Introduction
Monitoring pages, analysing site performance, ensuring the site is accessible to consumers with disabilities, and searching for optimization possibilities are all solid reasons for e-commerce business owners and managers to crawl their websites.
There are separate tools, web crawlers, and services available to assist you in monitoring your site for each of these.
While these solutions might be useful, you can design your own web crawler and monitoring system with only a little coding work.
Getting Started with Scraping
First of all, make sure that you have scrapy installed in your system. If not, execute the following command in the terminal to install scrapy.
pip install scrapyNow to use scrapy, we need to start a scrapy project. Navigate to a suitable directory and execute the following command in the terminal.
scrapy startproject ecomScraping
This command will create a scrapy project with some files and boilerplate code.
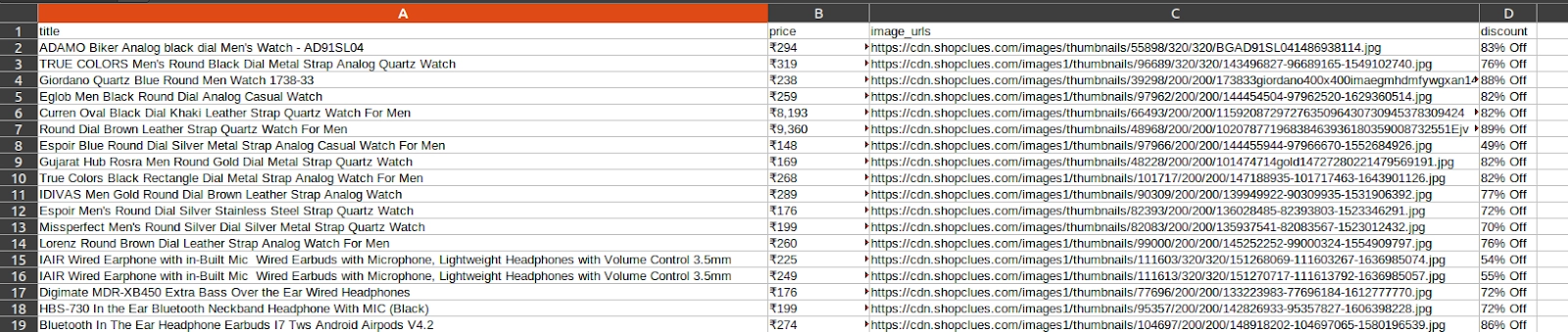
For our project, we will be scraping shopclues website. More specifically, we will be scraping the following information about their headphones and watches:
- Image link of the product
- Name of the product
- Discount of the product
- Discounted price of the product
Scrapy Shell
To understand how to extract the required information, we need to dig deeper into the HTML of the page.
To explore the HTML, execute the below command in the terminal to enter into the scrapy shell.
scrapy shell www.shopclues.com/mobiles-featured-store-4g-smartphone.html
First, we want to get the name of the product. We can get that in image attributes.
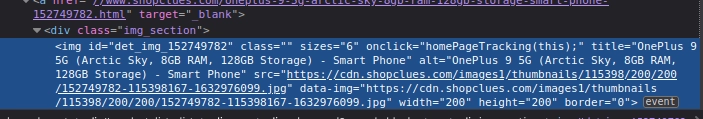
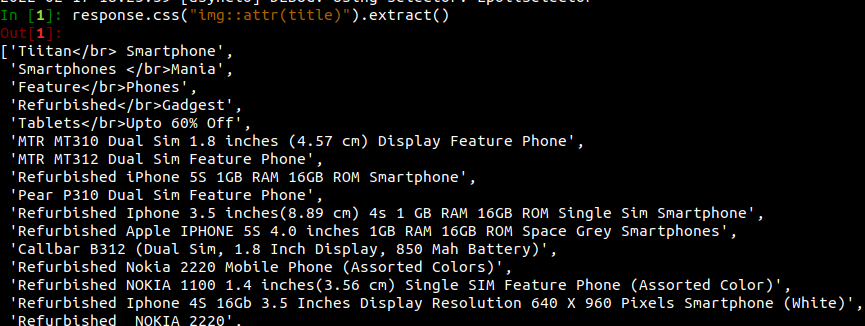
The title is stored in the title attribute of the image. So, we get a list of titles by executing the above command.
In [1]: response.css("img::attr(title)").extract()
Output:
Practice this code with the help of Online Python Compiler
Now we want to get the discount on the product. We can do so by executing the following command.
In [3]: response.css('.prd_discount::text').extract()
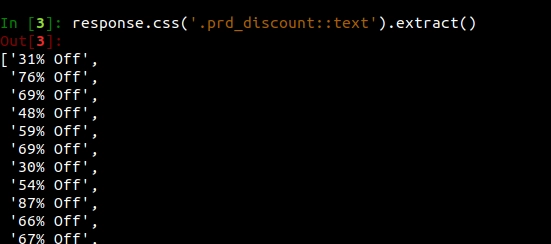
We can do the same for getting the price, discount, and image of the product.
Now coming back to scraping.
Navigate to the spider folder in the project and create a file named fetch.py (you can name it anything).
We need to fetch from the link headphone and watches.
We start by creating the spider class and naming it extractProduct. We then define the start_requests() function and write the URLs.
import scrapy
class ExtractProduct(scrapy.Spider):
name = "extractProduct"
# request function
def start_requests(self):
urls = ['https://www.shopclues.com/search?q=watch&sc_z=2222&z=0&count=9&user_id=&user_segment=default','https://www.shopclues.com/search?q=Headphones&z=0&user_id=&user_segment=default&trend=1']
for url in urls:
yield scrapy.Request(url = url, callback = self.parse)
We know that for extracting the information from the response, we use the below commands.
title = response.css('img::attr(title)').extract()
discount = response.css('.prd_discount::text').extract()
image = response.css('img::attr(data-img)').extract()
price = response.css('.p_price::text').extract()
Hence final code is after adding the parse function is.
import scrapy
class extractQuotes(scrapy.Spider):
name = "extractProduct"
def start_requests(self):
urls = ['https://www.shopclues.com/search?q=watch&sc_z=2222&z=0&count=9&user_id=&user_segment=default','https://www.shopclues.com/search?q=Headphones&z=0&user_id=&user_segment=default&trend=1']
for url in urls:
yield scrapy.Request(url = url, callback = self.parse)
def parse(self, response):
discount = response.css('.prd_discount::text').extract()
price = response.css('.p_price::text').extract()
image = response.css('img::attr(data-img)').extract()
title = response.css('img::attr(title)').extract()
for item in zip(title,price,image,discount):
product_information = {
'title' : item[0],
'price' : item[1],
'image' : item[2],
'discount' : item[3]
}
yield product_information
We can run it and store the information in a file using.
scrapy crawl extractProduct -o a.csv
Output: