#include <iostream>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Union by Size
class disjoint_set{
vector<int> size,parent;
public:
// constructor
disjoint_set(int n){
size.resize(n+1,1);
parent.resize(n+1);
for(int i = 0;i<n+1;i++){
parent[i] = i;
}
}
int find_ultimate_parent(int node){
// base case
if(parent[node]==node){
return node;
}
// applying recursion for path compression
return parent[node] = find_ultimate_parent(parent[node]);
}
void union_by_size(int u,int v){
int ulp_u = find_ultimate_parent(u);
int ulp_v = find_ultimate_parent(v);
// already belong to same component
if(parent[ulp_u] == parent[ulp_v]){return;}
// connect the smaller component to larger component
if(size[ulp_u] < size[ulp_v]){
parent[ulp_u] = ulp_v;
size[ulp_v] += size[ulp_u];
}
else{
parent[ulp_v] = ulp_u;
size[ulp_u] += size[ulp_v];
}
return;
}
};
int main() {
int n,m;
cin>>n;
cin>>m;
priority_queue<pair<int,pair<int,int>>,vector<pair<int,pair<int,int>>>,greater<pair<int,pair<int,int>>>>pq;
int times = m;
while(times--){
int u,v,wt;
cin>>u>>v>>wt;
pq.push({wt,{u,v}});
}
vector<pair<int,pair<int,int>>> ans;
disjoint_set ds = disjoint_set(n);
while(!pq.empty()){
int u = pq.top().second.first;
int v = pq.top().second.second;
int wt = pq.top().first;
pq.pop();
// if already belong to same component than can cause loop
if(ds.find_ultimate_parent(u)==ds.find_ultimate_parent(v)){
continue;
}
ans.push_back({wt,{u,v}});
ds.union_by_size(u,v);
}
for(auto it : ans){
int wt = it.first;
int u = it.second.first;
int v = it.second.second;
int v1,v2;
if(u<v){
v1 = u;
v2 = v;
}
else{
v1 = v;
v2 = u;
}
cout<<v1<<" "<<v2<<" "<<wt<<endl;
}
return 0;
}Problem of the day
Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Code : Kruskal's Algorithm
Hard
0/120
Average time to solve is 45m
7 upvotes
Asked in company

Problem statement
Given an undirected, connected and weighted graph G(V, E) with V number of vertices (which are numbered from 0 to V-1) and E number of edges.
Find and print the Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) using Kruskal's algorithm.
For printing MST follow the steps -
1. In one line, print an edge which is part of MST in the format -
v1 v2 w
where, v1 and v2 are the vertices of the edge which is included in MST and whose weight is w. And v1 <= v2 i.e. print the smaller vertex first while printing an edge.
2. Print V-1 edges in above format in different lines.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format :
Line 1: Two Integers V and E (separated by space)
Next E lines : Three integers ei, ej and wi, denoting that there exists an edge between vertex ei and vertex ej with weight wi (separated by space)
Print the MST, as described in the task.
Constraints :
2 <= V, E <= 10^5
Time Limit: 1 sec
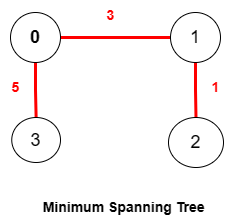
Sample Input 1 :
4 4
0 1 3
0 3 5
1 2 1
2 3 8

Sample Output 1 :
1 2 1
0 1 3
0 3 5
Code : Kruskal's Algorithm
Interview problems
Union by Size | Priority Queue | Kruskal
27 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
very very simple code using disjoint set in C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class disjointset{
vector<int> size,parent;
public:
disjointset(int n){
size.resize(n+1);
parent.resize(n+1);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
parent[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
int findUparent(int node){
if(node == parent[node]){
return node;
}
return parent[node] = findUparent(parent[node]);
}
int unionbysize(int u,int v){
int up_u = findUparent(u);
int up_v = findUparent(v);
if(size[up_u] < size[up_v]){
parent[up_u] = up_v;
size[up_v] += size[up_u];
}
else{
parent[up_v] = up_u;
size[up_u] += size[up_v];
}
}
};
int main() {
int V,E;
cin>>V>>E;
vector<pair<int,pair<int,int>>> edge;
for(int i=0;i<E;i++){
int u,v,wt;
cin>>u>>v>>wt;
if(u<V || v<V){
edge.push_back({wt,{u,v}});
}
}
sort(edge.begin(),edge.end());
disjointset ds(V);
vector<pair<pair<int,int>,int>> ans;
for(auto it:edge){
int wt = it.first;
int u = it.second.first;
int v = it.second.second;
if(ds.findUparent(u) != ds.findUparent(v)){
ds.unionbysize(u,v);
if(u<v){
// cout<<u<<v<<wt<<endl;
ans.push_back({{u,v},wt});
}
else{
// cout<<v<<u<<wt<<endl;
ans.push_back({{v,u},wt});
}
}
}
for(int it=ans.size()-1;it>=0;it--){
cout<<ans[it].first.first<<" ";
cout<<ans[it].first.second<<" ";
cout<<ans[it].second;
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
152 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
Why there is only one solution set for MST ?
In TEST CASE 3 →
i am getting
2 3 2
1 3 2
0 3 2
but the answer is
2 3 2
1 3 2
0 1 2
both have SAME weight therefore the mst is still true for my output too.
we can have multiple mst for a graph.
90 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
Discussion thread on Interview Problem | Code : Kruskal's Algorithm
Hey everyone, creating this thread to discuss the interview problem - Code : Kruskal's Algorithm.
Practise this interview question on Coding Ninjas Studio (hyperlinked with the following link): Code : Kruskal's Algorithm
247 views
3 replies
0 upvotes
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console