Introduction
The end result of a software application is defined by its Reliability. In today's world of intense competition, any product should perform the needed functions and provide additional benefits to its end consumers. Software development is a time-consuming and challenging process, so is testing. As a result, the ultimate purpose of any model used by an organization should be to ensure a reliable software product.
Let’s learn about Software Reliability Models in-depth.
Software Reliability Models
Software reliability can be defined as a characteristic of a software's quality that includes functionality, usability, performance, capability, maintainability, documentation, and so on.
As a software application grows, it will inevitably become more sophisticated. As a result, the estimations like its cost becomes difficult. Hence, various models have evolved, providing effective estimation techniques.
A software reliability model shows the form of a random process that describes how software failures behave over time.
As individuals endeavour to understand the characteristics of how and why software fails and quantify software reliability, software reliability models have emerged.
Since the early 1970s, over 200 models have been developed, yet the question of how to quantify software reliability remains largely unanswered.
There is no single model that can be applied in every circumstance. There is no such thing as a complete or even representative model.
Most of the Software Reliability Models are based on Assumptions and Factors.
Some of the Software Reliability Models that are used to achieve reliability in Software Development are:-
- Jelinski and Moranda Model
- Basic Execution Time Model
- Logarithmic Poisson Time Model
- The Bug Seeding Model
- Shooman Model
- Littlewood-Verrall Model
- Goel-Okumoto Model
- Musa-Okumoto Model
Software Reliability Modeling Techniques
Software Reliability Modeling techniques can be divided into two categories:-
1.) Prediction Modeling
2.) Estimation Modeling
These modeling techniques are based on observing and accumulating failure data and analyzing with statistical inference.
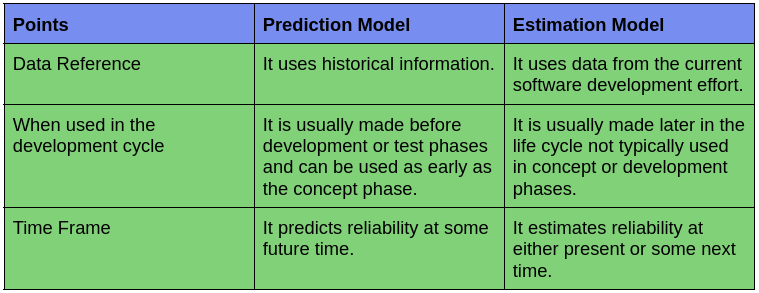
Prediction Models: This model is based on historical data. They analyze past data to conclude some facts to arrive at a consensus. They are usually made before development and regular test phases. The model follows the concept phase and the prediction from the future time.
Musa Model, Putnam Model, Rome Lab TR-92-52 Model, and Raleigh Model are the Prediction Models.
Estimation Models: This model uses the current data from the current software development effort and does not use the conceptual development phases, and can estimate at any time.
Weibull Model, Bayesian Model, J-M Model, Goel-Okumoto Model, and Thompson and Chelson’s Model are the Estimation Models.
The Major difference between the Prediction and Estimation Modeling Techniques is given in the below table:-
Also see, V Model in Software Engineering




