Introduction
HTML provides a set of basic tags that help structure web pages and define content elements such as headings, paragraphs, links, and images. These tags are essential for creating well-organized and readable web pages. Understanding these fundamental tags is crucial for beginners learning web development.

In this article, you will learn about the basic HTML tags, their syntax, and how to use them effectively in web design.
The Most Common HTML Tags
HTML tags are the building blocks of any webpage. They define how content is structured and displayed. Now, we’ll discuss the most common HTML tags, explain what they do, with the help of proper examples.
1. Headings (`<h1>` to `<h6>`)
Headings are used to create titles and subheadings on a webpage. There are six levels of headings, from `<h1>` (most important) to `<h6>` (least important).
For example:
<h1>Main Title of the Page</h1>
<h2>Section Heading</h2>
<h3>Subsection Heading</h3>
In this code:
- `<h1>` is the main heading. It’s usually the largest text on the page.
- `<h2>` is a smaller heading, often used for sections.
- `<h3>` is even smaller and can be used for subsections.
2. Paragraphs (`<p>`)
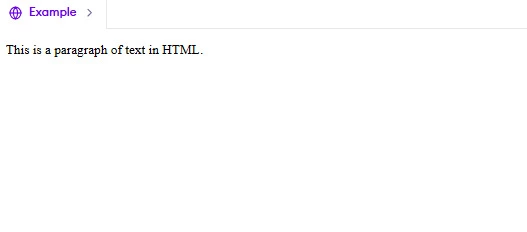
The `<p>` tag is used to add paragraphs of text. It’s one of the most common tags in HTML.
Example:
<p>This is the first paragraph of text. It explains something important about the topic.</p>
<p>This is the second paragraph. It provides additional details or examples.</p>
Each `<p>` tag starts a new block of text. Browsers automatically add space before and after paragraphs.
3. Links (`<a>`)
Links allow users to navigate between pages. The `<a>` tag creates a hyperlink.
Example:
<a href="https://www.example.com">Visit Example Website</a>
In this code:
- `href` specifies the URL the link points to.
- “Visit Example Website” is the clickable text users see.
4. Images (`<img>`)
The `<img>` tag is used to display images on a webpage. Unlike other tags, it doesn’t have a closing tag.
Example:
<img src="image.jpg" alt="Description of the image">
Here:
- `src` specifies the path to the image file.
- `alt` provides alternative text if the image fails to load.
5. Lists (`<ul>`, `<ol>`, `<li>`)
HTML supports two types of lists: unordered (`<ul>`) and ordered (`<ol>`). Each item in the list is marked with `<li>`.
Example of an unordered list:
<ul>
<li>First item</li>
<li>Second item</li>
<li>Third item</li>
</ul>
Example of an ordered list:
<ol>
<li>First step</li>
<li>Second step</li>
<li>Third step</li>
</ol>
Unordered lists use bullet points, while ordered lists use numbers.
6. Bold (`<b>`) & Italics (`<i>`)
You can make text bold or italic using `<b>` and `<i>` tags.
Example:
<p>This is <b>bold text</b> and this is <i>italic text</i>.</p>
These tags are useful for emphasizing certain parts of your content.
7. Divisions (`<div>`)
The `<div>` tag is a container used to group elements together. It’s often used with CSS for styling.
Example:
<div>
<h1>Title Inside a Div</h1>
<p>This paragraph is inside the same div as the heading.</p>
</div>
Think of `<div>` as a box that holds other elements.
8. Line Breaks (`<br>`)
The `<br>` tag adds a line break without starting a new paragraph.
Example:
<p>This is the first line.<br>This is the second line.</p>
This is helpful when you want to split text into multiple lines without extra spacing.