Introduction
Microsoft Azure, which was earlier known as Windows Azure. It is a public cloud computing platform of Microsoft. It offers a wide variety of cloud services, that includes computing, analytics, storage, and networking.
For these services, it also provides IP addresses which can be of two types - public and private.
In this article, we will discuss both these types of IP addresses in Azure in detail.
Public IP addresses in Azure
Public IP addresses enable Internet resources to communicate inbound to Azure resources. Public IP addresses allow Azure resources to communicate to the Internet and public-facing Azure services. The address is reserved for the resource until gets unassigned by the user. A resource can communicate outbound without a public IP address assigned. Azure assigns an available IP address that is not dedicated to the resource dynamically.
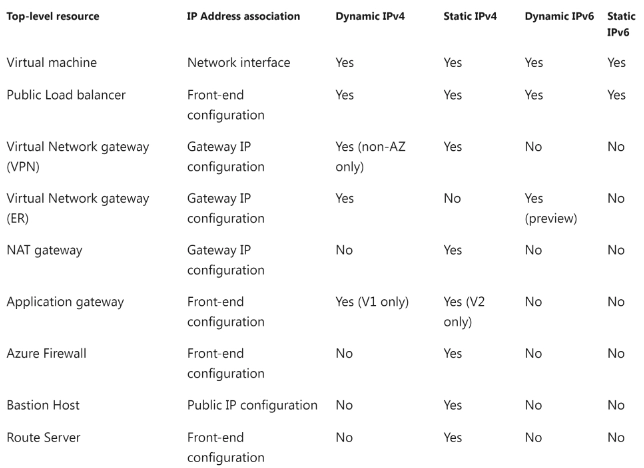
A public IP address in Azure Resource Manager is a resource and has its own properties. Some of the resources that public IP address resources can be associated with are:
- Virtual Network Gateways(VPN/ER)
- Application Gateways
- Virtual Machine Network Interfaces
- Virtual Machine Scale Sets
- Public Load Balancers
- NAT Gateways
- Azure Firewall
- Bastion Host
- Route Server
The below table shows the property a public IP can be related with a resource and the allocation methods. Note that public IPv6 support is not available for all resource types.
IP Address Assignment
Public IPs have two types of allocations:
- Static - The resource is given an IP address at that time it is created. When the resource is deleted, the IP address is released.
- Dynamic - The IP address is not given to the resource at the time of creation when selecting dynamic. The IP is assigned when the user associates the public IP address with a resource. The IP address is released when the user stops or deletes the resource
Static public IP addresses are usually used in the following situations:
- When the user must update firewall rules to communicate with the user’s Azure resources.
- DNS name resolution - where a change in IP address would require updating records.
- The user’s Azure resources communicate with other services or apps that use an IP address-based security model.
- The user uses TLS/SSL certificates connected to an IP address.
Limitations of public IP addresses for IPv6
- Either directly or peered with "UseRemoteGateway", VPN gateways cannot be used in a virtual network with IPv6 enabled, .
- Public IPv6 addresses are locked at a constant timeout of 4 minutes.
- While adding IPv6 to existing IPv4 deployments, IPv6 ranges can not be added to a virtual network with existing resource navigation links.
- Azure does not allow IPv6 communication for containers.
- The usage of IPv6-only virtual machines or virtual machines scale sets is not supported. Each NIC should include at least one IPv4 IP configuration (dual-stack).
- Reverse DNS for IPv6 is not supported. Forward DNS for IPv6 is allowed for Azure public DNS.
- Routing Preference and cross-region load-balancing are not allowed.





