Introduction
Hey Readers!!
Have you ever thought about when a client wants to fetch the API? What should he do?
There when GraphQL comes into play. It is a query language that helps the client to use the programming interface to fetch the APIs.
Let’s begin to learn more about it.
GraphQL
GraphQL is a query language which specifies how a client should use an application programming interface to seek information (API). Developers can use the GraphQL syntax to request specific data and receive it back from various sources. The exact structure of data is returned from the server once the client has specified the structure of the data that is required.
Sending GraphQL queries using Query Parameters
Now let’s learn about how to send GraphQL queries using Query Parameters:
- Create a Web Service Request object and select RESTful as the Request Type.
- Select the GET request method in the Web Service Request object editor.
- In the URL, add this:
https://countries.trevorblades.com/graphql?query=query Query { country(code: "VN") { name native capital emoji currency languages { code name } }}- Name: query
- Value: query Query { country(code: "VN") { name native capital emoji currency languages { code name } }}

- Save and click on Test Request and Verify.
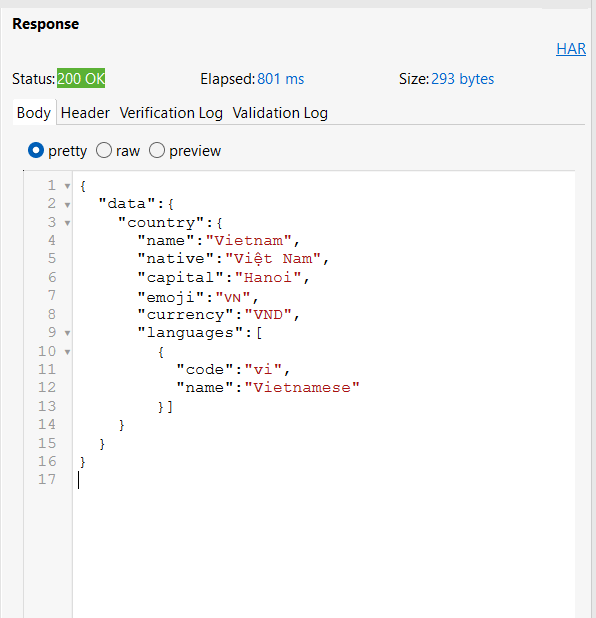
Result
The country information is displayed as JSON responses in the Response tab.
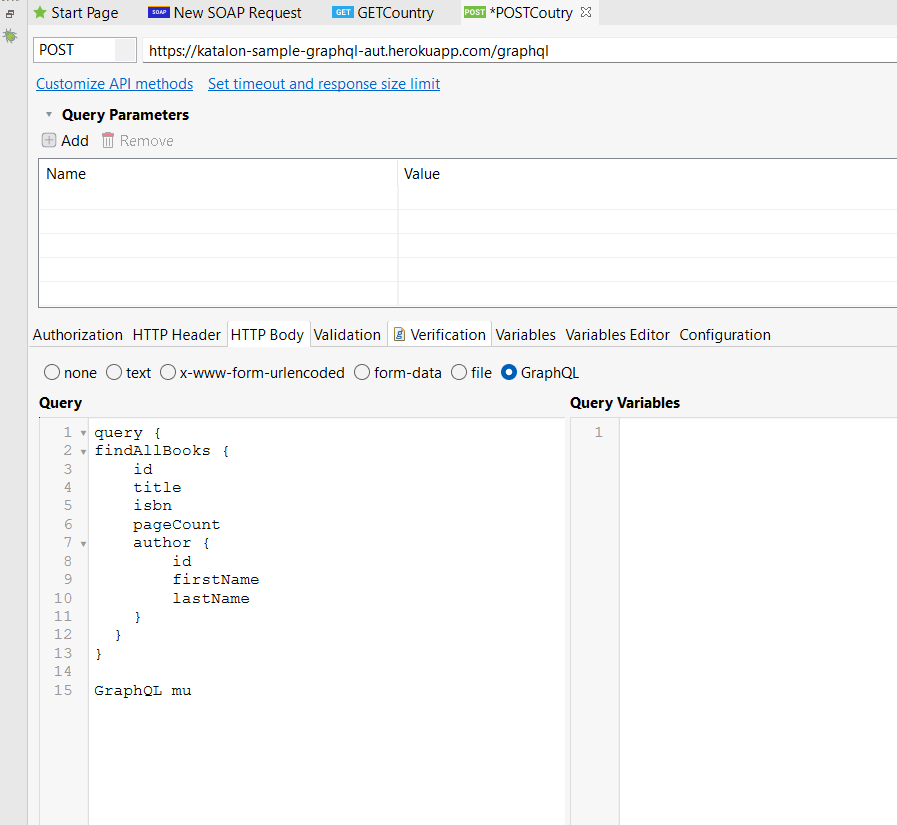
Sending GraphQL queries and mutations in the HTTP Body
Follow these steps to send a GraphQL query in the HTTP Body:
- Make a Web Service Request object and select RESTful as the Request Type.
- Select the POST request method in the Web Service Request object editor.
- In the URL, add this https://katalon-sample-graphql-aut.herokuapp.com/graphql
- Enter your GraphQL mutation or query in the Query textbox.
- GraphQL Query :
query {
findAllBooks {
id
title
isbn
pageCount
author {
id
firstName
lastName
}
}
}- GraphQL mutation
mutation {
deleteBook(id:3)
}
- Then click Test Request and Verify after saving your request.
- Look out for all the outcomes on the Response tab.
Result
- Use GraphQL to search for all books.

- Use a GraphQL mutation to create a new book.
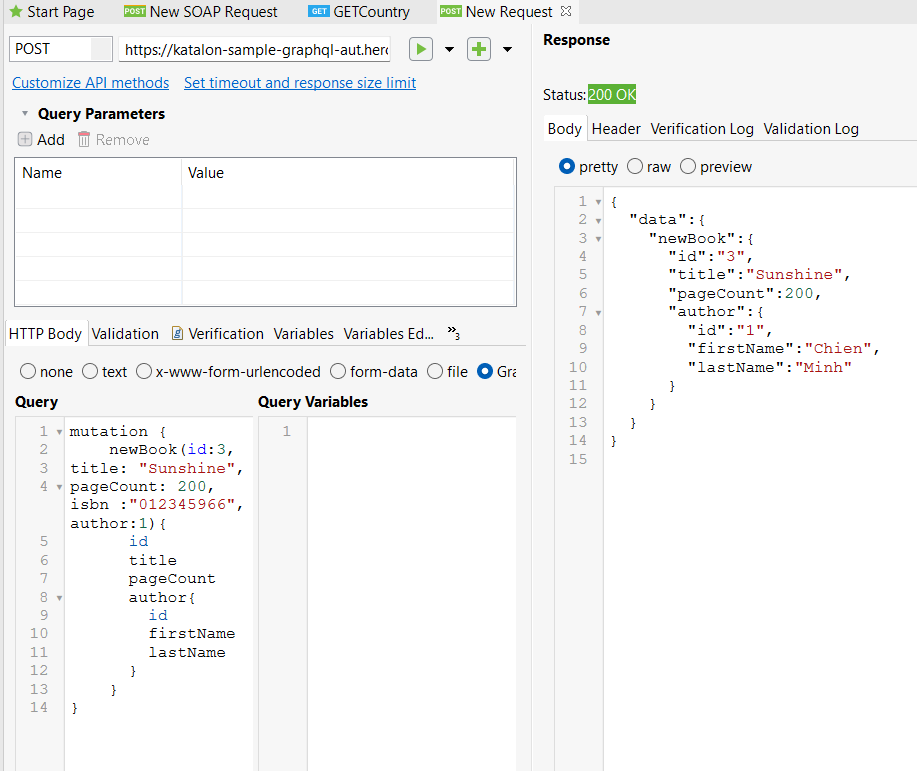
- Modify a book's name with a GraphQL mutation.
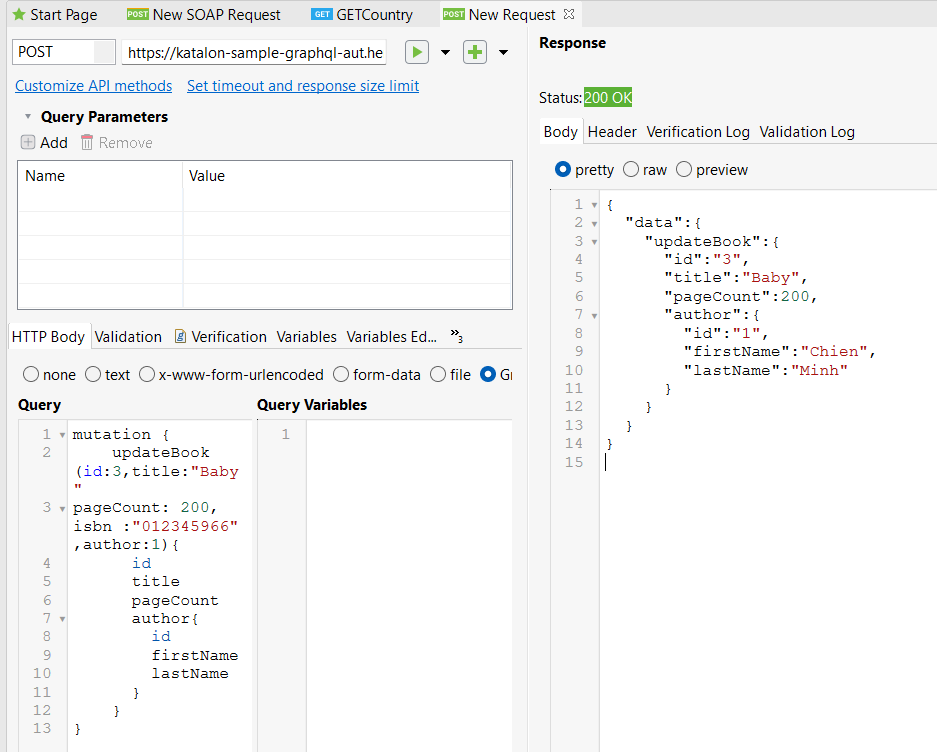
- Using a GraphQL mutation, delete a book.

Add a GraphQL request to a test case
A GraphQL request can be included in a test case.
Use GraphQL variables
A GraphQL request can be included in a test case.
- Select the GraphQL body type under the HTTP Body tab.
- Put your GraphQL query with defined variables into the Query textbox.

- Put the values of your GraphQL variables in the Query Variables textbox.
Example :
{
"id": "AU"
}Validate GraphQL requests and responses against schemas
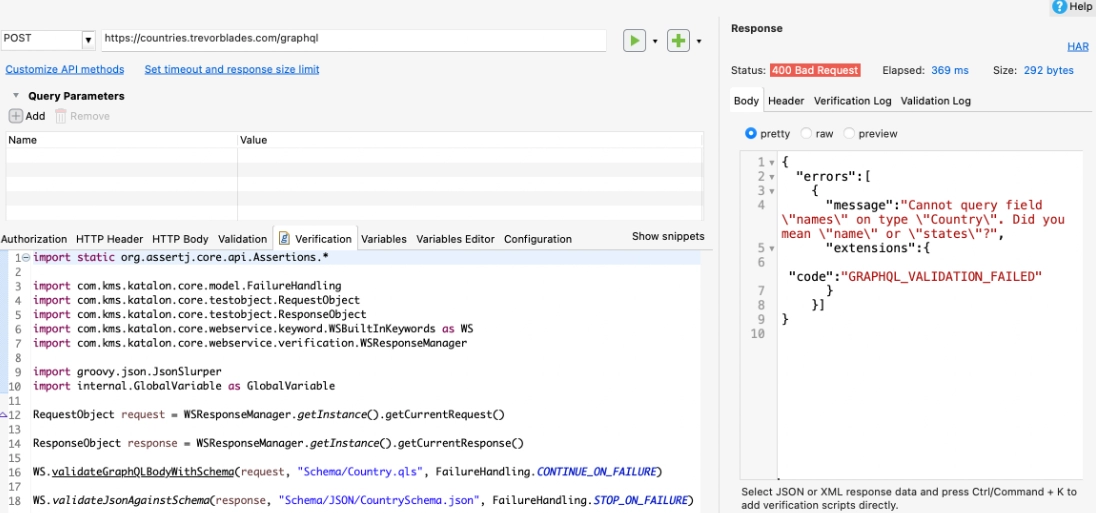
Do the following to check a GraphQL request body and the response returns against schemas:
- Make a web service request object in GraphQL.
- Select the Verification tab in the web service request object editor.
- Use the WS.validateGraphQLBodyAgainstSchema method in the Verification snippets, a schema, and the request body.
Example:
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*
import com.kms.katalon.core.model.FailureHandling
import com.kms.katalon.core.testobject.RequestObject
import com.kms.katalon.core.testobject.ResponseObject
import com.kms.katalon.core.webservice.keyword.WSBuiltInKeywords as WS
import com.kms.katalon.core.webservice.verification.WSResponseManager
import groovy.json.JsonSlurper
import internal.GlobalVariable as GlobalVariable
RequestObject request = WSResponseManager.getInstance().getCurrentRequest()
ResponseObject response = WSResponseManager.getInstance().getCurrentResponse()
WS.validateGraphQLBodyAgainstSchema(request, "Schema/Country.qls", FailureHandling.CONTINUE_ON_FAILURE)
WS.validateJsonAgainstSchema(response, "Schema/JSON/CountrySchema.json", FailureHandling.STOP_ON_FAILURE)- Click Save, Test Request, and Verify.
Result
The validation result is displayed in the Response section: