What is ALBERT MODEL?
ALBERT, also known as A-Light BERT, is a version of transformer model BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers).
BERT is a neural network architecture to model language-based tasks. BERT generates representations for different words by interpreting the text it is trained on (the text is usually a big dataset, consisting of millions of sentences). BERT uses a stack of self-attention & fully connected layers to encode a sentence.
ALBERT Model Architecture
There are three ways in which ALBERT is better than BERT:
1. Factorized Embedding Parameterization: The embedding dimensions are tied to the hidden layer in the BERT, which means we cannot increase the hidden layer size without increasing the embedding size & parameters; this problem is addressed in ALBERT effectively.
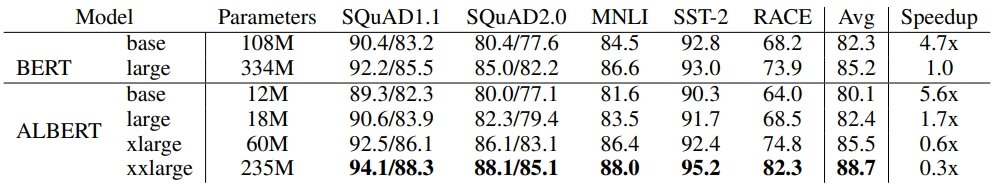
2. Cross-Layer Parameter Sharing: The ALBERT Model shares all its parameters across the stack of self-attention and fully-connected layers by which it decreases the parameters by many folds & hence improves the parameter efficiency. It leads to a 70 percent reduction in the overall parameters of the model.
3. Inter-Sentence Coherence Loss: The BERT model was trained on the NSP (Next Sentence Prediction) task, which was relatively easier to predict; the ALBERT was trained on a task that has to predict whether the sentences are coherent or not.
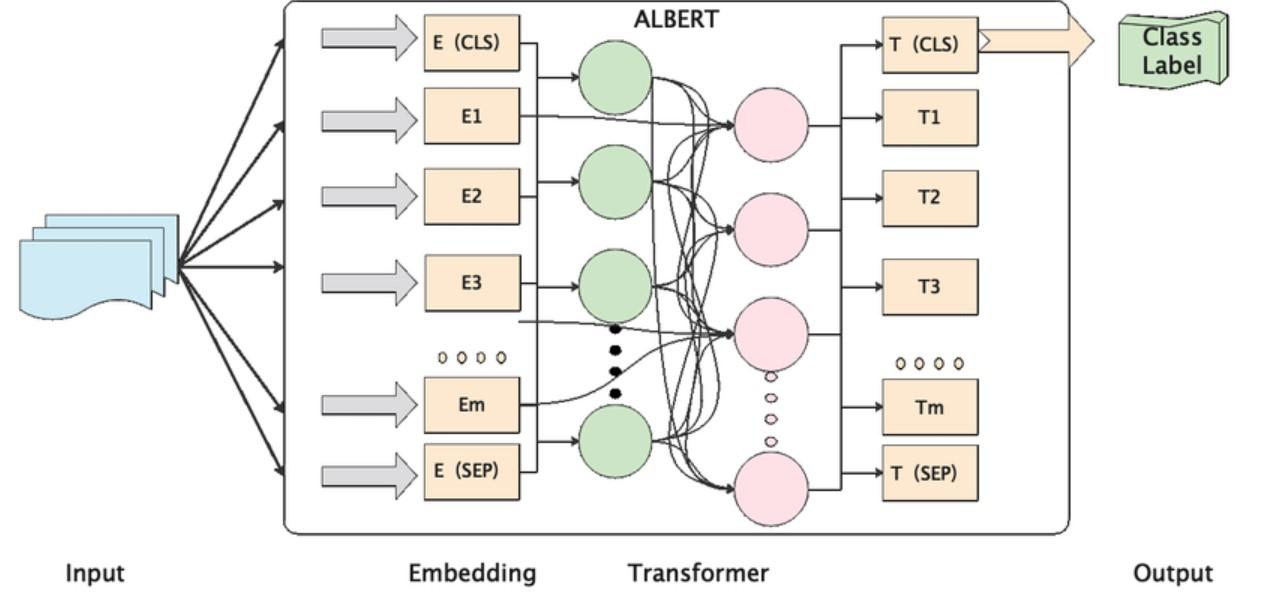
ALBERT Architecture
Source: ResearchGate
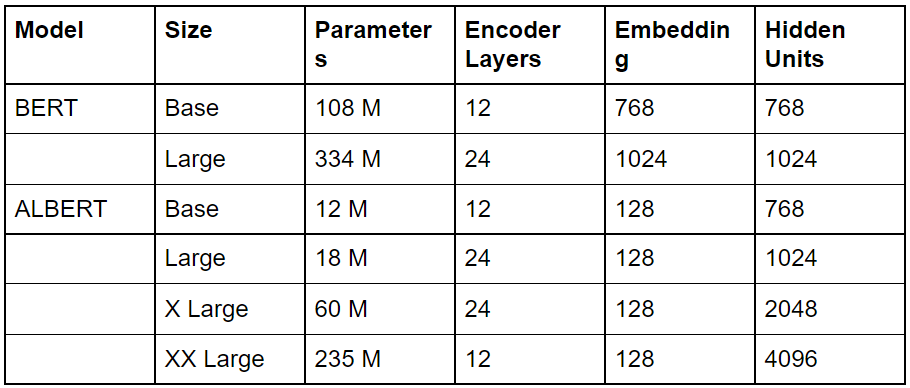
BERT is released in two, whereas the ALBERT Model is released in four different model sizes: