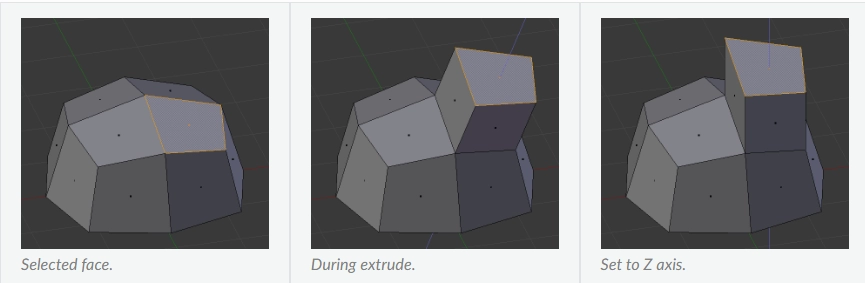
Introduction
Welcome readers! In this blog, we will learn about the Duplicate tool, which replicates the selected objects without connecting them to the rest of the mesh (unlike extrude, for example) and places the duplicate at the original location. It uses two methods, namely Object Duplicate and Linked Duplicate.
Further, we will learn two mesh tools, namely, Extrude and Snap in Blender. Mesh Edit Tool adds several tools to Blender that are not available in the built-in tools or provide different methods for similar tasks.
Duplicate
The Duplicate tool replicates the selected objects without connecting them to the rest of the mesh (unlike extrude, for example) and places the duplicate at the original location. When the duplication is complete, only the newly copied items are selected, and you are placed in move mode, allowing you to relocate your copy to a new location.
There are settings for Vector offset, Proportional Editing, Duplication Mode, and Axis Constraints in the toolbar.
There are two types of object duplication:
1. Object Duplicate
2. Linked Duplicates
Object Duplicate

Source: Blender
Object Duplicate creates a visually-identical copy of the selected object(s). The copy is made
in the exact location as the original object, and you are placed in Grab mode automatically.
Duplicate Objects is Blender's Copy/Paste. Selections are reproduced as independent objects from their originating parent but may include instanced references to material assignments, modifiers, UV maps, and other assignable characteristics (for mesh objects in particular). Make a selection, then click Duplicate Objects – Object > Duplicate Objects from the primary menu for the editor or editing context you're using, e.g., Object in Object Mode (3D View). Use the Shift + D shortcut instead. When you move the mouse over a group of objects, they will appear to move (and typically offset for visibility). To return the new selection to its original spot, right-click or hit Esc (coincidental to the parent from which it was duplicated).
Design Note: The menu labelled Object in Object Mode, Key in the Action Editor, Marker in the Timeline, and so on varies depending on the editor and/or active editing environment. In the 3D View, for example, the menu is labelled Object in Object Mode, Key in the Action Editor, Marker in the Timeline, and so on; regardless of whether the mouse cursor is over the editor/area/view before commencing, the shortcut keys Shift + D activate the function.
Source: Blender
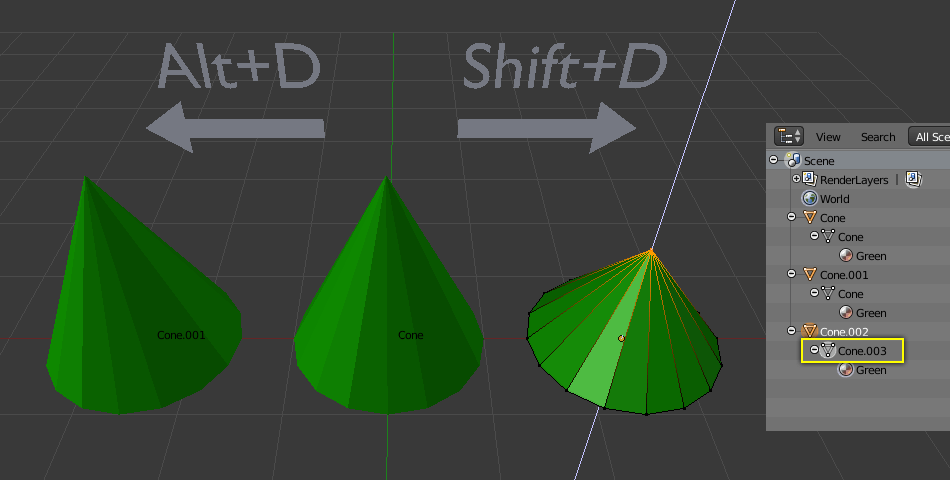
Object Cone.002's mesh Cone.006 is being updated. In the Outliner, the mesh's Unique data-block ID name is highlighted.
The central cone has been copied twice: once to the left and once to the right.
- The replicated right cone is being edited, but the original middle cone is being left alone. The mesh data was copied rather than connected.
- Likewise, the initial cone remains unaltered if the right cone is edited in object mode. The new object's transform properties or data block is a copy, not a connected copy.
- The material of the middle cone was passed down to the right cone when it was copied. The qualities of the materials were linked rather than duplicated.
Linked Duplicate
Source: Blender
Linked Duplicates vary from Duplicate Objects in that the data generated by this method is not unique. Thus it'll often keep references to any number of the parent object's properties, allowing changes to one to propagate to the others. In other words, while some characteristics of a selection may appear to be unique, such as object-based rotation, position, and scale, others, such as edit mode-based changes or adjustments, are not.
Where available, to use Duplicate Linked, select from the primary menu for the active editor or editing context, click Duplicate Linked – Object » Duplicate Linked. Alternatively, press Alt + D. A set of objects or elements will appear synced with the mouse, right-click or press Esc to release and reset back to their originating locations.
Design Note: The context menu for Duplicate Linked, like Duplicate Objects, is context-sensitive, having different locations based on the active editor and/or editing context; for example, in the 3D View, the menu is called Object in Object Mode, Key in the Action Editor, Marker in the Timeline, and so on. However, the function is activated regardless of the shortcut keys Alt + D.

Source: Blender
The object Cone.001 was linked and duplicated. Though both these cones are separate objects with unique names, the single mesh named cone, highlighted in the Outliner, is shared by both.