Introduction
Most people interact with C++ code from console input and output and are not aware that we can also make low-level graphics programs using C++. This means that we can draw shapes, designs and colour them using our C++ program. In this article, we will see how to implement the AVL tree using graphics in C++.
We will build the following functionalities in this project:
- Insertion of a node
- Displaying the AVL tree
- Visualise AVL rotations
- Print inorder, preorder, and postorder tree traversals.
Prerequisite: You need to set up the graphics library. You can follow this link to set up graphics.h in CodeBlocks.
Implementation
// C++ program for the implementation
// and execution of a self-balancing
// BST using rotations and graphics
#include <algorithm>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <graphics.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#define pow2(n) (1 << (n))
const int x = 600;
const int y = 100;
// Node Declaration
struct avl_node {
int data;
int height;
struct avl_node* left;
struct avl_node* right;
} * root, *temp1;
// Class Declaration
class avlTree {
public:
int height(avl_node*);
int diff(avl_node*);
avl_node* rr_rotation(avl_node*);
avl_node* ll_rotation(avl_node*);
avl_node* lr_rotation(avl_node*);
avl_node* rl_rotation(avl_node*);
avl_node* balance(avl_node*);
avl_node* balanceTree(avl_node*);
avl_node* insert(avl_node*, int);
void display(avl_node*, int);
void drawNode(avl_node*, int, int, int);
void drawTree(avl_node*, int, int);
void inorder(avl_node*);
void preorder(avl_node*);
void postorder(avl_node*);
int validate(string s);
bool checkInput(string s);
avlTree()
{
root = NULL;
temp1 = NULL;
}
};
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int choice, item, bf;
int c;
string str;
avlTree avl;
// Graphics
int gd = DETECT;
int gm;
initwindow(1200, 700, "AVL Tree Graphics",
0, 0, false, true);
cout << "\n---------------------"
<< endl;
cout << "AVL Tree Implementation"
<< endl;
cout << "\n---------------------"
<< endl;
cout << "1.Insert Element into the tree"
<< endl;
cout << "3.Balance Tree"
<< endl;
cout << "4.PreOrder traversal"
<< endl;
cout << "5.InOrder traversal"
<< endl;
cout << "6.PostOrder traversal"
<< endl;
cout << "7.Exit" << endl;
while (1) {
cout << "\nEnter your Choice: ";
cin >> choice;
switch (choice) {
case 1:
// Accept input as string
cout << "Enter the value "
<< "to be inserted: ";
cin >> str;
// Function call to check
// if input is valid or not
c = avl.validate(str);
if (c == 100) {
item = std::stoi(
str);
root = avl.insert(root, item);
cleardevice();
settextstyle(10, HORIZ_DIR, 3);
if (root == NULL) {
cout << "Tree is Empty"
<< endl;
outtextxy(400, 10,
"Tree is Empty");
}
outtextxy(10, 50,
"Before Rotation : ");
avl.drawTree(root, x, y);
}
else
cout << "\n\t\tInvalid Input!"
<< endl;
break;
case 2:
// Tree structure in
// the graphics window
if (root == NULL) {
cout << "Tree is Empty"
<< endl;
}
avl.display(root, 1);
cleardevice();
avl.drawTree(root, x, y);
break;
case 3:
// Balance Tree
root = avl.balanceTree(root);
cleardevice();
settextstyle(
10, HORIZ_DIR, 3);
outtextxy(10, 50,
"After Rotation : ");
avl.drawTree(root, x, y);
break;
case 4:
cout << "Preorder Traversal : ";
avl.preorder(root);
cout << endl;
break;
case 5:
cout << "Inorder Traversal:"
<< endl;
avl.inorder(root);
cout << endl;
break;
case 6:
cout << "Postorder Traversal:"
<< endl;
avl.postorder(root);
cout << endl;
break;
case 7:
exit(1);
break;
default:
cout << "Wrong Choice"
<< endl;
}
}
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
// Function to find the height
// of the AVL Tree
int avlTree::height(avl_node* temp)
{
int h = 0;
if (temp != NULL) {
int l_height = height(temp->left);
int r_height = height(temp->right);
int max_height = max(l_height, r_height);
h = max_height + 1;
}
return h;
}
// Function to find the difference
// between the left and the right
// height of any node of the tree
int avlTree::diff(avl_node* temp)
{
int l_height = height(temp->left);
int r_height = height(temp->right);
int b_factor = l_height - r_height;
return b_factor;
}
// Function to perform the Right
// Right Rotation
avl_node* avlTree::rr_rotation(
avl_node* parent)
{
avl_node* temp;
temp = parent->right;
parent->right = temp->left;
temp->left = parent;
return temp;
}
// Function to perform the Left
// Left Rotation
avl_node* avlTree::ll_rotation(
avl_node* parent)
{
avl_node* temp;
temp = parent->left;
parent->left = temp->right;
temp->right = parent;
return temp;
}
// Function to perform the Left
// Right Rotation
avl_node* avlTree::lr_rotation(
avl_node* parent)
{
avl_node* temp;
temp = parent->left;
parent->left = rr_rotation(temp);
return ll_rotation(parent);
}
// Function to perform the Right
// Left Rotation
avl_node* avlTree::rl_rotation(
avl_node* parent)
{
avl_node* temp;
temp = parent->right;
parent->right = ll_rotation(temp);
return rr_rotation(parent);
}
// Function to balance the tree
avl_node* avlTree::balance(avl_node* temp)
{
int bal_factor = diff(temp);
if (bal_factor > 1) {
if (diff(temp->left) > 0) {
temp = ll_rotation(temp);
}
else {
temp = lr_rotation(temp);
}
}
else if (bal_factor < -1) {
if (diff(temp->right) > 0) {
temp = rl_rotation(temp);
}
else
{
temp = rr_rotation(temp);
}
}
return temp;
}
// Function to display the AVL Tree
void avlTree::display(avl_node* ptr, int level)
{
int i;
if (ptr != NULL) {
display(ptr->right, level + 1);
printf("\n");
if (ptr == root)
cout << "Root -> ";
for (i = 0; i < level && ptr != root; i++) {
cout << " ";
}
int j;
cout << ptr->data;
display(ptr->left, level + 1);
}
}
// Function to balance the tree
avl_node* avlTree::balanceTree(avl_node* root)
{
int choice;
if (root == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
root->left = balanceTree(root->left);
root->right = balanceTree(root->right);
root = balance(root);
return root;
}
// Function to create the node
// int the AVL tree
void avlTree::drawNode(avl_node* root,
int x, int y,
int noderatio)
{
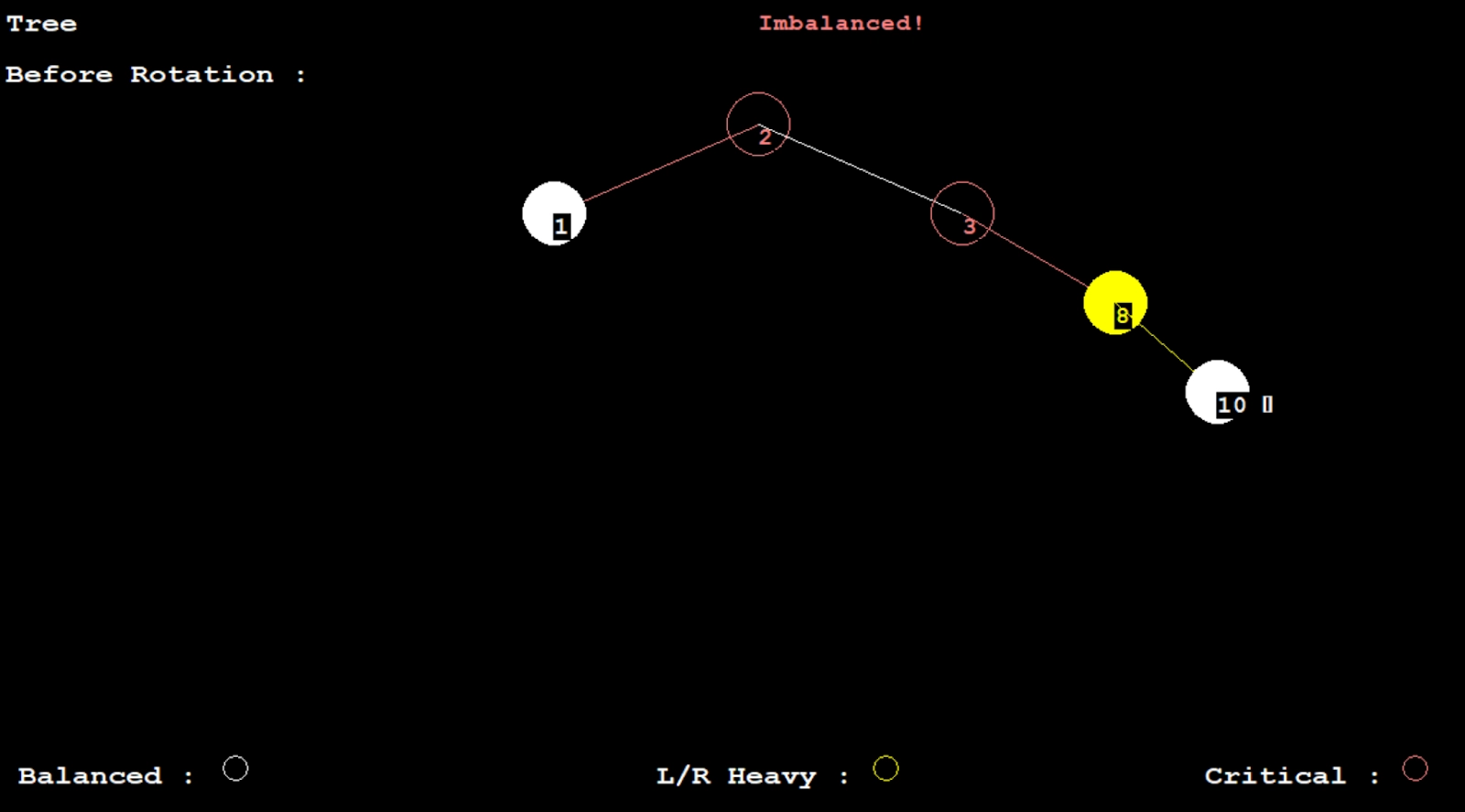
int bf = diff(root);
if (bf > 1 || bf < -1) {
setcolor(12);
outtextxy(600, 10, "Imbalanced!");
circle(x, y, 25);
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, 12);
}
else if (bf == 1 || bf == -1) {
setcolor(14);
circle(x, y, 25);
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, 14);
floodfill(x, y, YELLOW);
}
else {
setcolor(15);
circle(x, y, 25);
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, 15);
floodfill(x, y, WHITE);
}
//char arr[5];
//itoa(root->data, arr, 10);
stringstream ss;
ss << root->data;
string s1 = ss.str();
char arr[10];
for(int i=0; i<s1.length(); i++){
arr[i] = s1[i];
}
outtextxy(x, y, arr);
if (root->left != NULL) {
line(x, y, x - 20 * noderatio, y + 70);
drawNode(root->left, x - 20 * noderatio, y + 70,
noderatio - 2);
}
if (root->right != NULL) {
line(x, y, x + 20 * noderatio, y + 70);
drawNode(root->right, x + 20 * noderatio, y + 70,
noderatio - 2);
}
}
// Function to draw the AVL tree
void avlTree::drawTree(avl_node* root, int x, int y)
{
settextstyle(10, HORIZ_DIR, 3);
outtextxy(10, 10, "Tree");
outtextxy(20, 600, "Balanced : ");
circle(190, 605, 10);
// Floodfill(190, 605, WHITE);
outtextxy(520, 600, "L/R Heavy : ");
setcolor(14);
circle(700, 605, 10);
// Floodfill(700, 605, YELLOW);
setcolor(15);
outtextxy(950, 600, "Critical : ");
setcolor(12);
circle(1115, 605, 10);
// Floodfill(1115, 605, RED);
settextstyle(10, HORIZ_DIR, 2);
drawNode(root, x, y, 8);
}
// Function to insert element
// in the tree
avl_node* avlTree::insert(
avl_node* root, int value)
{
if (root == NULL) {
root = new avl_node;
root->data = value;
root->left = NULL;
root->right = NULL;
return root;
}
if (value < root->data) {
root->left = insert(
root->left, value);
}
else if (value > root->data) {
root->right = insert(
root->right, value);
}
else
cout << "\n\tValue already"
<< " exists!" << endl;
return root;
}
// Function to perform the Inorder
// Traversal of AVL Tree
void avlTree::inorder(avl_node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
inorder(root->left);
cout << root->data << " ";
inorder(root->right);
}
// Function to perform the Preorder
// Traversal of AVL Tree
void avlTree::preorder(avl_node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
cout << root->data << " ";
preorder(root->left);
preorder(root->right);
}
// Function to perform the Postorder
// Traversal of AVL Tree
void avlTree::postorder(avl_node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
postorder(root->left);
postorder(root->right);
cout << root->data << " ";
}
// Function to check the input
// validation
bool avlTree::checkInput(string str)
{
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)
if (isdigit(str[i]) == false)
return false;
return true;
}
// Function to validate AVL Tree
int avlTree::validate(string str)
{
if (checkInput(str))
return 100;
else
return 10;
}
You can also compile this code with the help of Online C++ Compiler