Last Updated: 12 Jan, 2021
Negative Cycle in a Directed Graph
Moderate
Asked in company

You have been given a directed weighted graph of ‘N’ vertices labeled from 1 to 'N' and ‘M’ edges. Each edge connecting two nodes 'u' and 'v' has a weight 'w' denoting the distance between them.
Your task is to detect whether the graph contains a negative cycle or not. A negative cycle is a cycle whose edges are such that the sum of their weights is a negative value.
Example:
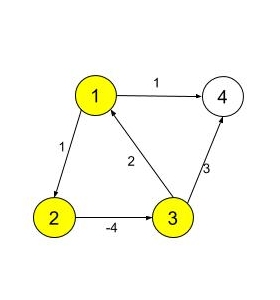
The above graph contains a cycle ( 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 1 ) and the sum of weights of edges is -1 (1 - 4 + 2 = -1) which is negative. Hence the graph contains a negative cycle.
Note:
It's guaranteed that the graph doesn't contain self-loops and multiple edges.
Input format:
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two single space-separated integers ‘N’ and ‘M’ denoting the number of vertices and the number of edges in the directed graph, respectively.
The next ‘M’ lines each contain three single space-separated integers ‘u’, ‘v’, and ‘w’, denoting an edge from vertex ‘u’ to vertex ‘v’, having weight ‘w’.
Output format:
For each test case, return “True” if there is a negative cycle, else “False”.
Note:
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 10
1 <= N <= 50
1 <= M <= 300
1 <= u,v <= N
-10^5 <= w <= 10^5
Time Limit: 1 sec
Approaches
Bellman-Ford Algorithm:
In this algorithm, we have a source vertex and we find the shortest path from source to all the vertices.
For this, we will create an array of distances ‘D[1...N]’, where ‘D[i]’ stores the distance of vertex ‘i’ from the source vertex. Initially all the array values contain an infinite value, except ‘D[source]’, ‘D[source]’ = 0.
The algorithm consists of several iterations and in each iteration, we try to produce relaxation in the edges. Relaxation means reducing the value of ‘D[i]’.
For this, we will iterate on the edges of the graph, let’s consider an edge (‘u’, ’v’, ’w’) :
- If ‘D[v]’ is greater than ‘D[u]’ + ‘w’, then ‘D[v]’ = ‘D[u]’ + ‘w’.
The algorithm claims that ‘N-1’ iterations are enough to find the distances of the vertices from the source vertex.
How to use this algorithm to detect a negative cycle in a graph?
Using this algorithm, we can find the distances of the vertices from the source vertex. But instead of ‘N-1’ iteration, we will do ‘N’ iterations and in the last iteration, if there is any change in the values of array ‘D’, then the given graph contains a negative cycle.
Algorithm:
- Iterate on the source (vertex 1 to vertex ‘N’).
- Make an array ‘D’ and initialize the array with an infinite value, except ‘D[source]’, ‘D[source]’ = 0.
- Do ‘N’ iterations and in each iteration follow the below steps:
- Iterate on the edges on the graph and for each edge (‘u’,’v’,’w’) update the value to ‘D[v]’, i.e., ‘D[v]’ = min(‘D[v]’, ‘D[u]+w’).
- In the Nth iteration, if there is an edge (‘u’,’v’,’w’) such that, ‘D[v]’ is less than ‘D[u]+w’, then the given graph contains a negative cycle.
Floyd-Warshall Algorithm:
In this algorithm, we calculate the shortest distance between every pair of vertices.
We will create a 2D array ‘D[][]’, where ‘D[i][j]’ stores the shortest distance from vertex ‘i’ to vertex ‘j’.
Initialise the 2D array with an infinite value.
Iterate on the vertices 1 to ‘N’, initialise ‘D[i][i]’ with 0.
Iterate on the edges of the graph, and each edge (‘u’,’v’,’w’) update ‘D[u][v]’, i.e., ‘D[u][v]’ = ‘w’.
Now we will use Dynamic Programming to find the minimum distance between every pair of vertices.
For(k: 1 to ‘N’){
For(i: 1 to ‘N’){
For(j: 1 to ‘N’){
‘D[i][j]’ = min(‘D[i][j]’, ‘D[i][k]’ + ‘D[k][j]’)
}
}
}
How to use this algorithm to detect a negative cycle in a graph?
After finding the shortest distance between every pair of vertices, iterate on the vertices, if there is a vertex ‘v’ such that ‘D[v][v]’ is not equal to zero, then the given graph contains a negative cycle.

