Introduction
In natural language processing, entity linking also referred to as named-entity linking (NEL), named-entity disambiguation (NED), named-entity recognition and disambiguation (NERD), or named-entity normalization (NEN), is the task of assigning a unique identity to entities (such as famous individuals, locations, or companies) mentioned in the text.
In entity linking, words of interest (names of persons, locations and companies) are mapped from an input text to corresponding unique entities in a target knowledge base. Words of interest are called named entities (NEs), mentions, or surface forms.
To give an example, "Paris is the capital of France," we want to know if the word "Paris" refers to the French capital, another city, Paris Hilton, or any of a number of other alternatives. like
"Paris(surname), a lit of fictional characters".
"Paris a prince of Troy in Greek mythology".
Let's look at another example to further grasp what entity linking is.
Assume we're creating an automated stock trader that will trade on news events. In a news story one morning, our algorithm comes across the phrase "Tesla Crashes, Jim Cramer Expects Rally." We immediately see an issue that our algorithmic trader must be able to solve: is the term "Tesla" referring to the public corporation, a Tesla vehicle, or (nonsensically) Nikola Tesla? If 'Tesla' refers to the firm, we know the headline is implying that Tesla stock has collapsed and that now is a good time to acquire Tesla stock at its current cheap price. If 'Tesla' refers to a Tesla vehicle, on the other hand, we know that this is a negative headline for Tesla (maybe a problem with self-driving technology caused a Tesla to crash on the highway), indicating that now is a good time to sell Tesla shares.
As humans, we find this challenge trivial: given references of the entities' Jim Cramer' and'Rally,' and their relationship to finance, we can relatively quickly and reliably deduce that this is, in fact, referring to Tesla stock from the context of the remainder of the story.
Named Entity Linking
Information extraction comprises multiple sub-tasks. In most cases, we will have the following sub-tasks. And they are performed in order to extract the information from unstructured data.
1. Named Entity Recognition (NER)
2. Named Entity Linking (NEL)
3. Relation Extraction
Named Entity Recognition(NER)
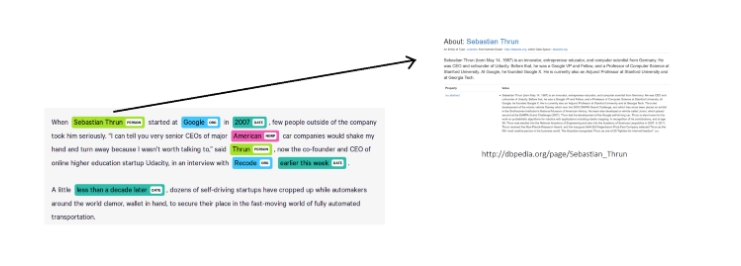
A named entity is a real-world object, such as persons, locations, organizations, etc. NER identifies and classifies named entity occurrences in text into pre-defined categories. NER is modelled as a task of assigning a tag to each word in a sentence. Below is an example result from a NER system.

NER will tell us what words are entities and what are their types. In the above example, NER will locate "Sebastian Thrun" as a person. But we still don't know exactly which "Sebastian Thrun" the text is speaking about in the above example. NEL is the next sub-task that will answer this question.
Named Entity Linking(NEL)
NEL will assign a unique identity to entities mentioned in the text. In other words, NEL is the task to link entities mentioned in the text with their corresponding entities in a knowledge base [1]. The target knowledge base depends on the application, but we can use knowledge bases derived from Wikipedia for open-domain text. In our above example, we can find exactly which "Sebastian Thrun" by linking the entities to DBpedia. DBpedia is a structured knowledge base extracted from Wikipedia. This process of linking entities to Wikipedia is also called Wikification.
NEL is also referred to as Entity Linking, Named Entity Disambiguation (NED), Named Entity Recognition and Disambiguation (NERD) or Named Entity Normalization (NEN). NEL has a wide range of applications other than Information Extraction. NEL is used in Information Retrieval, Content Analysis, Intelligent Tagging, Question Answering systems, Recommender Systems, etc.
NEL also plays a significant role in the Semantic Web. The Semantic Web is a term coined by Tim Berners-Lee for a web of data that can be processed by machines. A vital issue in the Semantic Web is automatically populating and enriching existing knowledge bases with newly extracted facts. NEL is inherently considered an essential subtask for the knowledge base population.





