Introduction
Ready API helps Agile and DevOps development teams improve API quality by allowing them to manage and run automated functional, security, and performance tests through a single centralized interface. Ready API empowers software teams to share testing projects and artifacts, report and fix errors straight from the testing IDE, and distribute licenses among team members.
This blog explains the details of Virtual Service Scripting and events in ready API, along with the details of Virtual Service Events and SSL Virtual Services in Ready API.
Without further ado, let's get started.

Virtual Service Scripting
Although you can create virtual APIs using ReadyAPI's strength and flexibility, you might want to employ scripts to implement particular behaviour for which there aren't already defined options. Here are some scenarios when using scripts might be appropriate:
-
Transfer values from the request to the answer, maybe with some modifications.
-
To choose the response to return, read some data from a request and use this value.
-
Instead of having the response hard-coded in service characteristics, read the response (or portions of it) from an external file or database.
- Designing unique HTTP responses.
Script properties
The Scripts can be used in a variety of contexts:
Service functioning
There are several script properties available for each virtual service that enable you to build script handlers for particular events:
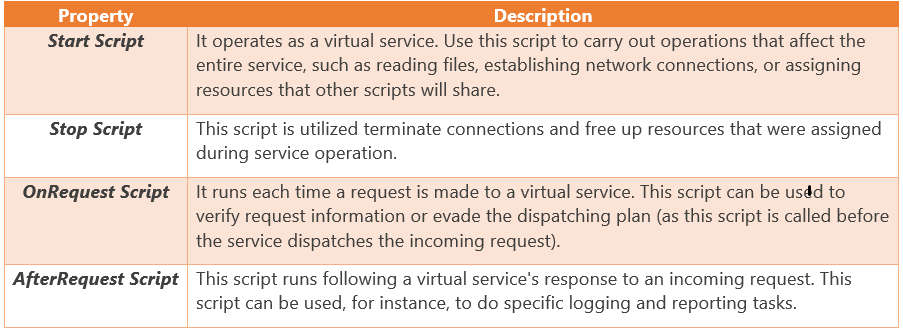
Virtual responses
Before the virtual service provides the response to the client, the script code that you enter in the Script's property of a virtual response is run.
VirtResponse test steps
The script core for SOAP and REST VirtResponse test phases are similar to what you define for virtual responses. It is executed before the test step sends a response to the client.
Response dispatching
You can utilize the script dispatch approach when checking incoming requests and returning the name of a fake answer that your virtual service should send to the client.
Response dispatching
With the help of the validation actions—for which ReadyAPI does not provide pre-defined checks—you may use them to validate incoming requests.
Script language
Groovy and JavaScript are supported using the "script" attributes. The language used by the virtual service is determined by the Script Language attribute of your project. Projects utilise Groovy by default. This language's syntax is similar to Java's and can interact with Java objects and libraries.
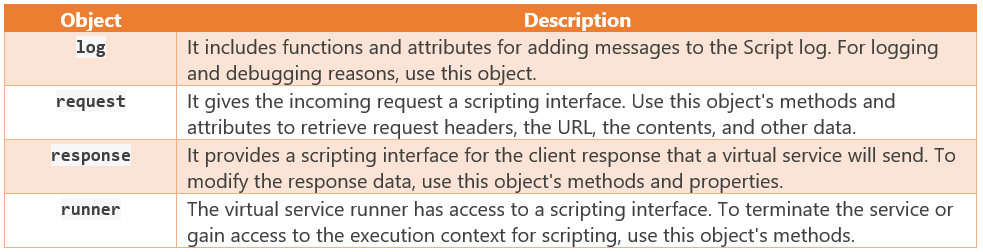
Script objects
The items that are frequently used in service scripts are listed below. You can look over the message above the script edit box in the product user interface to determine which objects are available in each script property:

Writing script code
The script editors support modern features that facilitate quicker and easier code authoring:
-
Use the Code Completion list to view the available objects, methods, and properties. Press CTRL+SPACE or choose Edit > Code Completion from the menu to bring up the list.
-
For easy editing, open a script in a separate window. Click the button in the script editor's toolbar to accomplish this.
-
Use the built-in Find/Replace dialogue to look for and replace a string. Press CTRL+F to activate it or choose Edit > Find / Replace from the menu.
-
Identify line numbers to improve navigation. Press ALT+L to reveal or hide the numbers or choose Edit > Show Line Number from the menu.
-
Press CTRL+G to swiftly navigate to a line by its number or choose Edit > Go to Line from the menu.
-
Expand or contract code areas. For this, select Edit > Folding from the menu.
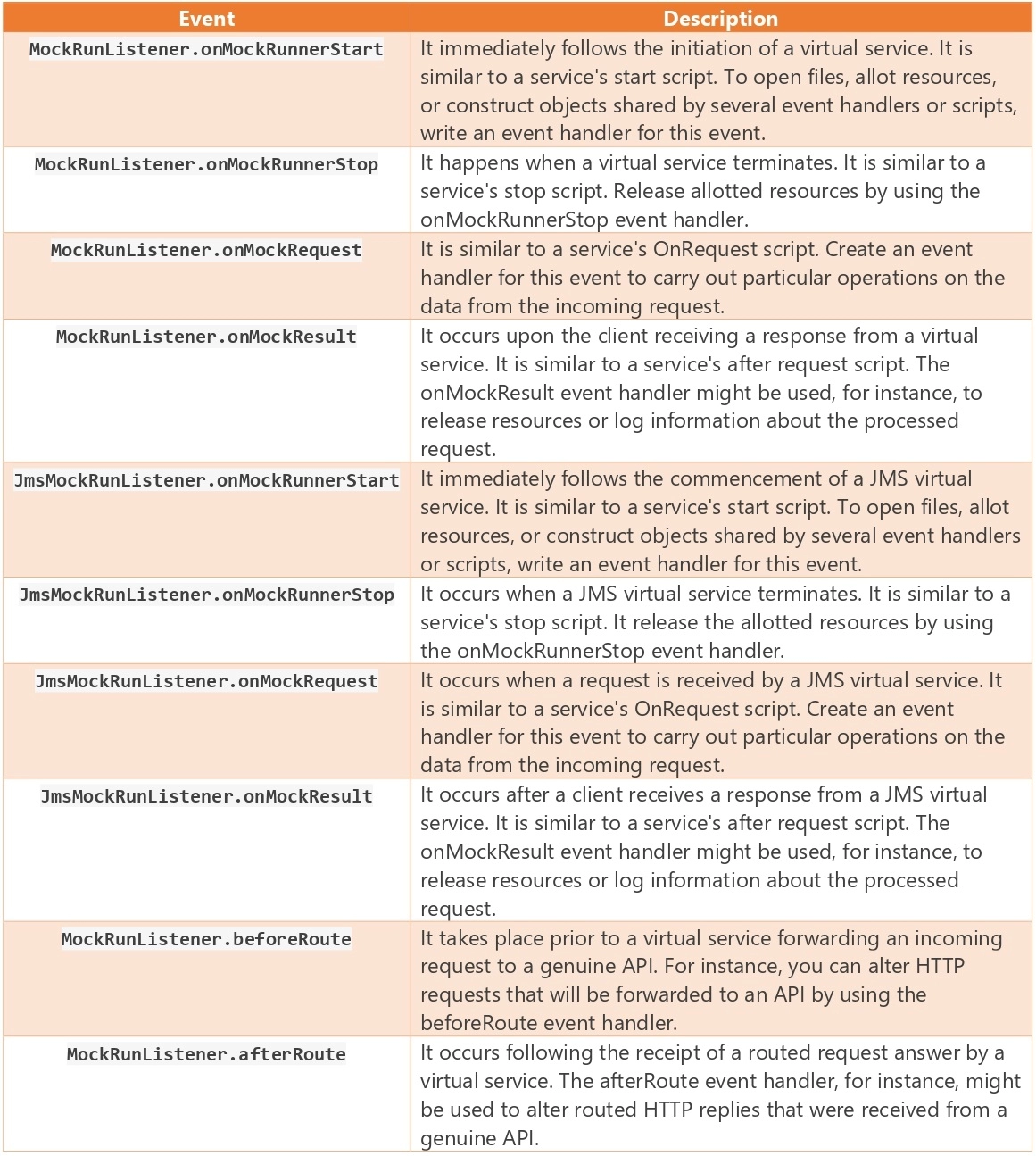
Let's look into the details of Virtual Service Events.