Migrating to HOCON format
Whitelist-based authentication and the older Puppet auth.conf file were deprecated and are now gone in Puppet Server 7.
A new HOCON format is introduced for the auth.conf file which can be used to define rules for authentication. Let’s first have a look at the structure of HOCON format.
HOCON structure
There are certain basic structure requirements for the HOCON auth.conf file:
It contains an authorization section that contains two different things one is version settings and the other is rules array of map values. Each member of the array represents an authorization rule.
Every rule has a following structure:
🔺A Match-Request section.
🔺A numeric sort-order value.
🔺A string name value.
🔺An allow value, a deny value or both or it can have allow-unauthenticated.
Unavailable rules and settings
Many of the rules and settings can be reimplemented in new HOCON format without any problem but there are some the deprecated rules and settings that we cannot migrate. They are as follows:
✴️ on value of auth.conf
✴️ allow_ip or deny_ip parameters
✴️ method parameter's search indirector.
Converting a Rule
Rules or settings that can directly be converted into a new HOCON format. Let’s see an example of that:

Old auth.conf
The picture above shows the way we used to write rules in the auth.conf file for puppet server. This rule can be migrated to new HOCON format using the following step:
1️⃣ In the match-request part of the new rule, add the path to the path setting.
2️⃣ In the section's type setting, add its type.
3️⃣ The old rule has a method setting. This can be implemented by adding an HOCON method setting in the rule's match-request section and specifying GET and POST as an array.
4️⃣ Set the allow setting after that. The old rule made use of a * glob, which HOCON also supports.
5️⃣ Finally, give the rule a unique name value.
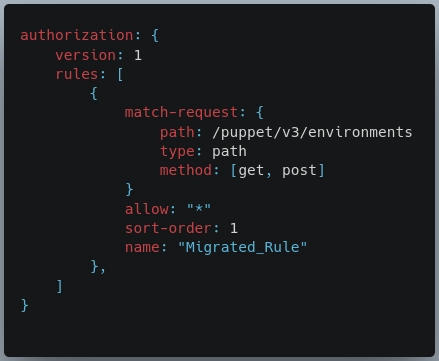
New HOCON auth.conf
Allowing unauthenticated requests
A deprecated rule would assign the any value to the auth parameter so that it would match any request regardless of its authentication state, which would include unauthenticated requests.
In HOCON rule, we can set the allow-unauthenticated option to true.
NOTE: This configuration is unsafe and should only be used with caution because it overrides the allow and deny settings.
Environment URL parameters
The environment parameter in obsolete rules adds a comma-separated list of query parameters as a suffix to the base URL. Whereas the query-params setting for HOCON rules allows you to give them as an array environment value.
Search indirector for method
The search indirector for the deprecated method setting has no direct equivalent. We can create a new corresponding rule, By passing GET and POST to the method and providing endpoint paths with the path argument.
Advanced logging configuration
The puppet server logs different things, and a file called logback controls how the puppet server should log. By default, the file is located at /etc/puppetlabs/puppetserver/logback.xml.
we can configure Logback to log messages in JSON format.
Configuring Puppet Server to log in JSON
Prior to setting up Puppet Server to log to JSON, take into account the following:
1️⃣ Do you want to change the default plain-text logging on Puppet Server to just log to JSON? Do you prefer plain-text logging by default, or would you also like JSON logging?
2️⃣ Do you wish to enable JSON logging for both HTTP access logs (puppetserver-access.log) and the main Puppet Server logs (puppetserver.log)?
3️⃣ Which log rotation technique do you intend to employ for the new JSON log files?
Note - Puppet Server also relies on Logback to manage, rotate, and archive Server log files. Logback archives Server logs when they exceed 200MB, and when the total size of all
Server logs exceed 1GB, it automatically deletes the oldest logs.
Sending the JSON data to logstash
We must configure the Puppet Server to send the logs to Logstash after setting it up to record messages in JSON format (or another external logging system). There are numerous approaches we can take here:
🔺 Set up Logback such that it sends information directly to Logstash from Puppet Server. To deliver the logs through TCP or UDP, refer to the Logstash-Logback encoder documentation. Keep in mind that UDP may silently discard log messages while TCP may bottleneck Puppet Server if your Logstash system is busy.
🔺 Filebeat is a tool from Elastic for shipping log data to Logstash.
Differing behavior in puppet.conf
Almost all of the settings defined in puppet.conf file are used by puppet server but there are some settings that differ. Some of them are listed below:

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Puppet tool?
A puppet is a tool that allows you to manage and automate server setup. Puppet is comprised of various packages. These are referred to as the Puppet platform, which you use to organize, store, and run your Puppet code.
Is Puppet free to use?
Puppet is open-source software, which means it can be altered and customized without cost. Right out of the box, you receive a full tool with the fundamental CM functionalities and capabilities.
Can Puppet Server be installed in Windows?
No, we can install a puppet server in a Linux environment only.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed the puppet server configuration files. We saw the basic structure of the HOCON.conf files, and learnt advanced logging configuration.
If you think this blog has helped you enhance your knowledge about the above question, and if you would like to learn more, check out our articles
🔥 Concept of Status API in Puppet
🔥 Deploying Puppet Code in Continuous Delivery
🔥 Puppet Service and Tools
🔥 Directories and Files in Puppet
And many more on our website.
Visit our website to read more such blogs. Make sure that you enroll in the courses provided by us, take mock tests and solve problems available and interview puzzles. Also, you can pay attention to interview stuff- interview experiences and an interview bundle for placement preparations. Do upvote our blog to help fellow ninjas grow.
Please upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
Happy Learning!