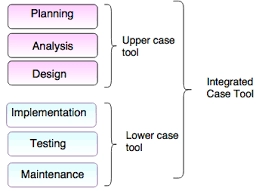
CASE is stand for Computer-Aided Software Engineering (CASE) is automated support for the software engineering process. It is used to support and automate activities throughout the systems development life cycle (SDLC). This automated software tool is used by systems analysts to increase productivity and improve the overall quality of systems.

CASE tools stand for any tools used to automate some action related to software development. It makes the software development process easy and efficient.
Types of CASE Tools:
1. Business process engineering tools
It represents business data objects, their relationships, and the flow of the data objects between company business areas.
2. Project planning tools
It is used for cost and effort estimation and project scheduling.
3. Process modeling and management tools
It represents key elements of processes and provides links to other tools that provide support to defined process activities.
4. Risk analysis tools
This tool helps project managers build risk tables by providing detailed guidance in the identification and analysis of risks.
5. Requirements tracing tools
provide a systematic database-like approach to tracking requirement status beginning with specification
6. Metrics and management tools
Management-oriented tools capture technically oriented metrics determine metrics that provide greater insight into the quality of design or code and project-specific metrics that provide an overall indication of productivity or quality.
7. Documentation tools
It provides opportunities for improved productivity by reducing the amount of time needed to produce work products.
8. System software tools
It is the network system software, object management services, distributed component support, and communications software.
9. Quality assurance tools
These are the tools that extract metrics to project the quality of software being built or metrics tools that audit source code to determine compliance with language standards.
10. Software configuration management tools
It uses the CASE repository to assist with all SCMtasks (identification, version control, change control, auditing, status accounting)
11. Database management tools
Database management tools are software applications designed to assist users in managing, storing, organizing, and manipulating data within a database system. These tools offer various functionalities to facilitate efficient management of databases.
12. Analysis and design tools
It enables the software engineer to create analysis and design models of the system to be built perform consistency checking between models.
What are use CASE tools?
- Improve the quality of systems developed
- Increase speed of development and design
- Ease and improve the testing process through automated checking
- Improve integration of development activities via common methodologies
- Improve quality and completeness of documentation
- Help standardize the development process
- Improve project management
- Simply program maintenance
- Promote reusability
- Improve software portability