HTML DOM Objects
The Document Object Model, or DOM, is the method through which a document's content is accessed. The Objects are arranged in a logical order. In a web document, the hierarchical structure is used to organize objects.
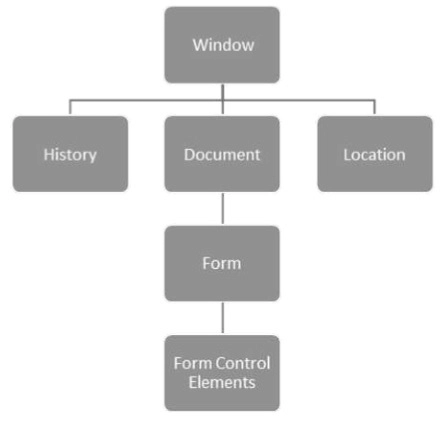
- Window: It is the most important position in the hierarchy. It is at the top of the object hierarchy.
- Document: A window object is created when an HTML document is loaded into a window. The contents of the page are included in the document.
- Elements: It denotes the webpage's content. For instance, title, text box, and so on.
- Nodes: These can be elements, attributes, comments, text, or other DOM types.
The hierarchy of the few significant DOM objects is shown below.
Using the dart:html library, we can control objects and elements in the DOM. The dart:html library is incompatible with the console-based applications. We need to import the dart:html library in order to work with the HTML library in the web application.
Syntax:
import 'dart.html';
In the following part, we'll look at the DOM operations.
Finding The DOM Elements
A document can have several attributes, and we may need to search for a certain attribute. The querySelector function in the dart:html library can be used to search for elements in the DOM.
Syntax:
Element querySelector(String selector);
The querySelector() function returns the first element matching the selector's provided group.
Event Handling
The onClick event for DOM Elements is provided by the dart:html library. The syntax demonstrates how an element might respond to a series of click events.
Syntax:
querySelector('#Id').onClick.listen(eventHandlerFunction);
The querySelector() function returns an element from the provided DOM, whereas onClick.listen() accepts an eventHandler method to be called when a click event is raised. The event handler syntax is listed below.
Syntax:
void eventHandlerFunction (MouseEvent event){ }
Frequently Asked Questions
Is DART suitable for web development?
Dart considers the web to be one of its primary platforms. Dart-to-JavaScript compilers are available for both development and production with a motive (of the rapid edit-refresh cycle) and (focus on code size and speed), respectively.
To add a component or element to the DOM, which method is used?
The appendChild() method is the simplest and most well-known technique for attaching an element to the DOM.
Does Dart have/support multiple interfaces?
Dart has the potential to implement multiple interfaces. The keyword implements enable a class to adhere to several interfaces, extending the polymorphic range of an object. The keyword implement is followed by the name of an existing named class, whose public fields are subsequently used to provide implementation requirements for the present class.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about Dart HTML DOM and its object hierarchy with DOM elements functioning and event handling.
If you want to learn more about Dart, here are some excellent blogs on Sets, Map, Symbol, Operator, Recursion, Variables, Libraries and Inheritance in Dart.
Happy Coding!





