Parameters
There are three parameters attached to animations in Kivy. These are explained below:
- duration or 'd': It sets the duration of the animation in seconds. Its default value is 1, and it takes float values.
- transition or 't': It sets the transition of the animation using in-built or custom transition functions. It takes a string or function as input.
- step or 's': It sets the step of animation in milliseconds. It takes float values, and its default value is 0. If we want to update the animation less frequently, we use a float value.
Events
There are three events connected to animation in Kivy. They are stated as follows:
- 'on_start': It is fired at the start of animation on the widget.
- 'on_complete': It is fired once the animation on the widget is complete or stopped.
- 'on_progress': It is fired while the animation is in progress on the widget.
Types of Animation
We have learned about the various parameters and events related to animation until now. Now let's use this knowledge to create multiple types of animations.
Simple Animation
The most basic animation would be to define a widget's position. In this, we describe the x and y coordinates of where the widget should be placed at the end of the animation.
Sequential Animation
As the name suggests, we add animations sequentially in this. The first animation is run for some duration, then the next one runs for some time, and this can go on further. To achieve this, we have to use the '+' operator.
Parallel Animation
We add animations parallel to each other in this type of animation. Here, all the animations are run together, parallel to each other. To do this, we have to use the '&' operator.
Implementation Approach
The basic approach one should follow while implementing the animation using Kivy is as follows:
Step 1: import libraries, classes, widgets and layouts required (in this case, kivyApp, FloatLayout, Animation, Button)
Step 2: create the required class (in this case, AnimationExample class)
Step 3: define the functions in the class stating the animation details and the basic build of the widgets
Step 4: return the layout/widget/class (in this case, layout)
Step 5: run the instance of the class (in this case, AnimationExample())
Implementation Code
Given below is the code showing the implementation of Animation in Kivy.
# implementation of Animation in Kivy
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.floatlayout import FloatLayout
from kivy.animation import Animation
from kivy.uix.button import Button
class AnimationExample(App):
def build(self):
self.layout = FloatLayout()
self.button = Button(text='Coding Ninjas', size_hint=(0.2,0.07), pos_hint={'x':0.5,'y':0}, on_press=self.animation)
self.layout.add_widget(self.button)
return self.layout
def animation(self,*args):
anim = Animation(pos_hint = {'x':0.5,'y':0.7}, d = 0.75, t='in_quad')
anim += Animation(pos_hint = {'x':0.1,'y':0.2}, d = 0.45 )
anim.start(self.button)
# Run the app
if __name__ == '__main__':
AnimationExample().run()
Code Explanation
In the .py file, we first import the required libraries, classes, widgets and layouts; then, we create the required class. In the class, we define two functions. One is 'build', where we specify layout and button properties. We say that only the animation will start once the button is clicked. In the second function, i.e. animation, we define the animation properties of the button. We specify the button's location, duration, and transition and then add another animation sequentially to change its position. Finally, we run the App.
Output
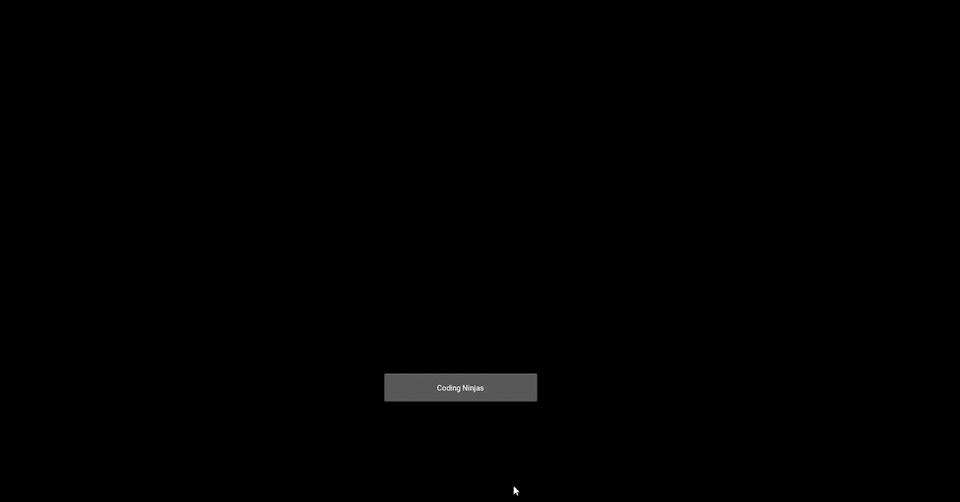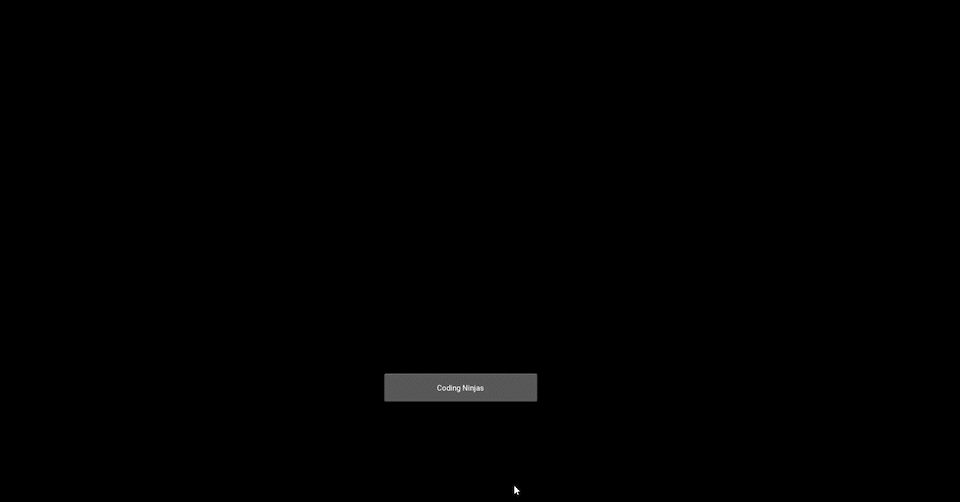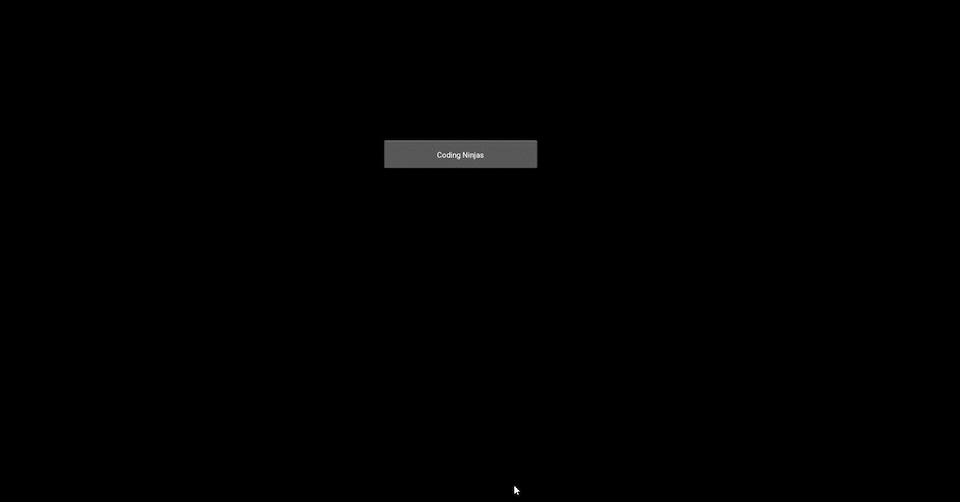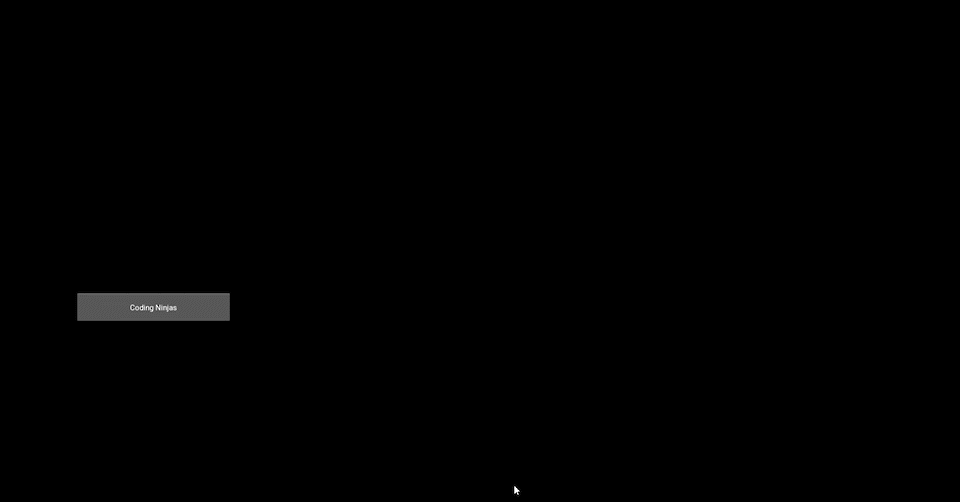
Output Image before pressing the button

Output Image after completion of animation

Frequently Asked Questions
What is a widget?
Kivy Widgets are used to create graphical user interfaces in Kivy. Labels, Canvas, drop-down menus, and many more widgets are available in Kivy.
What are Kivy properties?
Properties make defining and connecting events much easier. Different types of properties are used to describe the kind of data one wants to work with.
Which versions of Python support Kivy?
Kivy 2.1.0 is supported by Python versions from 3.7 to 3.10. As for Kivy 2.0.0, it is supported by Python2.
Why is animation used?
The uses of animation are as follows:
- When the application loads data and changes its state, the animation is helpful.
- It's utilised to give the app a more inviting appearance.
- It makes the user feel at ease with the interface.
- It can also be utilised to express a message in an unusual way.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned how to use animation in Kivy. We see the parameters and events attached to it, along with the various types of animations. We then implement all we have learned to create an animation using a .py file.
We hope this blog has helped you enhance your knowledge. If you want to learn more, check out our articles on Popular Python Libraries - Coding Ninjas Coding Ninjas Studio and Import and Modules in Python - Coding Ninjas Coding Ninjas Studio. Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
Head over to our practice platform Coding Ninjas Studio to practice top problems, follow guided paths, attempt mock tests, read interview experiences, interview bundle, solve problems, participate in contests and much more!
Happy Reading!







