Last Updated: 2 Dec, 2020
Remove a node from BST
Moderate
Asked in company

You are given a BST (Binary search tree) with’ N’ number of nodes and a node ‘X’ (which is definitely present in the input the BST). You need to remove the node ‘X’ and return the root of the updated BST.
For example:
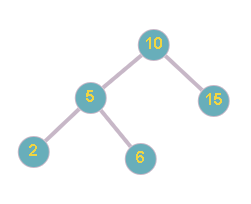

Figure1 : Input BST and Figure2: Output BST
In the above example, For the given BST (Fig.1) and X = 6, we have output( Fig. 2 ) after removing node 6.
Input Format:
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’, denoting the number of test cases. Then each test case follows.
The first line of each test case contains nodes in the level order form (separated by space). If any node does not have a left or right child, take -1 in its place.
The second and the last line of each test case contains ‘X’ denoting the node to remove.
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image.

10
5 15
2 6 -1 -1
-1 -1 -1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 10
Level 2 :
Left child of 10 = 5
Right child of 10 = 15
Level 3 :
Left child of 5 = 2
Right child of 5 = 6
Left child of 15 = null(-1)
Right child of 15 = null (-1)
Level 4 :
Left child of 2 = null (-1)
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
The first not-null node(of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null(-1).
Note :
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
10 5 15 2 6 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Output Format:
For each test case, print a single line containing ‘N’-1 single space-separated integers, which is the inorder traversal of updated BST..
The output of each test case will be printed on a separate line.
Note:
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 5
1 <= N <= 5 * 10 ^ 3
1 <= nodeVal[i] <= 10 ^ 9
Time Limit: 1 sec.
Approaches
The deletion of a node in BST is based on the following three observations.
- Node to be removed is the leaf node:
- Simply remove the node.
- Node to be removed has only one child:
- Copy the child to the node and delete the child
- Node to be deleted has two children:
- Find in-order successor of the node. Copy contents of the inorder successor to the node and delete the inorder successor. (Note that in order predecessor can also be used.)
- the inorder successor can be obtained by finding the minimum value in the right child of the node.
Algorithm :
Let the ‘removeNode’ be the function to remove the given node from BST. It accepts two parameters (root node of tree, key node to be deleted). It returns the root of the updated tree.
- If the root is NULL then return NULL
- If the ‘key’ to be deleted is smaller than the ‘root -> val', then delete from left subtree by recursively calling the function with ‘root -> left' and ‘key’, store the return value in 'root -> left'.
- If the ‘key’ to be deleted is greater than the ‘root -> val', then delete from the right subtree by recursively calling the function with ‘root’ -> right and ‘key’ and store the returned value in root -> right.
- Else this ‘root’ node is the node to be deleted.
- If the node has no child
- Delete node and return NULL
- If the node has an only right child
- Store right subtree in ‘temp’ as ‘temp’ = ‘root’ -> right
- Delete current node ‘root’
- Return ‘temp’
- If the node has only left child
- Store left subtree in ‘temp’ as ‘temp’ = ‘root’ -> left
- Delete current node ‘root’
- Return ‘temp’
- Else node has two children, find the inorder successor
- Store the min node in ‘minNode’ by calling the function minRightNode as ‘minNode’ = minRightNode( root -> right ).
- Copy the content of ‘minNode’ to ‘root’ node as root->val = minNode ->val.
- Recursively call removeNode on parameter root->right and minNode -> key to remove minimum value node from right subtree.
- If the node has no child
- Return root
Description of minRightNode function:
Let ‘minRightNode’ be the function that returns the minimum value node. It accepts the ‘root’ of the tree. Loop left down to find the leftmost node whose left child is NULL.
minRightNode( ‘root’ ):
- While root left is not NULL
- Move to left child i.e ‘root’ = ‘root’ - > left
- Return root
The idea is to avoid recursive calls for the deletion of the successor in the right subtree when a node with two children is found. We can use an extra pointer tailing the successor pointer and removing the successor pointer and linking the right subtree of the successor.
Algorithm :
Let the ‘removeNode’ be the function to remove the node from BST. It accepts two parameters (root node of tree, key node to be deleted). It returns the root of the updated tree.
- If the root is NULL then return NULL
- If the ‘key’ to be deleted is smaller than the ‘root -> val', then delete from left subtree by recursively calling functions with ‘root -> left' and ‘key’ and store the returned value in root -> left.
- If the ‘key’ to be deleted is greater than the ‘root -> val', then delete from the right subtree by recursively calling the function with ‘root -> right' and ‘key’ and store the returned value in root -> right.
- Else this ‘root’ node is the node to be deleted.
- If the node has no child
- Delete node and return NULL
- If the node has an only right child
- Store right subtree in ‘temp’ as ‘temp’ = ‘root’ -> right
- Delete current node ‘root’
- Return ‘temp’
- If the node has only left child
- Store left subtree in ‘temp’ as ‘temp’ = ‘root’ -> left
- Delete current node ‘root’
- Return ‘temp’
- Else node has two children, find the inorder successor and parent of this successor
- Let ‘succParent’ be a pointer that store the parent of a successor, initialized to ‘root’
- Let ‘succ’ be the pointer, which stores the successor.
- Run a loop while succ ->left is not NULL
- ‘succParent’ = ‘succ’
- ‘succ’ = ‘succ’ -> left
- If ‘succParent’ is equal to ‘root’
- ‘succParent’ -> right = ‘succ’ -> left
- Else
- ‘succParent -> left = ‘succ’ -> left
- ‘Root’ -> val = ’succ’ -> val
- Delete ‘succ’
- Return ‘root’
- If the node has no child
Similar problems
Guess Price
Easy
Posted: 13 Dec, 2021
Unique BSTs
Hard
Posted: 15 Dec, 2021
Unique BSTs
Hard
Posted: 15 Dec, 2021
Unique BSTs
Hard
Posted: 15 Dec, 2021
Kth Largest Element in BST
Moderate
Posted: 12 Mar, 2022
Two Sum IV - Input is a BST
Moderate
Posted: 22 Mar, 2022
Icarus and BSTCOUNT
Hard
Posted: 1 Apr, 2022

