First Level Cache
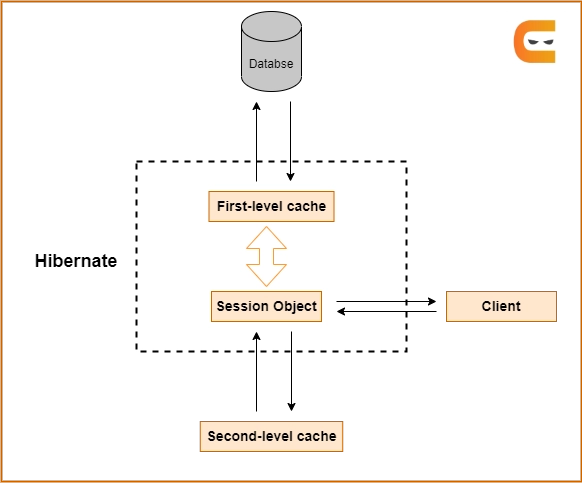
The First Level Cache is also known as "Session Cache." This is a basic cache that comes with hibernation by default. It receives and processes all request objects. Now, the application can use this cache by transmitting numerous session objects.
All cache objects will be kept until one session is open. If multiple update statements are ordered using the session cache. Then, the database attempts to reduce the number of hits. This cache is also cleaned depending on when the session ends. And the objects it contains are either committed, persisted, or deleted without updating.
Some Facts about First Level Cache
-
The First level cache in the Hibernate is enabled by default. There are no configurations needed for this.
-
The first level cache in Hibernate is session-specific. So, when we receive the same data in the same session, no query is issued. However, in another session, a query is issued to load the data.
-
A single object can be removed from the hibernate First level cache using the session evict() method.
-
We can use the session clear() method to clear the cache completely- delete every object from the cache.
- To check if an object is in the hibernate cache or not, we can use the session contains() method. If the item is discovered in the cache, it returns true; otherwise, it returns false.
Second Level Cache
Second Level Cache is disabled by default. The developer needs explicitly to enable the Second Level Cache. And the SessionFactory object is liable for maintaining it. Since the entire program has access to the Second Level Cache, all sessions can access the data held by the SessionFactory.
When the session factory closes, all of the connected caches are likewise deleted from the RAM.
Some Facts about Second Level Cache
-
We can use hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache to enable the second level cache.
-
We can use hibernate.cache.use_query_cache to enable the query cache. Without it, HQL query results will not be cached.
- We can use net.sf.ehcache.configurationResourceName to define the EHCache configuration file location. It is an optional parameter. And if it's not present, EHCache will try to locate the ehcache.xml file in the application classpath.
Working of Hibernate Caching
In the "What is Hibernate Caching" series, we will now discuss the working of Hibernate Caching. As we all know, Hibernate is an ORM tool used to optimize DB operations. To store data in a database, it "converts objects to relations and vice versa."
An entity or object is thus retrieved from the database and stored in the First level cache when you query it for the first time (associated with the hibernate session). The entity or object will be loaded from the cache, and no SQL query will be run if we query for it again with the same session object.
Advantages of Hibernate Caching
After learning "What is Hibernate Caching," Now, let's discuss some advantages of Hibernate Caching:
-
Hibernate is better than JDBC.
-
Mapping of Domain object to the relational database.
-
It supports Layered Architecture, and you can use the components as per application requirements.
-
It supports JPA and can work as a JPA provider.
-
It supports the Standard ORM solution.
-
It is Database Independent.
- Caching Framework.
Disadvantages of Hibernate Caching
If there are advantages, then there will be disadvantages too. So, in our ‘what is hibernate caching series’, let's discuss some disadvantages of Hibernate Caching:
-
You need to give a lot of effort to grasp everything in Hibernate Caching as there is a lot of APIs to learn.
-
As there are many APIs, it is obvious that it will take time to find a bug. So another disadvantage is sometimes debugging and tunning performance becomes hectic.
-
It is slower than JDBC.
- It is not suitable for Batch Processing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where can we store Hibernate Caching?
Hibernate Session is its First level cache. It is the object in a heap, so it is in RAM. Usually, a system has enough RAM (>256MB) to store queries. If you think the loaded objects are too many in session, you can evict some from the first-level cache before the session is closed.
What is Query Cache in Hibernate?
An application level cache for holding entity data is the Hibernate second level cache. Only query results are stored in the separate query cache. Since we often want to use one cache without the other, the two caches fully reflect one another.
What is the Cache region in Hibernate?
Hibernate will use a separate cache region to hold the state of instances for each entity class. The fully qualified class name is the region name. For instance, Foo instances are stored in a cache named com.
Conclusion
We have discussed the topic of "What is Hibernate Caching." We have seen types of Hibernate Caching. Along with this, we have discussed some pros and cons also.
We hope this blog has helped you enhance your knowledge of "What is Hibernate Caching." If you want to learn more, check out our articles HB Web Application, Hibernate Sessions, HB Generator Classes, and many more on our platform Coding Ninjas Studio.
But suppose you have just started your learning process and are looking for questions from tech giants like Amazon, Microsoft, Uber, etc. In that case, you must look at the problems, interview experiences, and interview bundle for placement preparations.
However, you may consider our paid courses to give your career an edge over others!
Happy Learning!