🎪Introduction
The BST resembles a tree with a single root at the top. Their ordered design enables quick searches and lookups, so they are perfect for storing numerical numbers.
The characteristics of BST are as follows as compared to a typical tree:
-
Every left child's value is lower than that of its parent.
-
Every right child has a value greater than that of its parent.
-
Every node has a child capacity of 0 to 2.

Also See, Interpolation in Angular
🎪Definition of a Binary Tree Node
In Javascript, we often define a Binary Tree Node with the following function:
function TreeNode(val, left, right)
{
this.val = val
this.left = left
this.right = right
}🎪Binary Tree Basic Traversals
Understanding how to loop around each BST node is the first thing to learn. It enables us to execute a function across all BST nodes.
There are mainly three methods for doing this.

🎨Inorder Traversal
The most straightforward technique to start with a binary tree, “Inorder Traversal,” is via a recursive algorithm. Here's the concept:
-
Recursively call the node's left child function until the node is not null.
-
Once you have gone through all the left children, perform the required operations on the node. In this case, print the node. The leftmost node will always be our current node.
-
Finally, call the node's right child.
The Inorder algorithm walks through the tree nodes from the left to the middle to the right.

Inorder: 4,2,1,7,5,8,3,6
const inorder = (root) =>
{
const nodes = []
if (root)
{
inorder(root.left)
nodes.push(root.val)
inorder(root.right)
}
return nodes
}
In the above code, we are recursively going towards the leftmost element of the binary tree. Then print all the root nodes one by one. Then moving towards the right node. This recursive call will print the “Inorder Traversal” of the binary tree in Javascript.
Time Complexity: O(n), where 'n' is the size of the binary tree.
Space Complexity: O(h), where ‘h’ is the height of the binary tree.
🎨Postorder Traversal
-
Recursively call the node's left child function until the node is not null.
-
Call the function on ‘node.right’ when there are no longer any children left.
-
Finally, perform the required node operations.
Postorder visits the tree nodes from left to right to the middle.

Postorder: 4,2,7,8,5,6,3,1
const postorder = (root) =>
{
const nodes = []
if (root)
{
postorder(root.left)
postorder(root.right)
nodes.push(root.val)
}
return nodes
}
In the above code, we are recursively going towards the leftmost element of the binary tree. Then print the rightmost element of that particular node using recursion at all nodes. This recursive call will print the “Postorder Traversal” of the binary tree in Javascript.
Time Complexity: O(n), where 'n' is the size of the binary tree.
Space Complexity: O(h), where ‘h’ is the height of the binary tree.
🎨Preorder Traversal
-
If the node is null, do nothing; if not, perform some action on it.
-
Repeat the process by moving to the node's left child.
-
Similarly, repeat the traversal for the right child of the node.
The tree nodes in postorder traversal are visited from the middle to the left to the right.
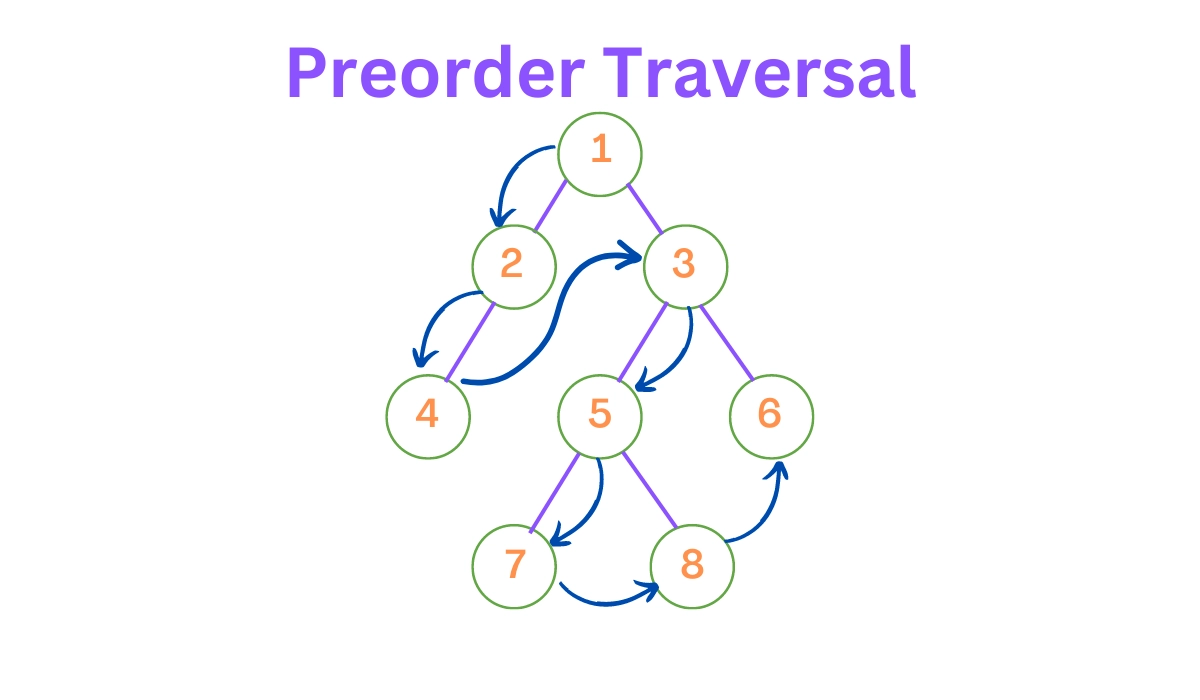
Preorder: 1,2,4,3,5,7,8,6
const preorder = (root) =>
{
const nodes = []
if (root)
{
nodes.push(root.val)
preorder(root.left)
preorder(root.right)
}
return nodes
}
In the above code, we first print the root value and then do a left and right traversal, respectively, using recursion at all nodes. This recursive call will print the “Preorder Traversal” of the binary tree in Javascript.
Time complexity: O(n), where 'n' is the size of the binary tree.
Space complexity: O(h), where ‘h’ is the height of the binary tree.







