Introduction
Hello, ninjas! You must have encountered terms like language processing in artificial intelligence, deep learning, searching, etc. In this article, we are going to study Adversarial search in NLP. With this article, you will learn what adversarial search in NLP is. But first, we shall review some basics about NLP.

Natural Language Processing
-
NLP, or Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence, concerns itself with the ability to perceive and analyze the human natural language and then give the outputs accordingly.
- It converts the natural language input into tokens. It is also called a Doc object. Then several operations are performed on these tokens, and the main result is produced.
Adversarial Search
There are situations where only one agent is not trying to search for something in the sample space in the field of artificial intelligence. Now, since all the agents are searching for the same thing, a competitive environment sets up. Generally, these types of situations arise in gaming, where multiple players play against each other.
Like, suppose a game of TIC-TAC-TOE. Now, there are two players, in this case, trying to achieve a goal. In this case, the goal is to make a straight line with three Xs or three Os. Both the players are trying to do that hence making it a competitive environment. Thus, one player is affected by the moves of the other and even while one player is making his/her move, he/she is considering the possibility of the next move of the other player.
We can see some of the winning states in the following patterns.
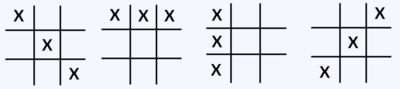
We can see in these images that if ‘X’ makes any such pattern, it wins. The same goes for ‘O’.
Thus, both of the agents are trying to gain a solution in the same search space. This is the basic foundation of an adversarial search.
Features of Adversarial Search
-
Adversarial Search in NLP is a search technique used when a multi-agent environment is analyzed.
-
It relates to a competitive environment in which the goals of multiple agents conflict.
-
Generally, only one agent performs some search technique(s) to gain some solution in the whole sample space. In single-agent situations, there is no competition.
-
In adversarial search in NLP, every agent is the opponent of every other agent. Each of them analyzes the moves of opponents and how those moves can affect their performance.
- Adversarial searches are also called games.
Types of Games
Now, there are two classifications of games in artificial intelligence. These are:-
-
Perfect and Imperfect Information
-
Deterministic and Non-deterministic
Now, let us know about these different types of games individually.
Perfect Information
A type of game in which every agent has all the information about the whole game. Every agent can see the moves of every other agent.
A simple example of this is chess.
Imperfect Information
A type of game in which an agent only has some of the information about the whole game.
Some examples of this are blind, battleship, etc.
Deterministic
These games follow a strict pattern during the game. There are clear rules, and there is no randomness in these games.
Some examples of this are chess, tic-tac-toe, etc.
Non Deterministic
These games have a factor of chance or luck in determining the result. There is a scope of happening of unpredictable events in such games. The course of action here is flexible, and randomness arises.
An example of this can be poker.
Elements of The Game
There are some aspects of a game. With these parameters, let us see the working of adversarial search in NLP.
Initial State
This state is the starting point of the game. It is the initial configuration of the game. For example, all the players have their tokens inside their boxes at the start of the game. Eg: Ludo.
Players
All the players present to play the game come under this element.
Actions
The cluster of all the moves a player can make.
Result
It depicts the result of the moves of players.
Terminal Test
It analyzes whether the game is finished or not. The terminal state is the state where the game ends.
Utility
It depicts the final result of the game, usually with numeric values. It tells each player's 'won' or 'lost' state.
TextAttack
Before learning TextAttack, let us understand adversarial examples.
An adversarial example is a data set fed to the machine to fool the machine so that the machine makes a false prediction. Generally, it is a simple and clean example, but with some permutations, it tricks the machine into making a wrong prediction. Although, a human does not recognize this permutation.
TextAttack generates a special type of adversarial example. TextAttack iterates over the input data set being fed to the machine. It searches the data set for adversarial perturbation when encountering a correctly predicted input. When the incorrect input fools the device, it does not search for adversarial perturbation as it encounters an already incorrectly predicted sample.
Example
Let us understand this by an example following the MIN-MAX approach.
-
In a MIN-MAX approach, there are two types of players, a minimizer and a maximizer. A minimizer tries to minimize the final result, while a maximizer tries to maximize the final result.
-
Both players take alternate turns.
-
For representation, we use the game tree. A game tree represents a game where the nodes depict the game state, and the edges show the moves made by the players. It involves all the elements of the game.
Let us look at the game tree below. It is the MIN-MAX of a hypothetical search space. For this example, the values of the nodes are their heuristic values.

Hence, it is a multi-agent environment with both players aiming for a goal.
For each sample space, if it is MAX, it chooses the maximum of the previous state values. Like, between nodes with values ‘4’ and ‘5’, ‘5’ is the maximum, so the selected node is ‘5’.
And, if it is MIN, it selects the minimum of the last state values. Like, between the nodes with values ‘5’ and ‘0’, ‘0’ is the minimum, so the chosen node is ‘0’.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Adversarial Search
-
A vital advantage of Adversarial search in NLP is that it does not support favoritism and analyzes all the agents' searches accordingly.
- Note that since all these tedious steps are involved, Adversarial search should not be applied to simple and easy situations.
Uses of Adversarial Search
Now, we will look at some of its uses below.
-
Since there is no scope for bias in these searches, valuable strategies can be made using these.
-
In legal systems, it helps in making the final decision by analyzing the inputs of both parties. It can also help the police since it makes non-bias decisions.
-
It helps in developing new technologies like Alpha-Beta pruning, etc.
- It helps companies in making decisions. These decisions can be dealing with hard negotiations, etc., in a competitive business.




