Introduction
In C++, a class is a user-defined type or data structure that includes data and functions as members and whose access is controlled by the three access specifiers private, protected, and public. Access to members of a C++ class is usually restricted.

A function is a code block that only executes when it is invoked. Parameters are data that may be sent into a function. Functions are used to accomplish specific tasks and are essential for code reuse: Once you've defined the code, you may use it repeatedly.
Also see, Literals in C.Fibonacci Series in C++
What is the Friend Function in C++?
When a function is defined as a buddy function in C++, it has access to the protected and private data of the class. The term friend specifies that the specified function is a friend function to the compiler. For accessing data, a friend function should be declared inside the body of a class, beginning with the term friend.
In the declaration above, the word friend is used to prefix the friend function. The function can be declared anywhere in the program, just like any other C++ function. Neither the keyword friend nor the scope resolution operator in the function declaration is utilized.
Characteristics of Friend Function
-
The friend function does not belong to the class of which it is a friend.
-
It can't be called with the object since it's not in the scope of that class.
-
It may be invoked just like any other function without the object.
-
It is unable to obtain member names directly. As a result, it must utilize the dot membership operator with the member name and an object name.
- It might be written in a private or public area.
Ways to Implement a Friend Function in C++
There are different ways to implement the friend function in C++.
-
Inside the class
- Outside the class
1. Implementing the friend function Inside the class in C++
While implementing the friend function, you can define it in the class file as well. Below is an example for better understanding.
Output

2. Implementing the friend function Outside the class in C++
While implementing the friend function, you can define it outside the class file as well. Below is an example for better understanding.
Output
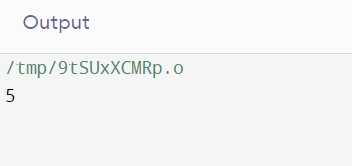
Program 1:
Output:
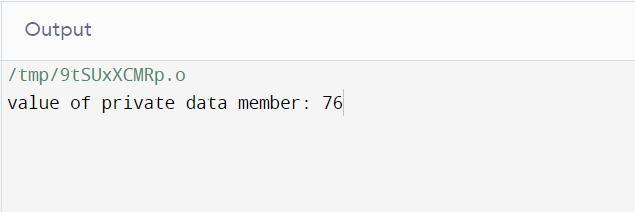
Try and compile with online c++ compiler.
Example of Friend Function in C++
Output

Features of Friend Functions in C++
- Allow access to private and protected members of a class
- Not members of a class but declared within its scope
- Can be declared within a class or outside it
- Can be declared as friend functions of multiple classes
- Cannot access the members directly using the dot operator
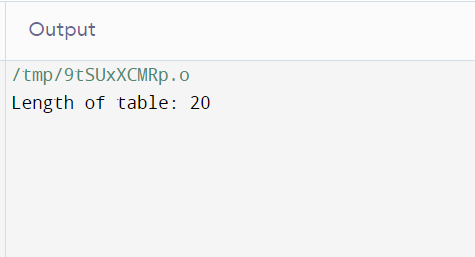
C++ Function Overloading Using Friend Function
Function overloading in C++ allows multiple functions with the same name but different parameter lists. Friend functions can be overloaded to work with different classes, providing flexibility in accessing private members.
Output:
Value of x: 0
Value of y: 10
Advantages of Friend Functions:
- Allows access to private and protected members of a class
- Can be used to implement operators for user-defined types
- Enhances encapsulation by restricting access to selected functions or classes
- Enables efficient code reuse by allowing non-member functions to operate on class objects
Disadvantages of Friend Functions:
- Breaks encapsulation by exposing private members to external functions
- Can make the code less readable and harder to maintain
- Increases coupling between classes, reducing flexibility and scalability
- Requires careful management to ensure proper access control and minimize security risks