of the word.
We check if the current cell matches the corresponding letter of the word. If it does, we mark the cell as visited and proceed to check the neighboring cells for the next letter. We continue this process recursively, incrementing the level of the word, until we either find the complete word or reach a dead-end.
If we successfully reach the level equal to the length of the word plus one, it means we have found the word on the board. Otherwise, if we exhaust all possible starting cells without finding the word, we conclude that it is not present on the board.
By utilizing DFS and backtracking, we efficiently explore different paths on the board, maximizing the chances of finding the desired word.
Algorithm:
- Iterate over each cell on the board using nested loops.
- If the current cell matches the first letter of the word, call the dfs function with the current position (i, j) and the starting index 0.
- If dfs returns true, it means the word was found on the board, so return true.
- If no matches were found, return false to indicate that the word is not present on the board.
The dfs function :
- If ‘k’ is equal to the length of the word, return true.
- If the current position (i, j) is out of bounds or the current cell is marked as visited or the current cell doesn't match the letter at index k in the word, return false.
- Store the value of the current cell in a temporary variable temp.
- Mark the current cell as visited by setting board[i][j] to '#'.
- Recursively call dfs for the neighboring cells with the index as 1 greater than the present one.
- Restore the original value of the current cell by setting ‘board[i][j]’ back to temp.
- Return true if any of the neighboring cells returned true (indicating the word was found in one of the paths), or false if none of them found the word.

