Making an Empty Rails Web Application
We will create a cookbook database and a table called recipes.
Open a command window and navigate it to where you want to create this application and to complete the directory structure, run the following command:
tp> rails new cookbook
Setting up the database
You can create the database by running in any SQL software here. We are running it in my SQL.
Mysql> create database cookbook;
mysql> grant all privileges on cookbook.*
to 'root'@'localhost' identified by 'password';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Run all three above commands individually.
We need to instruct rails to find the database and, to do so, change the database name to the cookbook and edit the configuration file cookbook\config\database.yml. For now, leave the password empty. The file should look as follows:
development:
adapter: mysql
database: cookbook
username: root
password: [password]
host: localhost
test:
adapter: mysql
database: cookbook
username: root
password: [password]
host: localhost
production:
adapter: mysql
database: cookbook
username: root
password: [password]
host: localhost
Using different databases, Rails lets you run in test mode, development mode, or production mode.
The Generated Scaffold Code
The rails generate all the needed code dynamically with the help of scaffold action. Users can get all the code written to disk by running scaffold as a script. With the code, we can tailor it according to our requirements.
Now let’s generate Scaffold code manually by using the scaffold helper script:
cookbook> rails generate scaffold recipe
It Generates auto files as shown below:
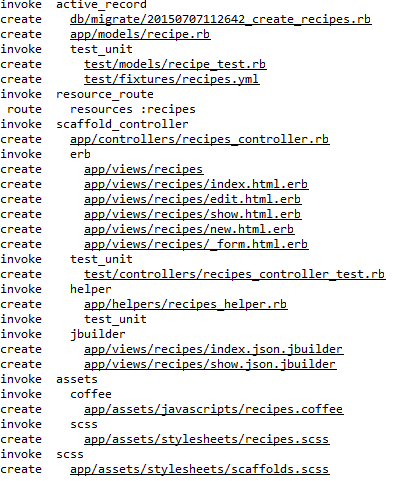
The Controller
Let’s look at the code created by the scaffold generator behind the controller. In app/controllers/recipes_controller.rb, the code should be something like this:
class RecipesController < ApplicationController
before_action :set_recipe, only: [:show, :edit, :update, :destroy]
# GET /recipes
# GET /recipes.json
def index
@recipes = Recipe.all
end
# GET /recipes/1
# GET /recipes/1.json
def show
end
# GET /recipes/new
def new
@recipe = Recipe.new
end
# GET /recipes/1/edit
def edit
end
# POST /recipes
# POST /recipes.json
def create
@recipe = Recipe.new(recipe_params)
respond_to do |format|
if @recipe.save
format.html { redirect_to @recipe, notice: 'Recipe was successfully created.' }
format.json { render :show, status: :created, location: @recipe }
else
format.html { render :new }
format.json { render json: @recipe.errors, status: :unprocessable_entity }
end
end
end
# PATCH/PUT /recipes/1
# PATCH/PUT /recipes/1.json
def update
respond_to do |format|
if @recipe.update(recipe_params)
format.html { redirect_to @recipe, notice: 'Recipe was successfully updated.' }
format.json { render :show, status: :ok, location: @recipe }
else
format.html { render :edit }
format.json { render json: @recipe.errors, status: :unprocessable_entity }
end
end
end
# DELETE /recipes/1
# DELETE /recipes/1.json
def destroy
@recipe.destroy
respond_to do |format|
format.html { redirect_to recipes_url, notice: 'Recipe was successfully destroyed.' }
format.json { head :no_content }
end
end
private
def set_recipe
@recipe = Recipe.find(params[:id])
end
def recipe_params
params.require(:recipe).permit(:title, :instructions)
end
end
The controller will execute any code according to the user's selected action, e.g., "Show" Then, by default, it looks for the template of the name-"show.html.erb".
The controller uses ActiveRecord methods such as new, save, update_Attributes, find_all, and destroy to move data from the database tables.
One advantage is you don’t have to write anything in SQL rails will automatically take care of them.
This will provide the table with many options like
- Creating new entries
- Editing current entries
- Viewing current entries
- Destroying current entries
While creating entries, the scaffold will do most of the work and provide you with many types of inputs like
- Simple Text strings
- Text areas
- Date selector
- Date time selectors
Users can you rails migrations to create and maintain tables.
rake db: migrate RAILS_ENV=development
Now run the web server with the following command:
cookbook>rails server
Now visit the site http://127.0.0.1:3000/recipie/new. There will be an option available to create new recipes.
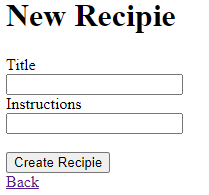
Once you press the create button, your record is added to the database and shows the following result:

You can also see the option to edit the records.
Enhancing the Model
Rails give you an advantage or error handling for free. In the empty recipe, the model adds some validation rules.
Modify app/models/recipe.rb as follows:
class Recipe < ActiveRecord::Base
validates_length_of :title, :within => 1..20
validates_uniqueness_of :title, :message => "already exists"
end
There are some automatic checking entries.
- Validates_length_of - The field is not too long and blank.
- Validates_uniqueness_of - Duplicate messages are not allowed, and instead of the default error message, we have provided a custom one.
Alternative Way to Create Scaffolding
Creates the above-shown application and the generated scaffold code as shown below
rails g scaffold Recipe title: string instructions: text
The above code uses sqlite3 with instructions and titles to generate files automatically.

The data must be migrated by below syntax
$ rake db: migrate RAILS_ENV=development
At last, run the application using the following command line:
rails server
This will generate the result as above images.
Views
The scaffold command generates the views and controllers and is available in the app/views/recipes directory.
Nested Scaffold
It is a command that produces a set of perfectly working nested resources on running.
Features
- Generate a nested child resource with a single command.
- Generates a beautifully working bunch of code.
- For Active records generates model associations automatically.
- Haml ready
Syntax
Use the following command to install the nested_scaffold
gem ‘nested_scaffold’
FAQs
-
Write the advantage of Scaffolding over methods like list, show, etc.?
We do not have to create all these methods while working with Scaffolding. It does all this work for us.
-
Write some benefits of Scaffolding?
Can quickly get in front of users for feedback, can learn working of rails by looking at the generated code.
-
How do you remove scaffolds in rails?
Perform a rollback first by performing the command rake db: rollback.
-
What is the difference between both static and dynamic Scaffolding?
Static Scaffolding needs user insertion commands to generate data fields, whereas Dynamic Scaffolding generates the entire content at run time.
Key Takeaways
In this blog, we have discussed Scaffolding, its features, Setting it up from scratch, Its type like Nested Scaffold.
If you want to know about Layout in Ruby on Rails, like what they are, how to create them, how to use them, etc. Then it would be best to refer to this blog here. You will get a whole idea about all this stuff and many more.








