Introduction
In this blog, we will dive deep into a switch case statement where we learn how to deal with cases. Conditional statements play a vital role in the programming world. A switch case statement is available in many programming languages, but R provides a different approach.
In this blog post, we will learn how to achieve switch-case-like logic in R. So, learners, let's look into this topic in-depth.
What is the Switch Statement?
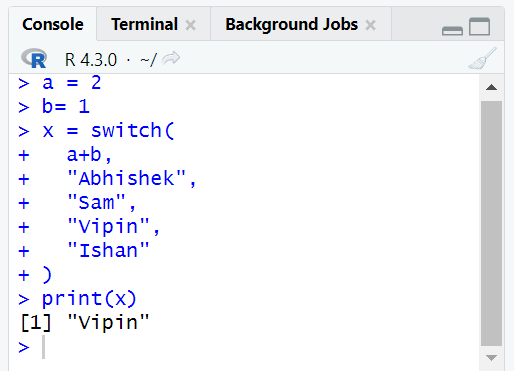
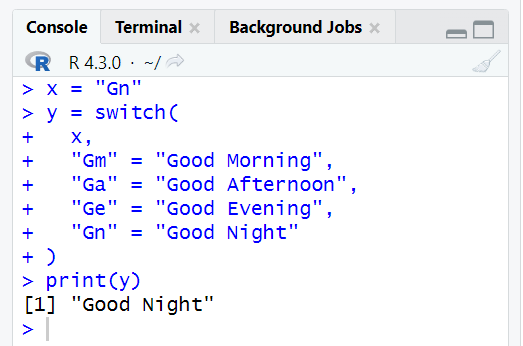
A switch statement is a common feature in programming languages. The switch statement is used in place of long if statements that compare a variable with several other values. We can say it is a selection control mechanism.
The switch statement is used for multiple conditional check statements with a list of values or cases. Below are the rules to understand more about the switch statement.
-
You can take any number of cases within a switch statement.
-
If the expression value is not a character string, then this expression is coerced to an integer.
-
The first match element will be used if there are multiple match cases.
-
There is no default case available.
- An unnamed case is used if there is no matched case.
Benefits of the Switch Statement
Below are some benefits of using the switch statement in R.
-
Concise code: The switch statement provides a simple way to handle multiple cases. Instead of using multiple if-else statements, you can use the switch to make your code simple.
-
Readability: With the help of a switch statement, you can improve your code readability.
-
Efficiency: Switch statements are more efficient than if-else statements because the switch directly jumps to the relevant case.
- Easy to add new cases: In switch statements, you can easily add new cases without having to modify existing code.
Flowchart of the Switch Statement
Below is the flowchart of the switch statement in R.
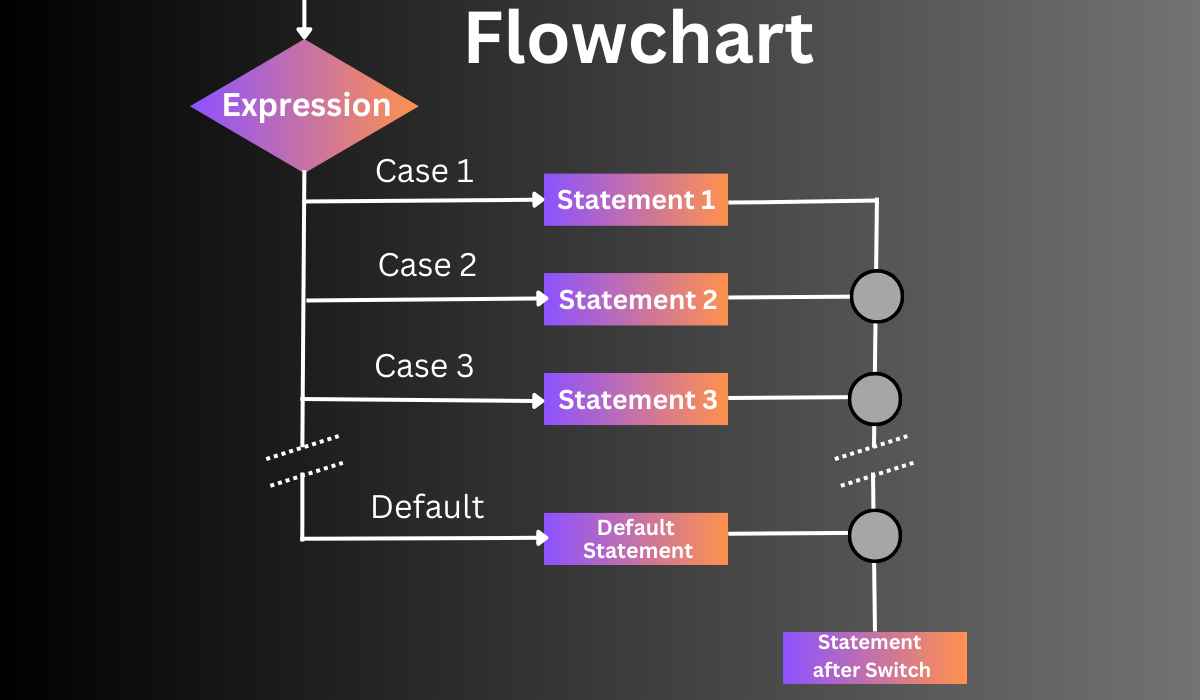
The flowchart of the switch case statement in R is explained in the below points.
-
The flowchart begins with an input expression that needs to be evaluated.
-
The switch statement checks the expression value with the cases.
-
If a case matches the expression value, the flow moves to that case statement, which gets executed.
-
After executing the case statement, flow exits the switch statement.
- If none of the cases matches the expression value, the flow moves to the default case, and the flow exits the switch statement.