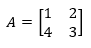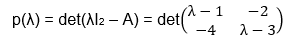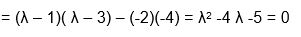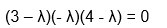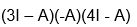Introduction
When you are working with matrices, you may have observed many cases when you want to use many powers of the same matrix. And even when you want to use the matrix in the linear equation, it is a lot of nuisance to calculate all these powers and equations again and again by just a tiny difference. So is there any method to solve this problem?
The answer to the above question is yes. We can solve all these problems with the Cayley-Hamilton theorem. We will learn more about this theorem while moving further with our blog so without wasting any time, let's proceed with our topic.
Cayley Hamilton Theorem and History
Cayley-Hamilton theorem states that every square matrix satisfies its characteristic equation when it is presided over by a commutative circle. A matrix with an equal number of rows and columns is known as a square matrix.
We use many terms in its equation to satisfy the characteristic equation. To find the characteristic polynomial of A, the equation is:
p(x) = det(xIn - A) ——— equation 1
In the above equation, A is a Square matrix, det refers to the determinant, I is the identity matrix, x is the variable, and p is the polynomial of the variable x.
This theorem states that in equation 1 when you substitute x with A, the result will be a zero matrix.
p(A) = 0
History
This theorem was made for working with linear algebra. It was theorized in the 17th century by two great mathematicians, Arthur Cayley and Rowan Hamilton. Arthur Cayley had given the basic idea, and Rowan Hamilton assisted him in succeeding with his idea.