Introduction
One of GWT's key selling points is that you can use an industry-standard language and a set of industry-standard tools to create industry-standard web apps. But like with any significant development endeavor, it's simple to back oneself into a hole. When developing GWT-based apps, we frequently throw code wherever needed to make the program function and—sometimes more importantly—look decent.
The good news is that this problem has a well-known solution: model your apps after the model-view-presenter (MVP) paradigm.
To avoid some frequent errors, the Model View Presenter (MVP) paradigm should be used while designing your GWT-based programs.

What is MVP?
It's a method for layering code that addresses various problems when building applications haphazardly.
A good alternative to MVC is the MVP architecture pattern, which can be used to address some of its drawbacks. It offers a simple way to consider the app's structure. It offers testability, modularity, and generally a cleaner and easier-to-maintain codebase.
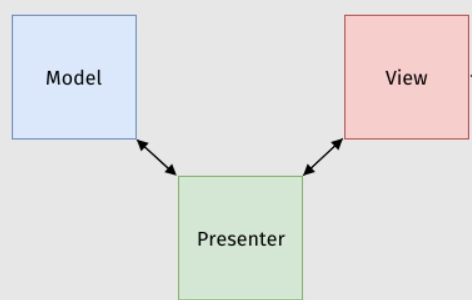
When the abbreviation is broken down, the following elements make up MVP:
- Model: The segment's model is made up entirely of data. It contains the business object that must be adjusted and calculated under application requirements.
- View: It just consists of the view, which displays the presenter's data. The code for the view can be reused because switching to a new view is so simple. It exclusively addresses HTML and CSS, which aids with independent testing.
-
Presenter: It includes all of the logic that must be used to create the application. Both the view and the model can communicate with it. It operates completely independently and offers independent JUnit testing.
In MVP, the controller and view components are separated, making both the presenter and the view more lightweight. Traditionally, the controller Activity class handled both updates to the model and what is displayed on the screen.





