Introduction
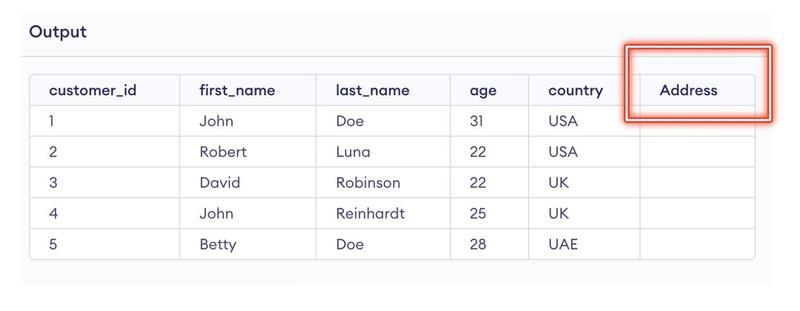
Consider yourself in a situation where you have created a table but missed out one column. What will you do to rectify it?
One solution is to recreate the table and add the missed out column. In that case, you will have to delete the existing table and then recreate the table with all the columns. That is gonna take a lot of yours time. So, what can be the alternative to this?
We have the solution for you right here: ALTER Command.
Alter Command in SQL is so powerful that it contributes significantly more than just helping to add the column. With the Alter Command, you can change anything you think needs modification.
Wondering how?
Let us get started with the SQL ALTER TABLE Statement.
What is Alter Command?
The ALTER command in SQL is used to modify the structure of an existing database object, such as a table, index, or view. ALTER Command is a DDL(Data Definition Language) command.
In SQL, the ALTER TABLE command is used to alter or modify the structure of an existing database table, such as adding or removing columns, changing data types, renaming the table or columns, and so on.
Below are some characteristics of ALTER command in SQL:
-
Flexibility: The ALTER command provides a lot of flexibility to modify an existing database object without having to delete and recreate it from scratch. This can be useful when you have a large amount of data in the object that you want to preserve.
-
Modifies existing object: The ALTER command modifies an existing object rather than creating a new one. This means that any data or metadata associated with the object will be preserved, and any dependencies on the object, such as indexes or constraints, will remain intact.
-
Requires appropriate permissions: The ALTER command typically requires appropriate permissions to be executed. Depending on the database management system and the object being modified, these permissions may include ALTER, DROP, CREATE, or other permissions.
-
Syntax may vary: The syntax of the ALTER command may vary slightly depending on the database management system and the type of object being modified. It is important to consult the documentation for your specific database management system to ensure that you are using the correct syntax.
-
Can be used to undo changes: The ALTER command can also be used to undo changes that have been made to an object. For example, if you accidentally added a column to a table, you can use the ALTER command to remove it.
Let us now see the working of Alter command.
Following are a number of use cases of using ALTER Table Command in SQL: