Introduction
Before playing any game, our first look is into the essential part of the game is the guidebook. Without knowing the game rules, no one can go ahead. The same is with the administration guide for RediSearch. It's the guidebook for developers working on Redis. Most of the developers working with Redis already know how beneficial it is that Redis supports all the important data structures.
Suppose you are a software developer and use Redis due to its advantages, but you don't comprehend where to start and how to go ahead. To solve these problems, Redis comes with RediSearch, a source available in the Redis module that provides query ability, secondary indexing, and an Administration Guide for RediSearch, a full-text search for Redis. Before using any of these, developers need to understand the Administration Guide for RediSearch, which provides the explanatory written materials provided to the Licensee with the Administrator's use of the Software. So let's go ahead and learn about the administration guide for RediSearch.
Administration guide for RediSearch
This section will discuss the general administration guide for RediSearch. Even though RedisSearch doesn't require any configuration to work, but few things which are worth noting when running RedisSearch on top of Redis.
Persistence
RediSearch supports persistence based on RDB and AOF.
RDB Persistence
The RDB persistence performs point-in-time snapshots of the dataset at specified intervals. Beyond the standard Redis RDB configuration, nothing special is needed for an RDB setup.
AOF Persistence
As of version 1.1.0 of Redis, the RedisSerach supports working with AOF-based persistence. It doesn't support the "classic AOF" mode, which uses AOF rewriting. Instead, it solely supports AOF with RDB preamble mode. Rewriting the AOF log creates an RDB file in this mode, which is then appended.
To enable AOF persistence with RediSearch, add the two following lines to your redis. conf:
append-only yes
aof-use-rdb-preamble yesMaster/Slave Replication
Redis Replication uses an asynchronous method for transferring data from the master to the slave. A single master node can have multiple slaves, and after receiving data, the slave acknowledges it. Redis support cascading replication for the interconnection of slave with one another. Enabling persistence options is a good option in the master and the slave nodes; otherwise, one must restart an instance to lose all data.
Every Redis has a replication ID consisting of a sizeable pseudo-random string and the offset value on the master, and this replication ID is the key replication process. Every byte streaming from master to slave offset is incremented.
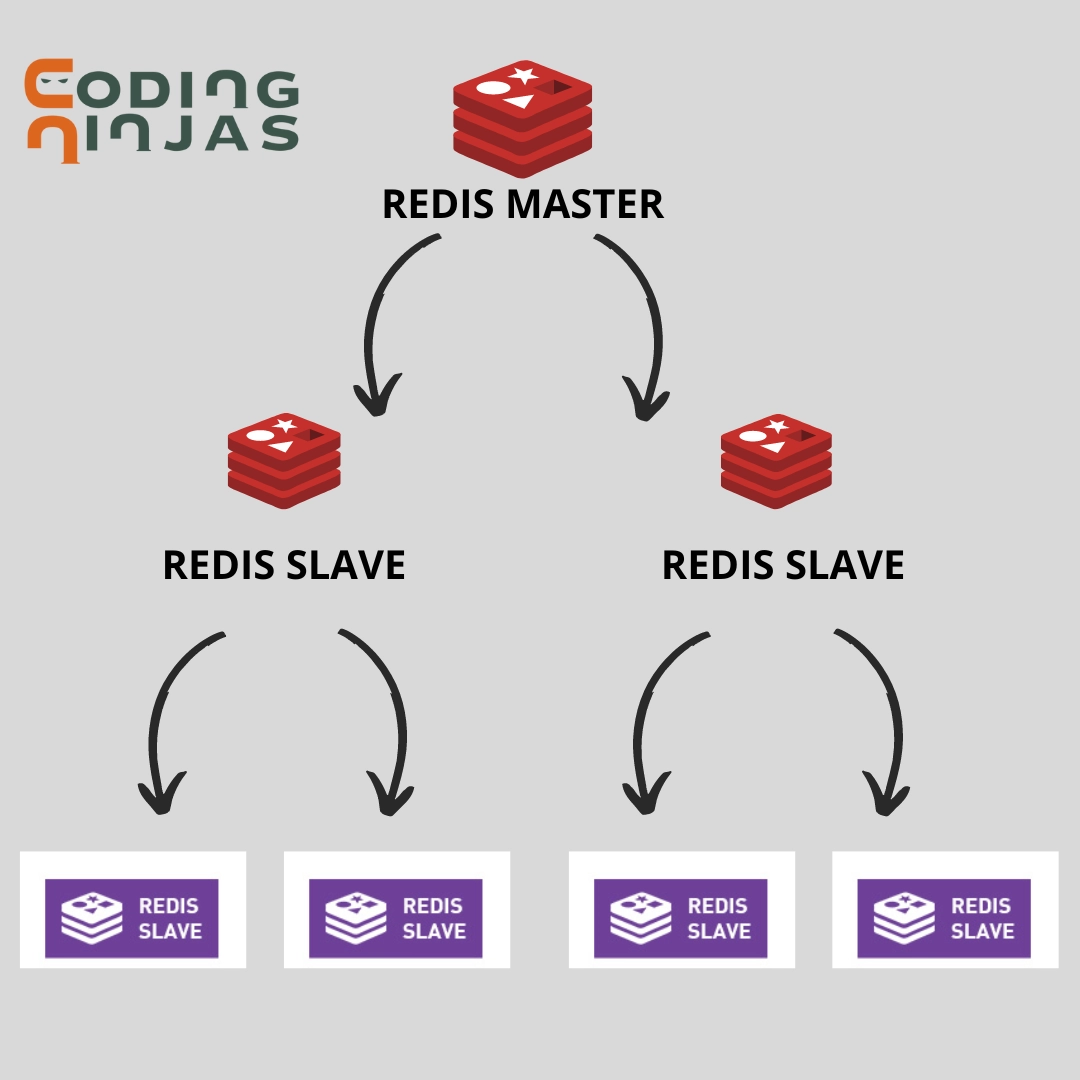
MASTER-SLAVE REPLICATION
On the flip side, slaves connect to their master using PSYNC for sending the replication ID and offsetting processed in the slave. In this way, the master node will need to send the needed incremental data.
RediSearch supports replication using a master/slave setup, and we use slaves for high availability. On top of that, slaves can also be used for searching, to load-balance read traffic.






