Why do we need Word Embeddings?
We need Word Embeddings to
- represent words in a lower-dimensional space as higher-dimensional and sparse representations don’t do well in machine learning algorithms, as we will need higher computational resources for training.
- capture semantics, the meaning of words.
- approximate meaning of words using known words.
- visualize or understand the underlying pattern of text data.
Word Embeddings helps in various tasks such as analyzing survey responses where they capture the relationship between survey responses and the context of the survey to get actionable insights for our business quickly.
Similarly, Word Embeddings are very useful in recommendation systems such as movies or songs. While recommending songs to a user with analyzing what other similar people listen to, it is important to analyze what songs are similar in nature to what the user listens to. For example, the Word2Vec model, which is a word embedding, can help map the songs heard by a user on a map and then predict the context in which the song was played so that we can recommend songs of similar context, which is so amazing!
Types of Word Embeddings
Now we will discuss some prominent word embedding techniques.
-
TF-IDF
- It is a statistical model that helps capture the relevance of words from the corpus and the collection of words. It doesn’t capture the semantics of words.
- It combines TF - Term frequency, frequency words in the doc, and IDF - Inverse Document frequency, which focuses on finding the rarity of words. IDF balances TF as TF focuses on more frequently occurring words, and IDF focuses on rare words, and rare words can also store important information.
- It is helpful for keyword extraction, information retrieval, etc.
-
Word2Vec
- This technique helps to gain contextual information and capture the semantics from the text.
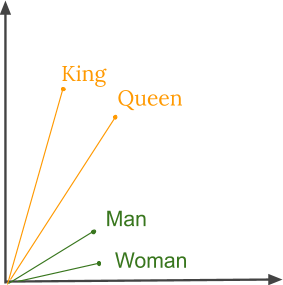
- It uses cosine similarity to find the similarity among words. A cosine angle of 0 means that words are overlapping, and a cosine angle of 90 means that the words have no contextual similarity. Similar words are assigned similar vectors.
- It is helpful in sentiment analysis, recommendation systems, etc.
-
It has two types
-
CBOW - Continuous Bag of Words
Here the neural network model takes multiple words as input to generate a feature space where every word is assigned a vector.
It can efficiently represent frequently occurring words.
-
Skip gram
It takes only one word as input and predicts words in a limited range before and after the current word.
It efficiently represents rare words as we do not average the word embeddings for predictions. It takes longer to train than Word2Vec as it involves more calculations.
-
FastText
- It is an extension of Word2Vec, and it represents every word as n-grams of characters instead of directly learning word vectors as in Word2Vec.
- This approach helps in representing rare words can give representation for out of vocabulary words, too, as the words are broken into n-grams.
-
It works great on small datasets, even better than Word2Vec and GloVe.
-
GloVe - Global Vectors
- It captures global contextual information by using the global word-to-word co-occurrence matrix and solves the limitation of Word2Vec as Word2Vec only captures local context. Overall, both Word2Vec and GloVe are good at capturing contextual information, and performance varies with different tasks.
- This technique requires low computational cost for training as it has a simple error function.
- It is helpful in jobs such as word analogy, named entity recognition.
-
BERT - Bidirectional Encoder Representations From Transformers
- It has an attention-based transformer mechanism that helps capture high-quality contextual information. The word embeddings also keep track of the pattern in words by the positional encoding of words.
- It is used in the google search engine to understand the search queries. It can be used in question-answering, language translations, and tasks that highly depend on the contextual information of the data.
FAQs
1. What is Word Embeddings?
Word Embeddings refers to numeric vectors used to represent words in lower-dimensional space, and it allows words with similar meanings to have similar representations.
2. Why is Word Embeddings used in NLP?
Word Embeddings are helpful to represent words in lower-dimensional space. It allows words with similar meanings to have similar representations, and it can be used to approximate the meaning of words.
3. Is Bag of Words a word embedding?
Yes, Bag of Words (BoW) is a word embeddings technique that uses the vocabulary of known words and the measure of the presence of words to represent words.
4. What is Word2Vec Word Embeddings?
Word2Vec Word Embeddings helps capture text's contextual information and semantics. Using the Gensim library, we can easily use the Word2Vec model to generate word embeddings.
5. What is GloVe in NLP?
GloVe, which stands for global vectors is an unsupervised learning algorithm used for getting word embeddings. It uses a global word-to-word co-occurrence matrix from the text to generate the embeddings.
Key Takeaways
This article discussed Word Embeddings, why we need them, their uses, and the different types of Word Embeddings algorithms present.
We hope this blog has helped you enhance your knowledge regarding Word Embeddings and NLP and if you would like to learn more, check out our free content on NLP and more unique courses. Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
Happy Coding!