Introduction
We will be making a model that will be generating new baby names. Technologies used while making this model is deep learning and natural language processing. To be specific, we will be using recurrent neural networks, which are part of deep learning.
Recommended topic: Machine Learning
Model Building
I will be implementing the following model in google colab. As google colab provides GPU, it will make the model training process fast.
Importing libraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import plotly.graph_objects as go
import plotly.figure_factory as ff
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import random
import string
import tensorflow as tfReading Dataset
You can download the dataset from here.
with open('/content/drive/MyDrive/Names.txt','r') as f:
names = f.read().split("\n")[:-1]Analyzing the Dataset
Printing size of the dataset and maximum length of the name from the dataset.
print("Number of Names: ",len(names))
print("\nMax Length of a Name: ",max(map(len,names))-1)Number of Names: 3668
Max Length of a Name: 13
Printing 10 random names from the dataset.
names_size = len(names)
for i in range(10):
a = random.randint(0, len(names))
print(names[a])Rolfe
Jagger
Farrell
Warner
Woodford
Kirkpatrick
Jordon
Boulton
Caton
Till
Furthermore, we will plot name vs length distribution.
fig = ff.create_distplot([list(map(len,names))], group_labels=["Length"])
fig.update_layout(title="Name-Length Distribution")
fig.show()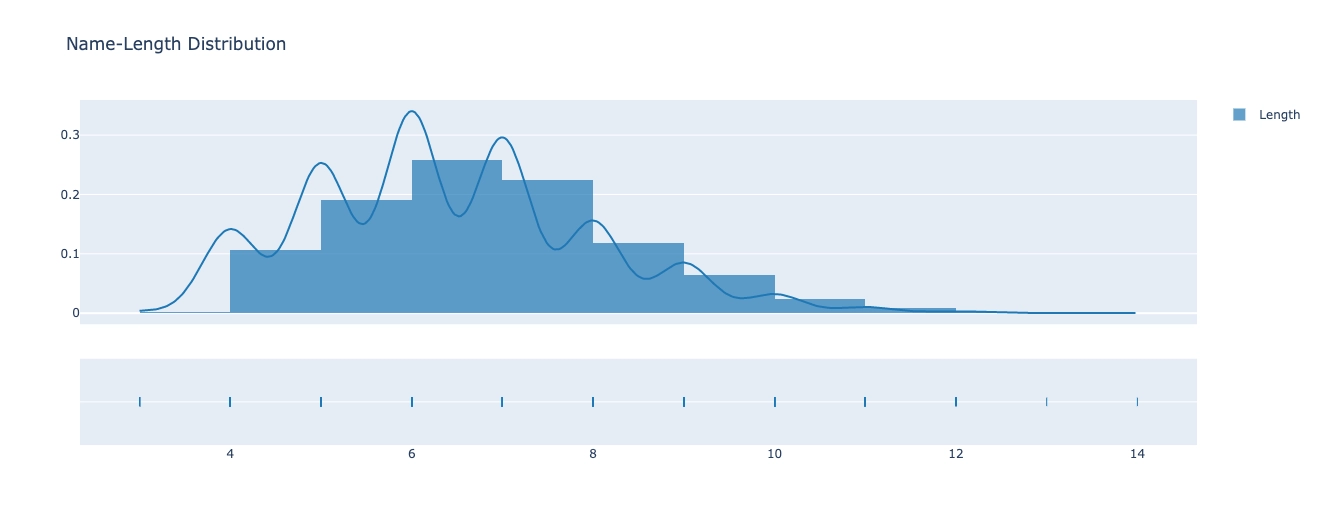
Data Preprocessing
Removing all the names having length more than 10.
MAX_LENGTH = 10
names = [name for name in names if len(name)<=MAX_LENGTH]
print("Number of Names: ",len(names))
assert max(map(len,names))<=MAX_LENGTH, f"Names length more than {MAX_LENGTH}"Number of Names: 3628
Now, we will tokenize the names.
start_token = " "
# we will use this pad_token to make size of each name equal
pad_token = "#"
#Add start token in front of all Names
names = [start_token+name for name in names]
MAX_LENGTH += 1
# set of tokens
tokens = sorted(set("".join(names + [pad_token])))
tokens = list(tokens)
n_tokens = len(tokens)
print("Tokens: ",tokens)
print ('n_tokens:', n_tokens)Tokens: [' ', '#', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'Y', 'Z', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z']
n_tokens: 53
As we know neural networks can understand only numbers so we will map each letter with a number.
ttd = dict(zip(tokens,range(len(tokens))))
def to_matrix(names, mx_ln=None, pad=ttd[pad_token], dtype=np.int32):
mx_ln = mx_ln or max(map(len, names))
names_ix = np.zeros([len(names), mx_ln], dtype) + pad
for i in range(len(names)):
name_ix = list(map(ttd.get, names[i]))
names_ix[i, :len(name_ix)] = name_ix
return names_ix
Let us see print some integer vectored names.
print('\n'.join(names[::200]))
print(to_matrix(names[::200]))Abbas
Bailey
Cain
Daley
Ealy
Farnsworth
Garrett
Harden
Irwin
Kewley
Lewis
Mcgrory
Norgrove
Pemberton
Renwick
Simon
Tilston
Wadham
Yarnall
[[ 0 2 28 28 27 45 1 1 1 1 1]
[ 0 3 27 35 38 31 51 1 1 1 1]
[ 0 4 27 35 40 1 1 1 1 1 1]
[ 0 5 27 38 31 51 1 1 1 1 1]
[ 0 6 27 38 51 1 1 1 1 1 1]
[ 0 7 27 44 40 45 49 41 44 46 34]
[ 0 8 27 44 44 31 46 46 1 1 1]
[ 0 9 27 44 30 31 40 1 1 1 1]
[ 0 10 44 49 35 40 1 1 1 1 1]
[ 0 12 31 49 38 31 51 1 1 1 1]
[ 0 13 31 49 35 45 1 1 1 1 1]
[ 0 14 29 33 44 41 44 51 1 1 1]
[ 0 15 41 44 33 44 41 48 31 1 1]
[ 0 17 31 39 28 31 44 46 41 40 1]
[ 0 19 31 40 49 35 29 37 1 1 1]
[ 0 20 35 39 41 40 1 1 1 1 1]
[ 0 21 35 38 45 46 41 40 1 1 1]
[ 0 24 27 30 34 27 39 1 1 1 1]
[ 0 25 27 44 40 27 38 38 1 1 1]]As we can see that every name is converted in the form of vector of integers.
Transforming all the names in the integer vectored format.
X = to_matrix(names)
X_train = np.zeros((X.shape[0],X.shape[1],n_tokens),np.int32)
y_train = np.zeros((X.shape[0],X.shape[1],n_tokens),np.int32)
for i, name in enumerate(X):
for j in range(MAX_LENGTH-1):
X_train[i,j,name[j]] = 1
y_train[i,j,name[j+1]] = 1
X_train[i,MAX_LENGTH-1,name[MAX_LENGTH-1]] = 1
y_train[i,MAX_LENGTH-1,ttd[pad_token]] = 1Defining Model
def make_model():
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential()
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Embedding(n_tokens,
16,input_length=MAX_LENGTH))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.SimpleRNN(256,
return_sequences=True,
activation='elu'))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.SimpleRNN(256,
return_sequences=True,
activation='elu'))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(n_tokens,
activation='softmax'))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.001))
return modelmodel = make_model()
model.summary()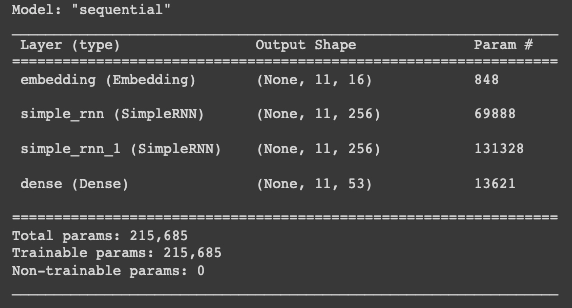
Declaring some variables like batch size, steps_per_epoch, name_count, training_dataset will help in the training model.
name_count = X.shape[0]
BS = 32
STEPS_PER_EPOCH = np.ceil(name_count/BATCH_SIZE)
AUTO = tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE
ignore_order = tf.data.Options()
ignore_order.experimental_deterministic = False
train_dataset = (
tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((X,y_train))
.shuffle(5000)
.cache()
.repeat()
.batch(BS)
.prefetch(AUTO))
We will also define the cyclic learning rate function in the model.
class CyclicLR(tf.keras.callbacks.Callback):
def __init__(self,base_learning_rate=1e-5,mx_learning_rate=1e-3,ss=10):
super().__init__()
self.base_learning_rate = base_learning_rate
self.mx_learning_rate = mx_learning_rate
self.ss = ss
self.iterations = 0
self.history = {}
def clr(self):
cycle = np.floor((1+self.iterations)/(2*self.ss))
x = np.abs(self.iterations/self.ss - 2*cycle + 1)
return self.base_learning_rate + (self.mx_learning_rate - self.base_learning_rate)*(np.maximum(0,1-x))
def on_train_begin(self,logs={}):
tf.keras.backend.set_value(self.model.optimizer.lr, self.base_learning_rate)
def on_batch_end(self,batch,logs=None):
logs = logs or {}
self.iterations += 1
self.history.setdefault('lr', []).append(tf.keras.backend.get_value(self.model.optimizer.lr))
self.history.setdefault('iterations', []).append(self.iterations)
for k, v in logs.items():
self.history.setdefault(k, []).append(v)
tf.keras.backend.set_value(self.model.optimizer.lr, self.clr())Training Model
We are using cyclic learning rate for our model. To know more about cyclic learning rate visit this blog.
%%time
cyclicLR = CyclicLR(base_lr=1e-4,max_lr=1e-3,stepsize=6000)
EPOCHS = 100
history = model.fit(train_dataset,steps_per_epoch=STEPS_PER_EPOCH,epochs=EPOCHS,callbacks=[cyclicLR])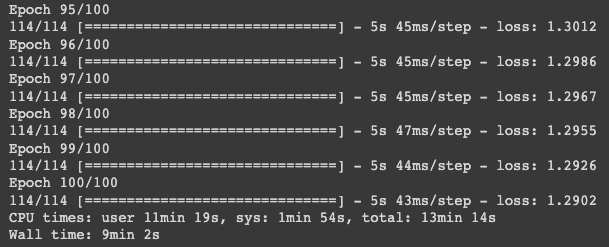
Plotting the loss vs epochs graph.
plot = go.Figure()
plot.add_trace(go.Scatter(x=np.arange(1,len(history.history['loss'])+1), y=history.history['loss'], mode='lines+markers', name='Training loss'))
plot.update_layout(title_text="Training loss")
plot.show()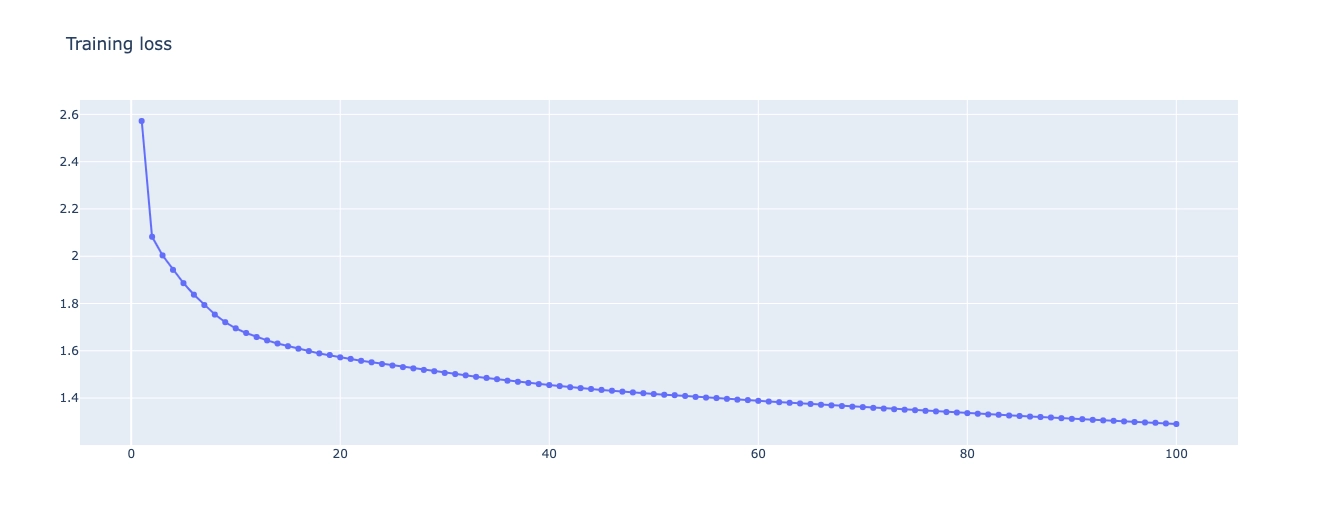
Generating New Names
We will create an function that will generate new names.
def generateName(model=model, sp=start_token, mxl=MAX_LENGTH):
assert len(sp)<mxl, f"Length of the Seed-phrase is more than Max-Length: {mxl}"
name = [sp]
x = np.zeros((1,mxl),np.int32)
x[0,0:len(sp)] = [ttd[token] for token in sp]
for i in range(len(sp),mxl):
p = list(model.predict(x)[0,i-1])
p = p/np.sum(p)
index = np.random.choice(range(n_tokens),p=p)
if index == ttd[pad_token]:
break
x[0,i] = index
name.append(tokens[index])
return "".join(name)
Saving the weights of the trained model.
weights = 'IndianNamesWeights.h5'
model.save_weights(weights)
Loading the model.
predictor = make_model()
predictor.load_weights(weights)
Seed phrase with single alphabet.
sp = f" {np.random.choice(list(string.ascii_uppercase))}"
for _ in range(20):
name = generateName(predictor,sp=sp)
if name not in names:
print(f"{name.lstrip()} (New Name)")
else:
print(name.lstrip())Mallan (New Name)
Manderlann (New Name)
Mtcurwost (New Name)
Mtoustan (New Name)
Mackullan (New Name)
Mottell (New Name)
Mcgue (New Name)
Mcgeerall (New Name)
Maller (New Name)
Mindhim (New Name)
Miceinaroe (New Name)
Memingtan (New Name)
Maddeil (New Name)
Mymie (New Name)
Mcchien (New Name)
Melingy (New Name)
Maclley (New Name)
Murthe (New Name)
Maler (New Name)
Mattinson (New Name)
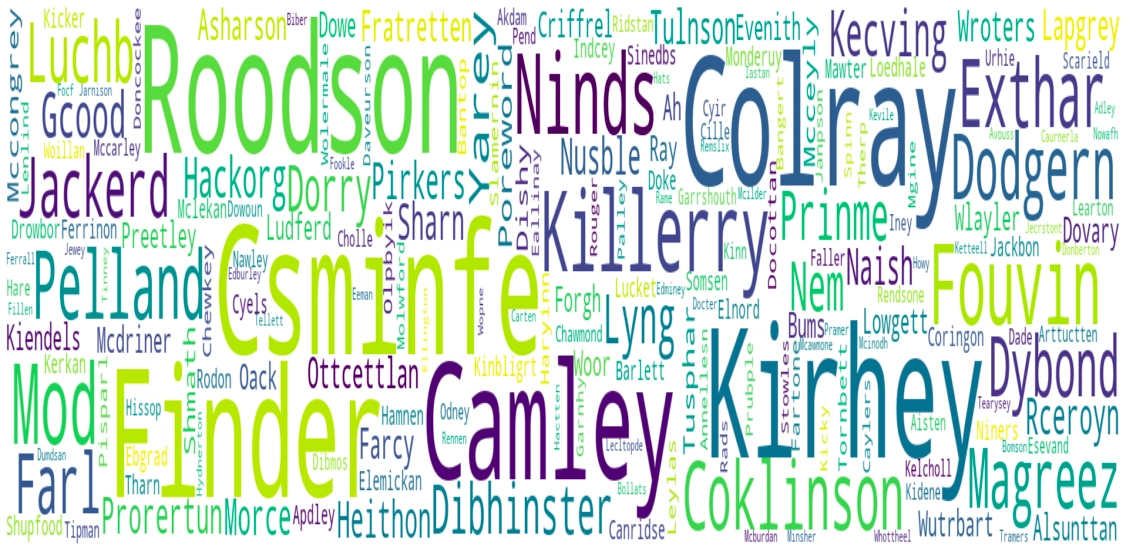
Interactive plotting of newly generated names using wordcloud.
A = []
while len(A) is not 200:
new_name = generateName(predictor)
if new_name not in names:
A.append(new_name.lstrip())
WC = WordCloud(background_color="white",height=400,width=1900).generate(" ".join(A))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(20, 10))
ax.imshow(WC, interpolation='bilinear',aspect='auto')
ax.axis("off")
plt.show()