Introduction
Redis is an in-memory data structure store that may be used as a database, cache, message broker, and streaming engine. It is open source (BSD licensed). Strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets with range searches, bitmaps, hyperloglogs, geographic indexes, and streams are all available in Redis.
RediSearch
RediSearch is a strong and powerful indexing, querying, and full-text search engine for the Redis, available on the premises and as a managed service in the cloud.

Source: WPBullet
History
Users have come to demand the most relevant results for the search phrases they enter as search engines have become more refined. Redis then developed RediSearch, a full-text search engine that uses the Redis Modules API to enhance Redis with some new commands and capabilities, in order to adequately fulfill customers' needs and expectations.
Our developers then decided to model Inverted Indexes using a custom data structure rather than Redis' default data type to enable more efficient data packing. RediSearch allows modules to designate and then locate data on Redis string keys by modeling an inverted index, which holds a map between words or keywords to the respective documents in which they appear. This is a straightforward procedure that produces significant benefits.
Working
RediSearch additionally uses a combination of Delta Encoding and Variant Encoding to encode entries, reducing the amount of space necessary for indexes and allowing for faster decompression and index traversal. RediSearch offers a variety of unique capabilities as a result of this meticulous structure, ranging from speedy indexing and multi-language compatibility to exact phrase search and a sophisticated auto-suggest engine. To understand more about RediSearch's extensive capabilities, please read our ebook.
When giving search results, it's vital to note that RediSearch does not use any automatic methods to judge content quality. Instead, users can provide each indexed document with their own personalized quality scores, which RediSearch then combines with tf-idf scoring of each word to rank search results. Nonetheless, we're constantly trying to improve RediSearch, so new relevance ranking algorithms are likely to appear in the future.
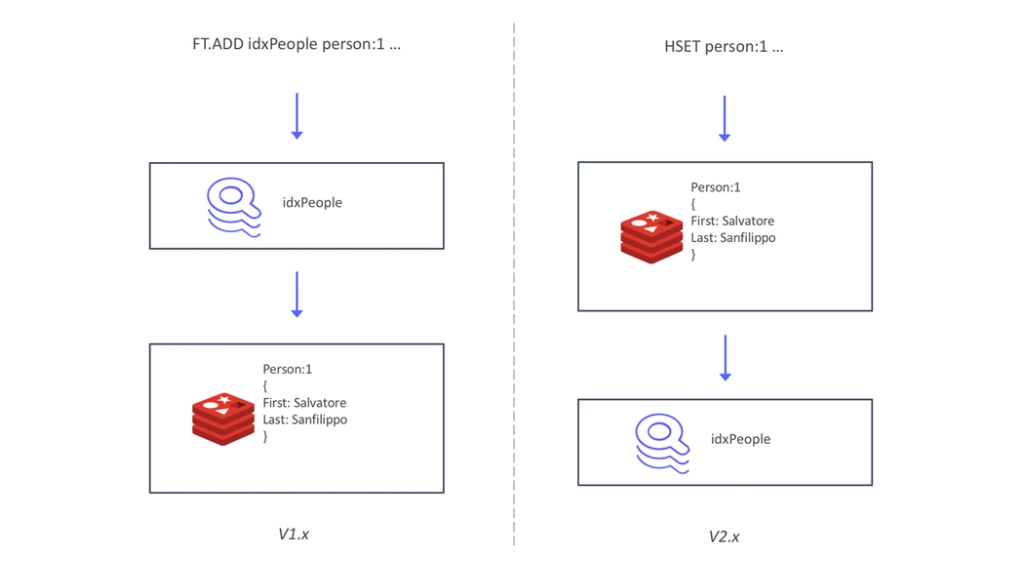
Source:Redis.com
RediSearch can also store documents, index existing Redis data, support numeric range filtering of results, execute queries using a chained-iterator-based approach, provide stemming for over 15 languages using the Snowball stemming library, auto-complete search terms, and accommodate Fuzzy Suggestions, in addition to being fast and memory efficient. Furthermore, if an index is too huge, RediSearch can be expanded out and partitioned across numerous machines.






