Introduction
Ansible is a well-known IT automation tool used to configure, deploy and orchestrate advanced tasks like rolling updates and handling continuous deployments. Ansible has different types of content stored in various locations for users. Let us discuss the directory structure of Ansible Collections.
Collection Structure
Modules, plugins, roles, playbooks and documentation are distributed across the Ansible community as Collections. The distribution is done by Ansible Galaxy, where users can access a developer's shared content. Ansible content is converted into a single portable Collection as a new directory structure. The following diagram shows the structure of a collection directory and its contents.
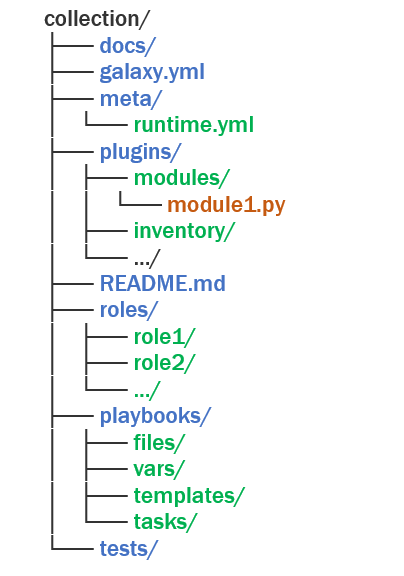
Galaxy.yml
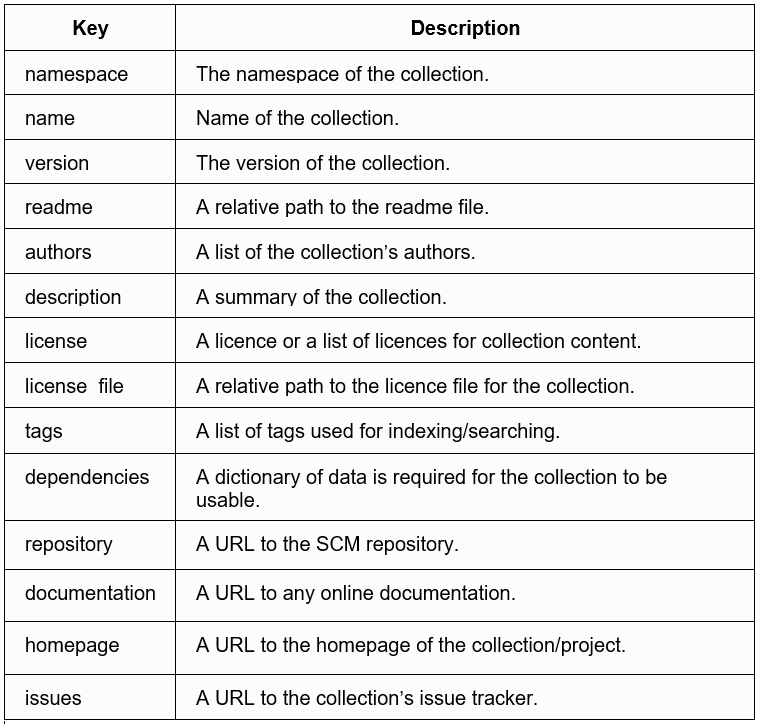
A Collection should have a galaxy.xml containing the necessary information to build a collection artefact. It is a file at the root level of the collection that holds the metadata and tools to package and publish the collection. It contains the following keys in YAML format.
The docs directory
This folder contains information on how to use the roles and plugins provided by the collection. The structure of extra documentation and its link is defined in the docs/docsite/extra-docs.yml. The file also defines the index page's title in the collection's documentation. Any additional links to the plugins or the collection index pages are added to the docs/docsite/links.yml file. Plugin-specific documentation is embedded as Python docstrings. They can be accessed and viewed by using the ansible-doc command.
ansible-doc -t lookup namespace_1.collection_1.lookup_1Here, namespace_1 is the Galaxy namespace, and collection_1 is the name of the namespace containing that collection. The galaxy namespace of the collection is defined in the galaxy.xml file.
The plugins directory
All plugins involved must be present in the collection plugins directory. These plugins are accessible to all the roles of a collection, so it distributes modules, filters and lookups without importing roles. Plugins are stored under a subdirectory known as plugin_type, which contains folders like callback_plugins, inventory_plugins, cache_plugins, strategy_plugins and many more. The plugins directory contains one prominent subdirectory called module_utils which is used by modules and plugins using a fully qualified collection name. The functions and classes of module_utils can be imported in Python using the following statement.
from ansible_collections.{namespace}.{collection}.plugins.module_utils.{util} import {something}The roles directory
Roles help load vars, files, tasks, handlers, and other Ansible artefacts based on a given file structure. Ansible looks for roles in the roles/ directory relative to the playbook file. Collection role names start with an alpha character and can contain only lowercase characters and underscore. They can not have plugins. All the roles can access plugins from the plugins directory.
An Ansible role is composed of many folders under a directory, each containing multiple YAML files. The role name is the same as the directory name and must comply with the naming rule.
The playbooks directory
Ansible playbooks offer reusable and repeatable configuration management and deployment systems to deploy complex and advanced applications. They can launch tasks synchronously and manage the steps of any ordered process. The playbooks directory stores all the playbooks involved in the collection. They can be accessed by their fully qualified collection name from the command line as namespace.collection.playbook or from import_playbook. The owner can store documentation for each playbook in the docs directory.
The tests directory
Testing collections ensure that the code executes correctly and integrates well with the other components of the Ansible environment. The tool used to test Ansible collections is called ansible-test. The ansible-test tool is always executed from the root directory of the collection. Users can add unit tests tests/unit/plugins/ folder and integration tests in the tests/integration/targets/ folder. Python requirements for unit tests can be specified in tests/unit/requirements.txt.
The meta-directory and runtime.yml
Additional metadata of a collection is stored in the runtime.yml file present in the meta directory. It supports top-level keys like requires-ansible, plugin_routing, import_redirection and action_groups. The requires_ansible key defines the version of the ansible-core to use the collection. Plugin_routing contains the content needed to be loaded from a location that is deprecated or removed. Mapping names for import statements in Python and their locations are specified in the import-redirection key. Action_groups contains a mapping of groups and the list of action plugins they hold.





