Introduction
JavaFX is an open-source platform for desktop, mobile, and embedded systems whose goal is to take client experience to the next generation. It is the result of the efforts made by many individuals and companies with the aim to produce an efficient, modern, and fully featured toolkit facilitating the development of rich client applications. In this blog, we will try to make you understand JavaFX transformations that are in-built, in detail.
JavaFX Transformation
By the word Transformation, we understand that it is a change in form, nature or appearance of the graphics. These changes are done keeping some rules in reference. The JavaFX Transformation enables us to perform transformations such as translation, rotation, and scaling on Java FX nodes attached to the JavaFX graph screen. All these JavaFX transformations are done using different classes belonging to the same package, that is their parent class, javafx.scene.transform. In this blog, we will take a closer look at these transformations and their implementation using Java.
Types of JavaFX Transformations
We already learned that certain in-built transformations allowed in JavaFX are Translation, Rotation, and Scaling. To know more about these JavaFX transformations and for a clearer understanding, refer to the descriptions below.
Translation
When we say Translation, it means to displace. Translation in JavaFX is used to relocate or change the position of any node present in the graph screen. The class used to represent translation is javafx.scene.transform.Translate in which javafx.scene.transform is the parent class. You can use the images below for a better understanding.

Before Translation

After Translation
From the images, we could imagine that how actually performing translation would look like. The image has been translated to a new position.
Rotation
When we say Rotation, it means to turn the object from its origin. Rotation in JavaFX is used for the same, that is, to rotate any object by a certain angle present in the graph screen. The class used to represent translation is javafx.scene.transform.Rotate in which javafx.scene.transform is the parent class. You can refer to the images below for a better understanding.

Before Rotation

After Rotation
From the images, we could imagine that how actually performing rotation would look like. The image has been rotated around a pivot point.
Scaling
When we say Scaling, it means to either increase or decrease the size. Scaling in JavaFX is used to change the size of any object present in the graph screen, that is, either to scale up or scale down. The class used to represent translation is javafx.scene.transform.Scale in which javafx.scene.transform is the parent class. You can refer to the images below for a better understanding.

Before Scaling

After Scaling down
From the images, we could imagine that how actually performing scaling would look like. The image has been scaled down.
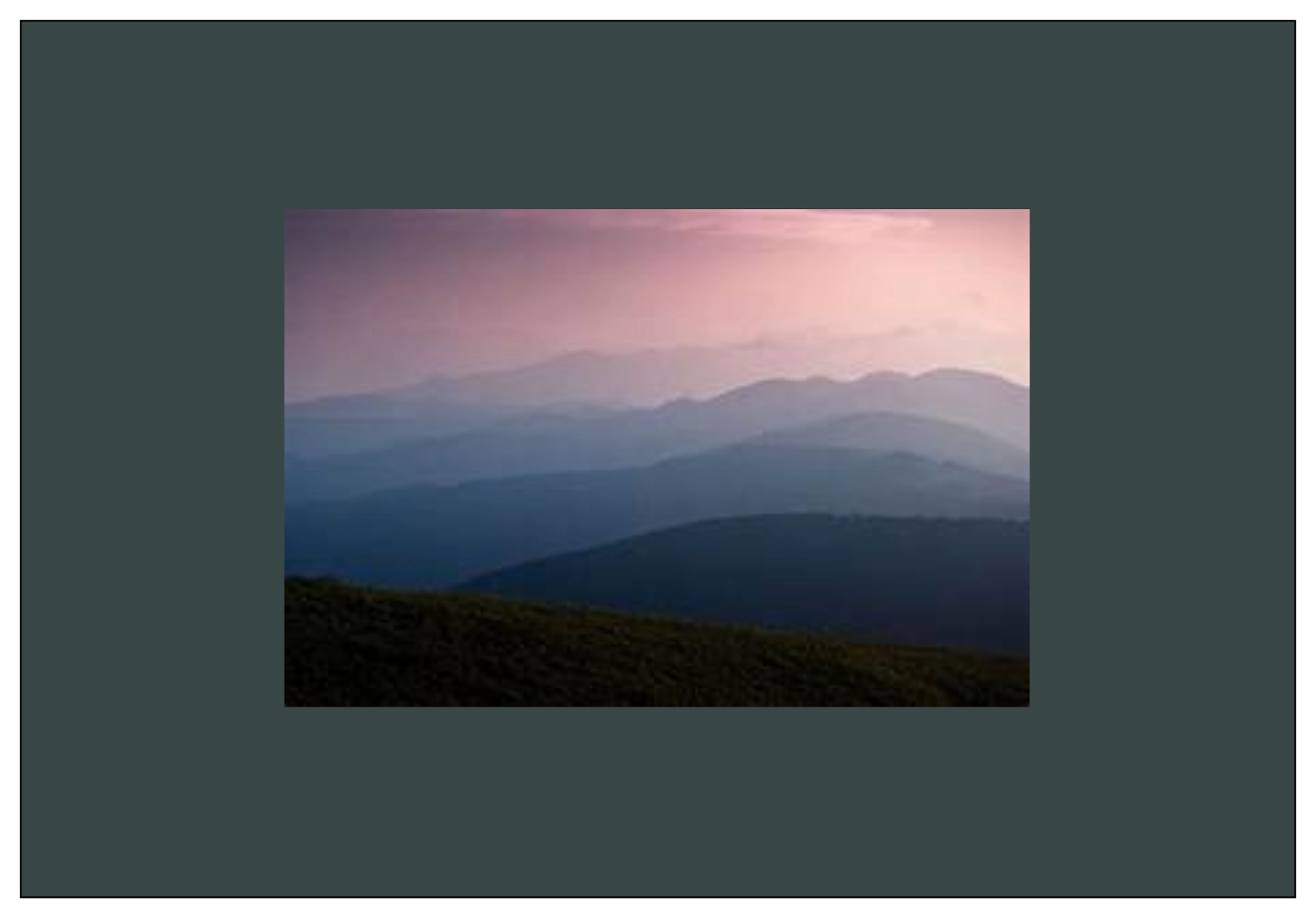
Multiple Transformations
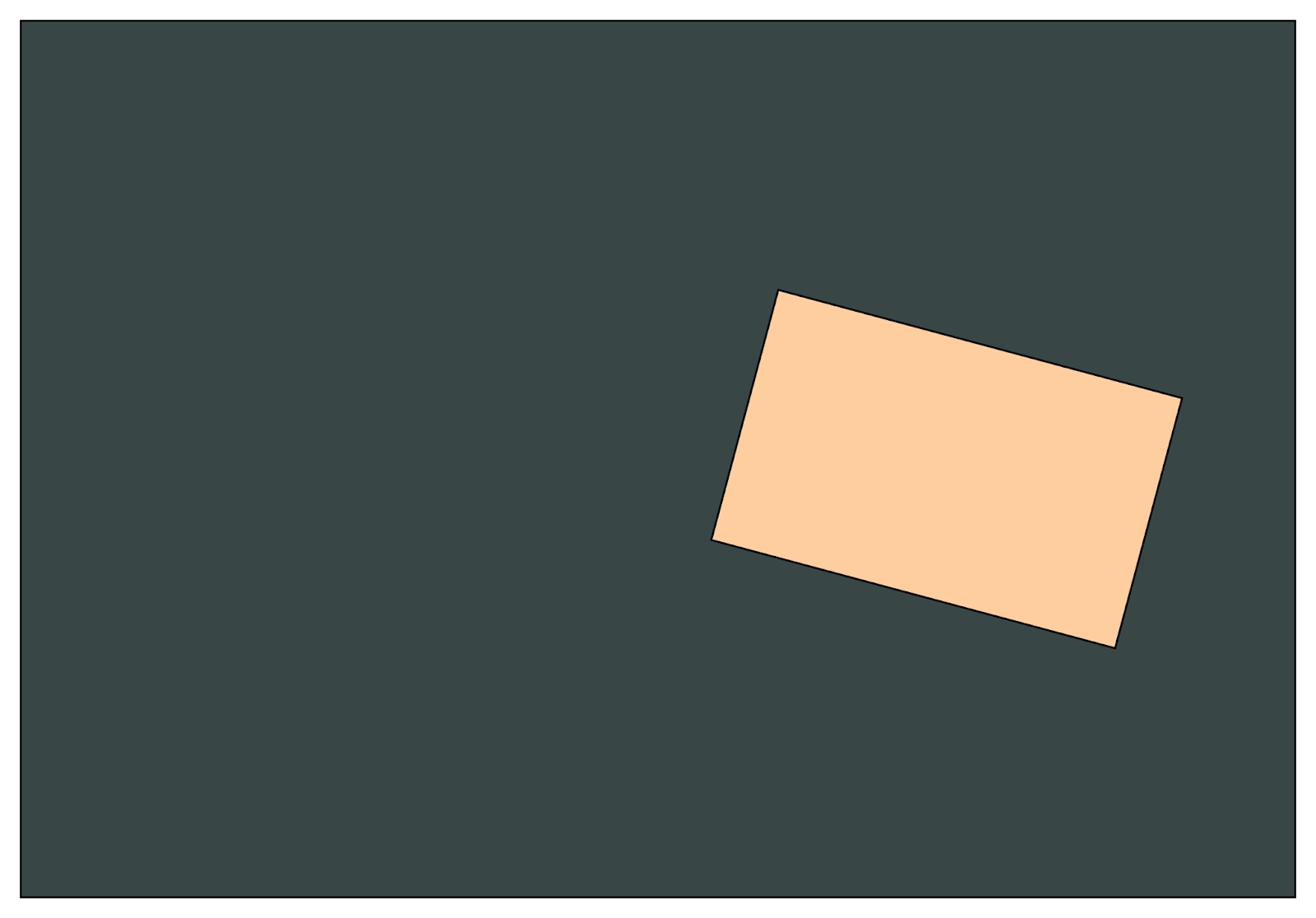
You can apply multiple in-built transformations such as Translation, Rotation, and Scaling on nodes in JavaFX simultaneously. The following implementation of various transformations in Java shows how these transformations are performed in a Rectangle. You can refer to the images below for a better understanding.

Before Transformations
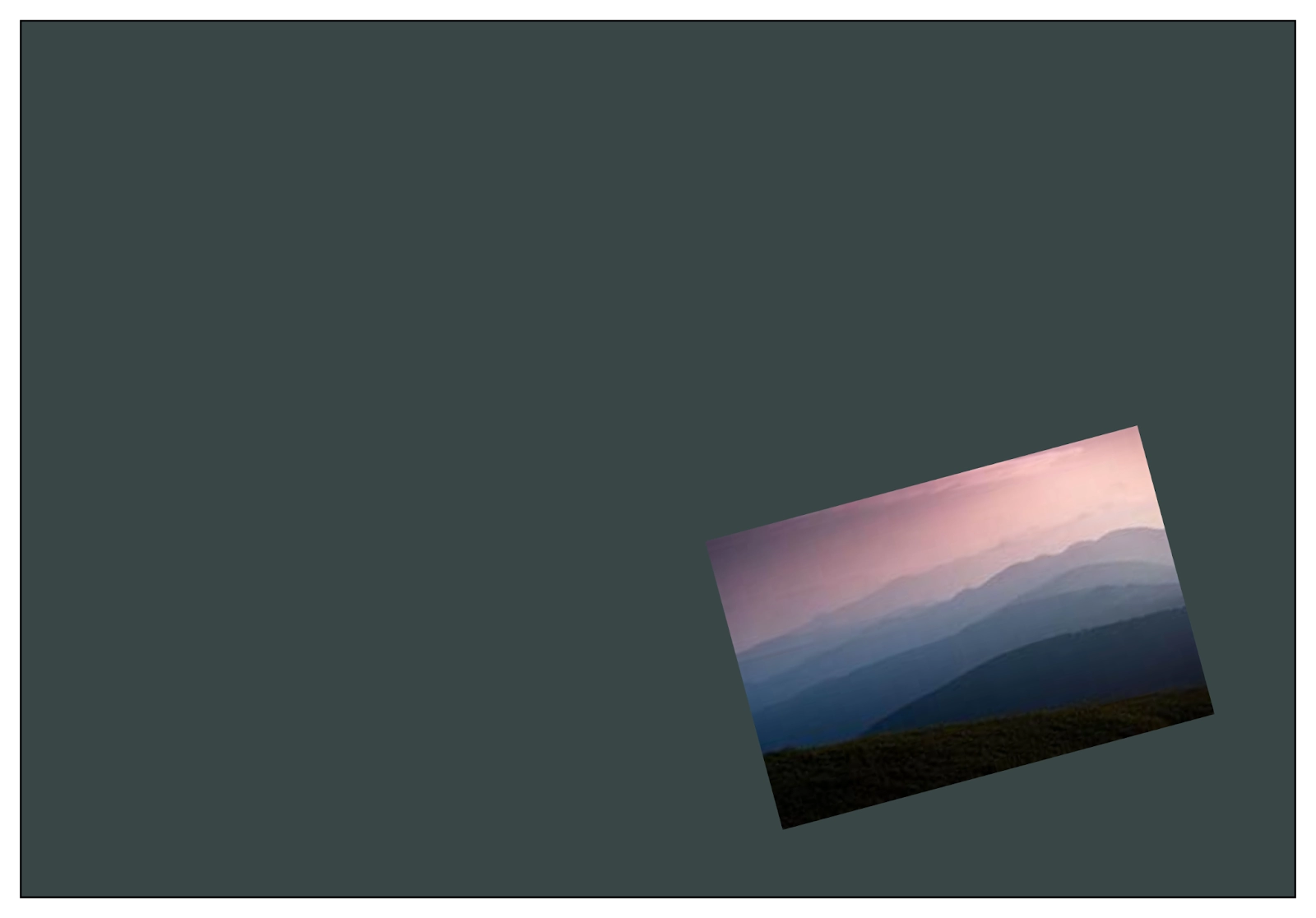

After Transformations
From the images, we could imagine that how actually performing multiple transformations would look like. The image has been translated, rotated, and scaled-down simultaneously.
Implementation in Java
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Rectangle;
import javafx.scene.transform.Rotate;
import javafx.scene.transform.Scale;
import javafx.scene.transform.Translate;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class MultipleTransformationsExample extends Application
{
@Override
public void start(Stage stage)
{
//Forming a Rectangle
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(50, 50, 100, 75);
rectangle.setFill(Color.BURLYWOOD);
rectangle.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
//performing Rotation
Rotate rotate = new Rotate();
rotate.setAngle(20);
rotate.setPivotX(150);
rotate.setPivotY(225);
//performing Scaling
Scale scale = new Scale();
scale.setX(1.5);
scale.setY(1.5);
scale.setPivotX(300);
scale.setPivotY(135);
//performing Translation
Translate translate = new Translate();
translate.setX(250);
translate.setY(0);
translate.setZ(0);
//Adding all the transformations
rectangle.getTransforms().addAll(rotate, scale, translate);
Group root = new Group(rectangle);
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
stage.setTitle("Multiple transformations");
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
Output:
On executing the implementation above, we get the output image as: