Reasons for using hibernate
The JDBC API is used to establish a connection between a Java program and a database.
- We must create a few lines of code using JDBC to map objects from the model class to the appropriate relational database. Consequently, developers using Hibernate don't need to write these lines of code. The mapping is handled by Hibernate itself using XML files.
- JDBC only supports the SQL language. Contrary to this, Hibernate offers a Hibernate Query Language that will improve the efficiency of our code.
- The developer in JDBC must handle the JDBC resultset. This laborious task is managed by object table mapping in Hibernate.
- Caching in JDBC is kept up by manual code. It is automated in contrast to this.
Hibernate ORM Model
The term "ORM" stands for the object-relational mapping tool, which makes it simple for developers to write code. It offers relational database data persistence. You can map Java
classes to database tables and Java data types to SQL types with the aid of an ORM tool.
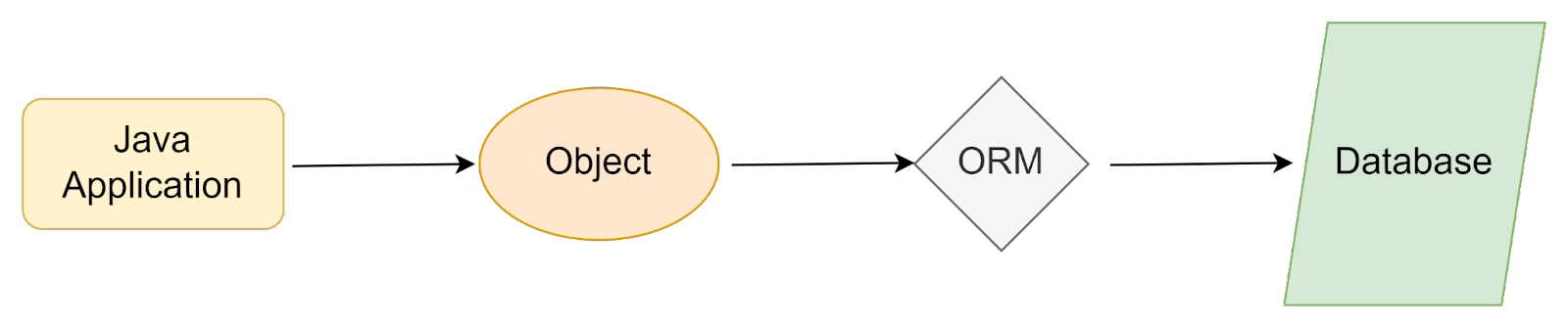
The following entities make up it:
- It offers an API for carrying out fundamental CRUD operations.
- It offers a query-specific API.
- It offers a setting for metadata mapping.
- Transactional objects are offered.
What is JPA?
A Java specification called Java Persistence API (JPA) offers specific capabilities and standards to ORM tools. The JPA classes and interfaces are contained in the javax.persistence package.
Functionalities provided by Hibernate
- It is database-independent because Hibernate uses the Hibernate Query Language.
- It supports automatic DDL procedures.
- Hibernate supports Auto Primary Key Generation.
- Memory cache is supported.
- Hibernate does not demand exception handling.
Architecture of Hibernate
A framework called Hibernate makes use of objects to create software-free persistence logic. A layered framework makes up the architecture. It has the subsequent layer.
- Java Application Layer
- Backend API
- Database Schema
- Hibernate Framework
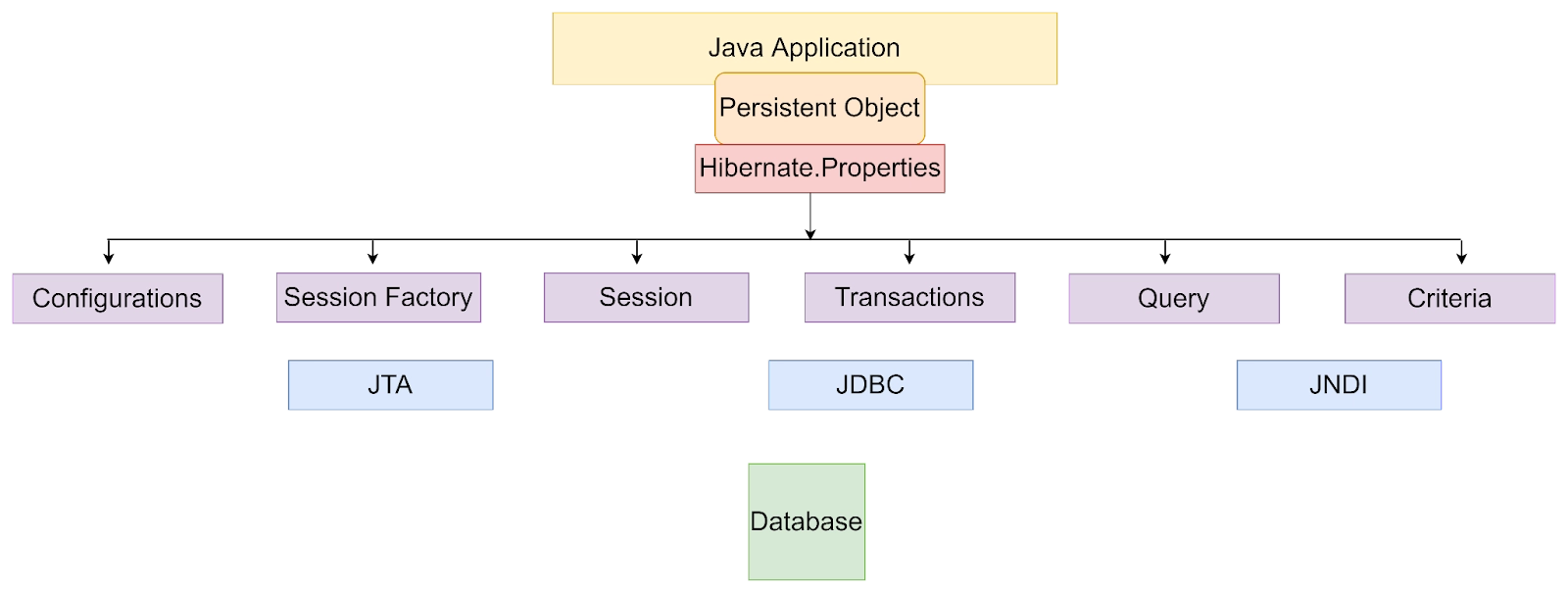
Configuration
- A class called configuration turns on the Hibernate Framework.
- It comprises a properties file and a configuration file.
- Configuration can be found in the package org.hibernate.cfg.
- When the application is first launched, the configuration is loaded.
SessionFactory
- The configuration object first creates the SessionFactory before the session Object is formed in org.hibernate.
- We require a single SessionFactory instance per database.
- It is a thread-safe and immutable object.
Sessions
- SessionFactory creates a Session object.
- It offers the actual database connection.
- The session objects are used to retrieve items saved in the database.
Transaction
- In computer science, the term "transaction" refers to whether all operations are completed or not. it is found in org.hibernate.
- It is handled by the transaction manager in Hibernate.
Query
- To get or create things, use the query object.
- It employs HQL or SQL.
- It is employed to carry out a question.
Criteria Object
- It is an entity retrieval object.
- Typically, it is employed for features like "search" displays.
Functionalities Supported by Hibernate
1. Object-Relational Mapping (ORM):
- Entity Mapping: Maps Java objects (entities) to database tables, allowing developers to interact with the database using high-level object-oriented code.
- Automatic Schema Generation: Can automatically generate database schema from entity classes.
2. Data Persistence:
- CRUD Operations: Supports Create, Read, Update, and Delete operations on persistent objects.
- Transactional Handling: Provides built-in support for transactions, ensuring data integrity and consistency.
3. Query Language:
- HQL (Hibernate Query Language): A powerful, object-oriented query language similar to SQL but designed for working with Java objects.
- Criteria API: Allows dynamic query construction using a type-safe, programmatic approach.
4. Caching:
- First-Level Cache: Automatically managed within the session scope, improving performance by reducing database access for repeated queries.
- Second-Level Cache: Optional and configurable, stores data across sessions to further reduce database access and improve performance.
5. Lazy Loading and Eager Loading:
- Lazy Loading: Delays the fetching of associated data until it is accessed, which can improve performance by reducing unnecessary data loading.
- Eager Loading: Fetches associated data at the same time as the primary data, which can be useful for complex queries where associated data is always needed.
6. Mapping Strategies:
- One-to-One, One-to-Many, Many-to-One, Many-to-Many: Supports various types of relationships between entities and allows for comprehensive mapping strategies.
- Inheritance Mapping: Provides strategies for mapping class hierarchies to database tables, including Single Table, Table per Class, and Table per Subclass.
7. Automatic Dirty Checking:
- Change Detection: Automatically detects changes to persistent objects and synchronizes the changes with the database at transaction commit.
8. Schema Validation and Export:
- Validation: Validates entity mappings against the database schema to ensure consistency and correctness.
- Export: Supports exporting schema definitions to create or update database schemas.
9. Event System:
- Event Listeners: Allows customization of behavior through event listeners for operations like save, update, and delete.
- Custom Callbacks: Provides hooks for custom actions before or after certain operations.
10. Integration with Other Technologies:
- JPA (Java Persistence API): Can be used as a JPA provider, integrating seamlessly with Java EE and Spring applications.
- Spring Integration: Provides support for integrating Hibernate with the Spring framework for dependency injection and transaction management.
11. Support for Multiple Databases:
- Database Independence: Supports various relational databases (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle) through its abstraction layer, allowing for flexible database management.
Advantages of Hibernate
- Its speed is fast because the hibernate framework uses cache internally. First-level cache and second-level cache are the two different forms of cache in the hibernate framework. By default, the first-level cache is enabled.
- The lightweight Hibernate framework is open source and licensed under the LGPL.
- The object-oriented equivalent of SQL is called HQL (Hibernate Query Language). It produces queries that are not dependent on a database.
- The database tables can be created automatically using the Hibernate framework. Therefore, there is no need to manually build tables in the database.
- The Hibernate framework makes it simple to fetch data from various tables.
- Hibernate offers statistics about the status of queries and databases and provides query caching.
Disadvantages of Hibernate
- Performance Overhead: Adds extra processing layers, which can slow down performance.
- Complexity: Steep learning curve and complex configuration.
- Debugging Difficulties: Harder to debug due to abstracted SQL queries.
- Session Management Issues: Risk of performance problems and memory leaks if not managed properly.
- Configuration Dependence: Requires precise configuration; errors can affect performance.
- Lazy Loading Problems: Can lead to issues if accessed data is no longer available.
- Database Compatibility: May not fully support all database-specific features.
Frequently Asked Questions
What distinguishes spring boot from hibernate?
While Hibernate framework is good for object-relational persistence, access data layers, and query retrieval services for enterprise-level applications, the Spring framework is useful for transaction management, dependency injection, and aspect-oriented programming for applications.
What are ORM and JPA?
Java objects are changed into database tables through a technique known as object-relational mapping (ORM). In other words, this enables SQL-free interaction with a relational database. How to persist data in Java programs is specified by the Java Persistence API (JPA) specification.
What does Hibernate's lazy loading mean?
The lazy setting is used to determine whether to load child objects while loading the parent object This setting must be made in the parent class's appropriate hibernate mapping file. True = Lazy (means not to load child) then the child objects' sluggish loading is enabled by default.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed what hibernate is. Hibernate is a powerful Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) framework that simplifies database interactions by mapping Java objects to relational database tables. It provides a range of features, including automatic schema generation, advanced querying capabilities, and efficient data management through caching. Hibernate’s ability to handle complex relationships and support for various database systems make it a versatile tool for Java developers.








