Introduction
There are many operations performed on arrays in Python. Some of them take a lot of time, while some of them occur fast. Also, there are different techniques used for performing operations on arrays. Vectorisation and Broadcasting are two such essential techniques. Moreover, broadcasting is a technique that helps implement vectorization on arrays of different dimensions.

In this article, we will study the difference between Vectorisation and Broadcasting.
What is Vectorization?
Vectorization is a technique used in Python on arrays to implement functions on arrays without using for loops. It is implemented using the numpy module and uses pre-defined functions. These functions are optimized and reduce the calculation time. Numpy is a C implementation of arrays in Python, and thus, vectorized functions implemented using numpy are faster.
Let us see some examples of vectorization as follows. First, let us see a simple Python program to find a new array with its elements as the sum of two elements at the same index of two arrays.
OUTPUT
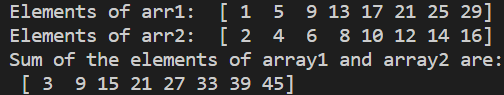
Here, we use the .arange() function to generate an array with a maximum value of 30, a common difference of 4, and starting with 1. Next, we develop a 1D array using the .array() function. Then, we create a function named .myfunc() to return the sum of two passed parameters. We use the .vectorize() function to store the functionalities of the .myfunc() function in the vectorfunction. And finally, we print it.
Now, let us see an example that will clarify that vectorization reduces the time taken to complete the computations.
OUTPUT

Here, we use the time module to find the time at that point of time in the code. We take an array and find its sum using two methods. We can see that the sum using for loop takes more time than the vectorization method. Thus, we use the vectorization methods.





