Introduction
The Azure IoT Hub facilitates highly secure and reliable communication between IoT applications and their connected devices. It is a cloud-hosted solution that can connect to any device virtually. It offers per-device authentication, built-in device management and scaled provisioning to help developers build efficient IoT solutions. The access to Azure IoT Hub can be configured as per the user's choice. It provides various options to grant permissions and control the access to each IoT Hub endpoint. There are two main ways to control access to IoT Hub in Azure. The Azure Active Directory Integration and by using Shared Access Signatures.
Azure Active Directory Integration
Azure Active Directory is an enterprise identity service that provides multi-factor authentication, single sign-on and conditional access to guard against most cybersecurity attacks. Its identity control plane grants complete visibility of your environment and ensures that only the right people can access the resources when needed. Azure RBAC (Role-based access control) is an authorisation system built on the Azure Resource Manager to provide fine-grained access management of Azure resources. The integration between Azure AD and Azure RABC is supported only for IoT Hub service APIs.
Azure AD can authenticate requests to service APIs, not device APIs, on IoT Hub. When it receives an access request, the identity is first authenticated. The request needs to contain an OAuth 2.0 access token at runtime. Applications running in an Azure resource like an Azure VM or Azure App Service need not have credentials and can be represented as a managed service. Authentication is followed by authorisation. IoT Hub uses Azure AD’s role assignment service to determine the permissions granted to the identity. IoT Hub authorises the request if the permissions match the requested resource or API.
Azure RBAC role
Azure IoT Hub provides some in-built roles to allow access to its service APIs. They are as follows.

Assigning RABC roles requires one to know the resource scope the identity must be allowed to have. The levels of the scope of access, starting from the narrowest, are as follows.
-
The IoT hub is the smallest scope that can be offered to an identity.
-
The resource group - At this scope, the role has access to all IoT hubs in the resource group.
-
The subscription - In this level, the role has access to all IoT hubs in all resource groups under a subscription.
- A management group - It is the largest scope offered. Roles can access all IoT hubs in all resource groups in all subscriptions in the management group.
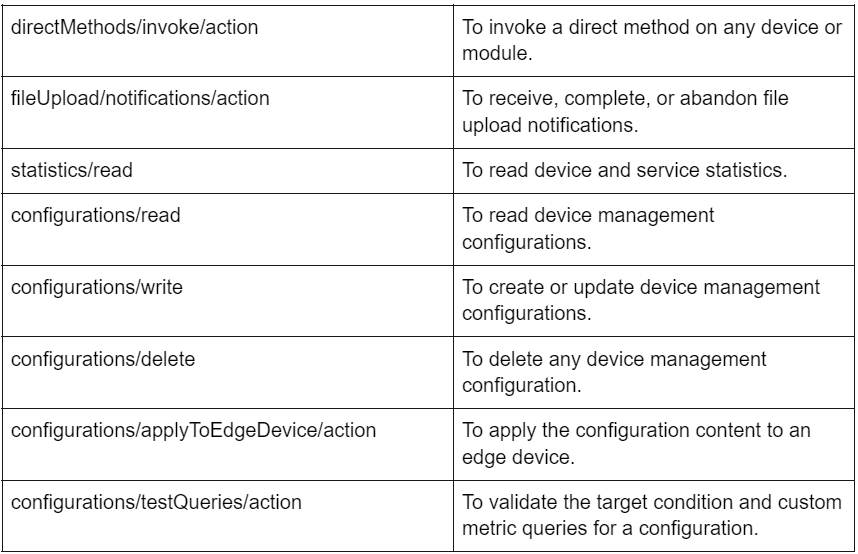
IoT Service Hub APIs Permissions
Permissions can be set to specific roles to perform operations such as create, update, read, write or delete. All the following permissions are prefixed with Microsoft.Devices/IoTHubs/.

Azure AD access in Azure Portal
When requesting access to IoT Hub, the Azure portal first checks if the identity has already been assigned an Azure role with Microsoft.Devices/iotHubs/listkeys/action. If it does, the Azure portal uses keys from shared access policies to access IoT Hub. Otherwise, the Azure portal tries to access data using the identity’s Azure AD account.
Accessing IoT Hub from the Azure portal using an Azure AD account requires permissions to access IoT Hub data resources and to go to an IoT Hub resource in the Azure portal. The built-in roles provided by IoT Hub only grant access to resources like devices and twins and not to the IoT Hub resource. This requires the assignment of an Azure Resource Manager role like Reader. The Reader role is a restricted role that only allows navigation in the portal. It doesn't include the permission to access all IoT Hub data resources via shared access policies.
Azure IoT extension for Azure CLI
The type of authentication can be controlled and set using the --auth-type parameter, which accepts key or login values. The key value is the default.
The Azure CLI automatically discovers a suitable policy to interact with IoT Hub when- auth-type has a matching key value. If it is just another key value, an access token from the Azure CLI logged in by the identity is used for the operation.






