Introduction
JavaServer Pages or JSP is a Java-based technology used to create dynamic web pages. JSP helps insert Java code in an HTML file using special JSP tags. For example, a JSP page to display the first five even numbers will look like this,
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>JSP Page</title>
</head>
<style>
body{
padding: 50px;
}
</style>
<body>
<%
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
if(i%2==0)
out.print("<h1>Even No: "+i+"</h1>");
}
%>
</body>
</html>
Pagination
Suppose we have multiple records in our database. In that case, we use Pagination to break the records into more convenient readable bits, both for the user and the processor, as a single page having multiple records may take time to load and can be tiring for the user to go through. Let us look at an example of Pagination,
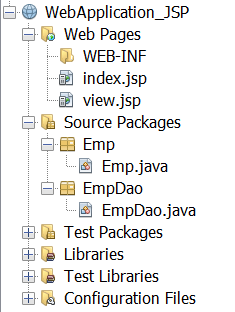
We will be creating our project in Netbeans, using a XAMPP server to connect to our SQL Database. Following will be the project structure.
index.jsp
<%@page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>JSP Page</title>
</head>
<body>
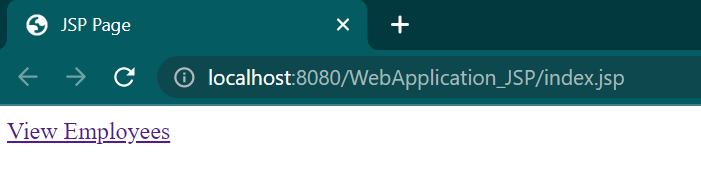
<a href="view.jsp?page=1">View Employees</a>
</body>
</html>
view.jsp
<%@page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>JSP Page</title>
</head>
<style>
body{
padding: 50px;
}
</style>
<body>
<%@ page import="java.util.*,Emp.*,EmpDao.*" %>
<%
String spageid=request.getParameter("page");
int pageid=Integer.parseInt(spageid);
int total=5;
if(pageid!=1){
pageid=pageid-1;
pageid=pageid*total+1;
}
List<Emp> list=EmpDao.getRecords(pageid,total);
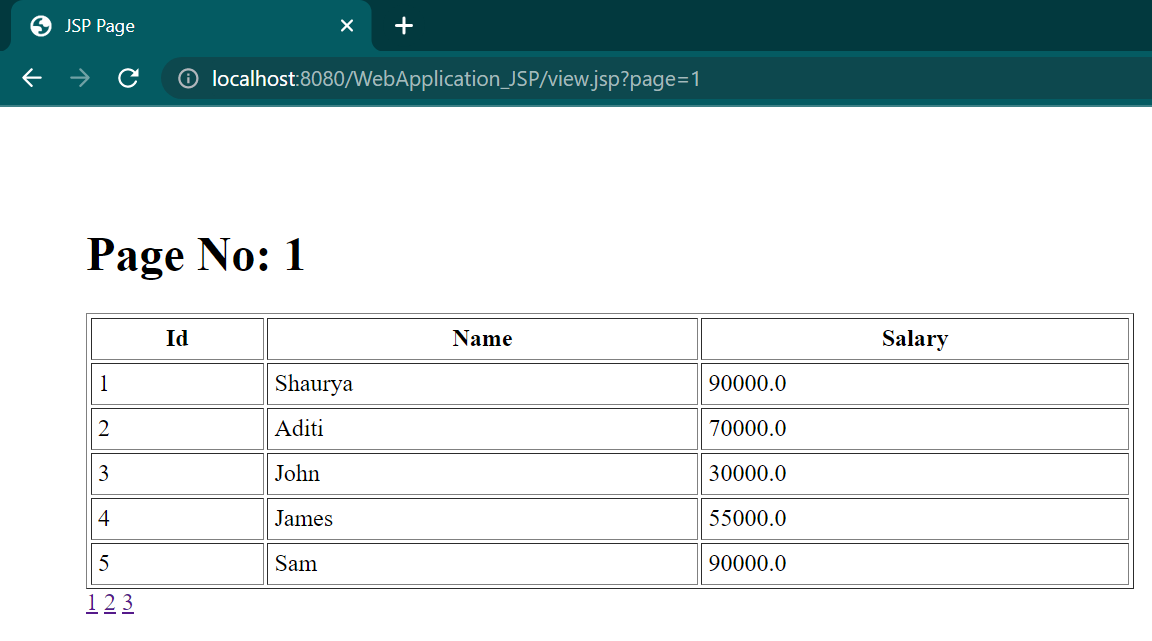
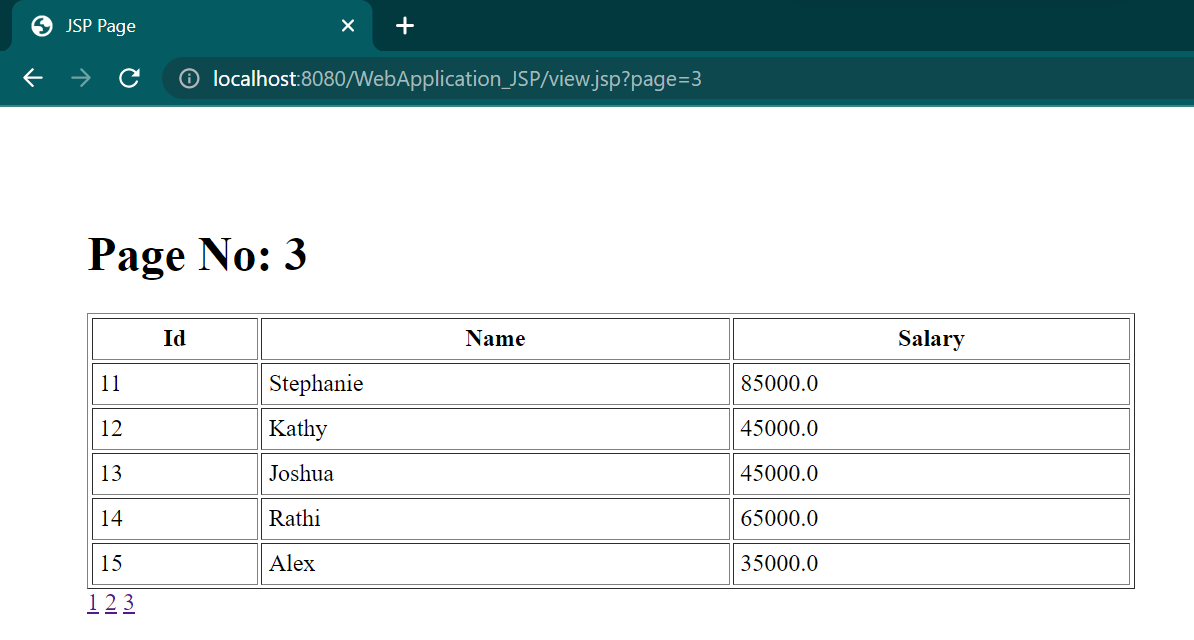
out.print("<h1>Page No: "+spageid+"</h1>");
out.print("<table border='1' cellpadding='4' width='60%'>");
out.print("<tr><th>Id</th><th>Name</th><th>Salary</th>");
for(Emp e:list){
out.print("<tr><td>"+e.getId()+"</td><td>"+e.getName()+"</td><td>"+e.getSalary()+"</td></tr>");
}
out.print("</table>");
%>
<a href="view.jsp?page=1">1</a>
<a href="view.jsp?page=2">2</a>
<a href="view.jsp?page=3">3</a>
</body>
</html>
Emp.java
package Emp;
/**
*
* @author 91963
*/
public class Emp {
private int id;
private String name;
private float salary;
public void setId(int aInt) {
id = aInt;
}
public void setName(String string) {
name = string;
}
public void setSalary(float aFloat) {
salary = aFloat;
}
public int getId(){
return id;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public float getSalary(){
return salary;
}
}
EmpDao.java
package EmpDao;
import java.sql.*;
import Emp.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
*
* @author 91963
*/
public class EmpDao {
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection con=null;
try{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test","root","");
}catch(ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e){System.out.println(e);}
return con;
}
public static List<Emp> getRecords(int start,int total){
List<Emp> list=new ArrayList<>();
try
{
try (Connection con = getConnection()) {
PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement("select * from emp limit "+(start-1)+","+total);
ResultSet rs=ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
Emp e=new Emp();
e.setId(rs.getInt(1));
e.setName(rs.getString(2));
e.setSalary(rs.getFloat(3));
list.add(e);
} }
}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);}
return list;
}
}
Output