Introduction🗒️
A web application is software or a program with multiple features and commands running whenever a client accesses a URL. A web application can be created using a variety of technological languages, but creating one from scratch can be time-consuming. To create a web app quickly, developers typically employ web frameworks. A web framework comprises modules, libraries, and APIs that lets programmers create web applications fast, effortlessly, and without worrying about web development's technical language and protocols. Moving towards insert, commit, and rollback in Web2Py.

One of the most well-known Python programming languages, Web2Py, will be this blog's exclusive topic of discussion. We will be discussing insert, commit and rollback in Web2Py. Let's get started.
🚀Insert
Let's understand the insert from the insert, commit and rollback in Web2Py.

>>> dBase.person.insert(name="Amit")
1
>>> dBase.person.insert(name="Shyam")
2
The "Insert" returns the unique "id" value of each record inserted. Here 1 and 2 are unique IDs that were returned.
🤔How to reset the id❓
⭐If needed, you can truncate the table, i.e., delete all of the records and reset the id counter.
>>> dBase.person.truncate()
⭐Now, if you insert a data again, the counter starts again from 1 (this is back-end specific and does not apply to major databases like Google NoSQL):
>>> dBase.person.insert(name="Divya")
1
⭐This is to be noted that you can pass a parameter to truncate the data in Table. For example, you can tell the database SQLite to restart the id counter.
>>> dBase.person.truncate('RESTART IDENTITY CASCADE')
The argument is in raw SQL and, therefore, engine specific.
web2py also provides a bulk_insert method. It executes many inserts at once using a list of dictionaries that contain the fields that need to be added. The list of "id" values for the inserted records is returned. Using this function instead of looping and executing individual inserts has no advantage on the supported relational databases, but on Google App Engine NoSQL, there is a significant speed advantage.
>>> dBase.person.bulk_insert([{'name': 'Amit'}, {'name': 'Shyam'}, {'name': 'John'}])
[3, 4, 5]
Now I hope you have got a fair idea of Insert from the insert, commit and rollback in web2py.
Let's continue our discussion of insert, commit and rollback in Web2Py and learn about commit and rollback.
♻️Commit and Rollback
When web2py issues the commit command, the insert, truncate, delete, and update operations are committed. Depending on the database engine, the create-and-drop actions could be carried out immediately. Actions are automatically wrapped around calls to web2py operations. If you used the shell to run commands, you must manually commit, and this explains commit and rollback from the insert, commit, and rollback in Web2Py.
❓Confused
Ok Ok! This is too much stuff in one paragraph from the insert, commit, and rollback in Web2Py let us understand by the below graphic image. I am sure that will help understand insert, commit and rollback in Web2Py!
Firstly some data is inserted into the database as we have seen in insert of insert, commit, and rollback in Web2Py.

⭐Now, we committed our data using,
>>> dBase.commit()
⭐This query commits our data. Now, let's add some more data to the person table.
>>> dBase.person.insert(name="Divya")
3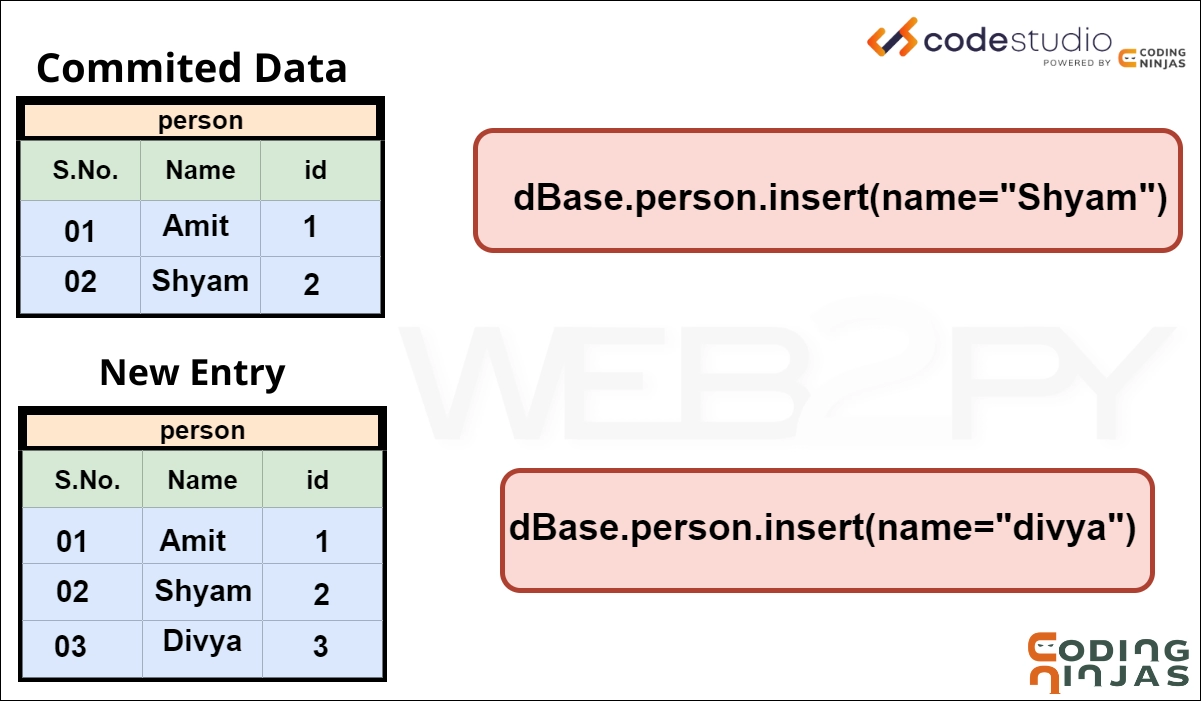
So Divya is inserted into the person table after committing. Remember this fact for a while!
⭐Now, we call the rollback function,
>>> dBase.rollback()
rollback() ignores all operations since the last commit.
⭐Now adding More data to check how ID is changing with rollback,
>>> dBase.person.insert(name="Anurag")
3
Notice that rollback() only removed Divya from the person table.
If you now insert an element again in the person table, the counter will again be set to 3 since the previous insert was rolled back. Recall the first image of this section.
I hope now you have completely understood the insert, commit and rollback in Web2Py. Let’s move on to the FAQs of insert, commit and rollback in Web2Py.







