Introduction
CASE is a tool that helps a software engineer to maintain the level of the software. This CASE tool is an integrated part of the workshop of Software Engineering, which is called the integrated project support environment (IPSE). It is used to support and automate activities throughout the systems development life cycle (SDLC). It makes the software development process easy and efficient.
To know about Computer-Aided Software Engineering (CASE) from basics, visit the article on Introduction to CASE and its tools.
Let’s see the architecture of CASE.
Architecture of CASE
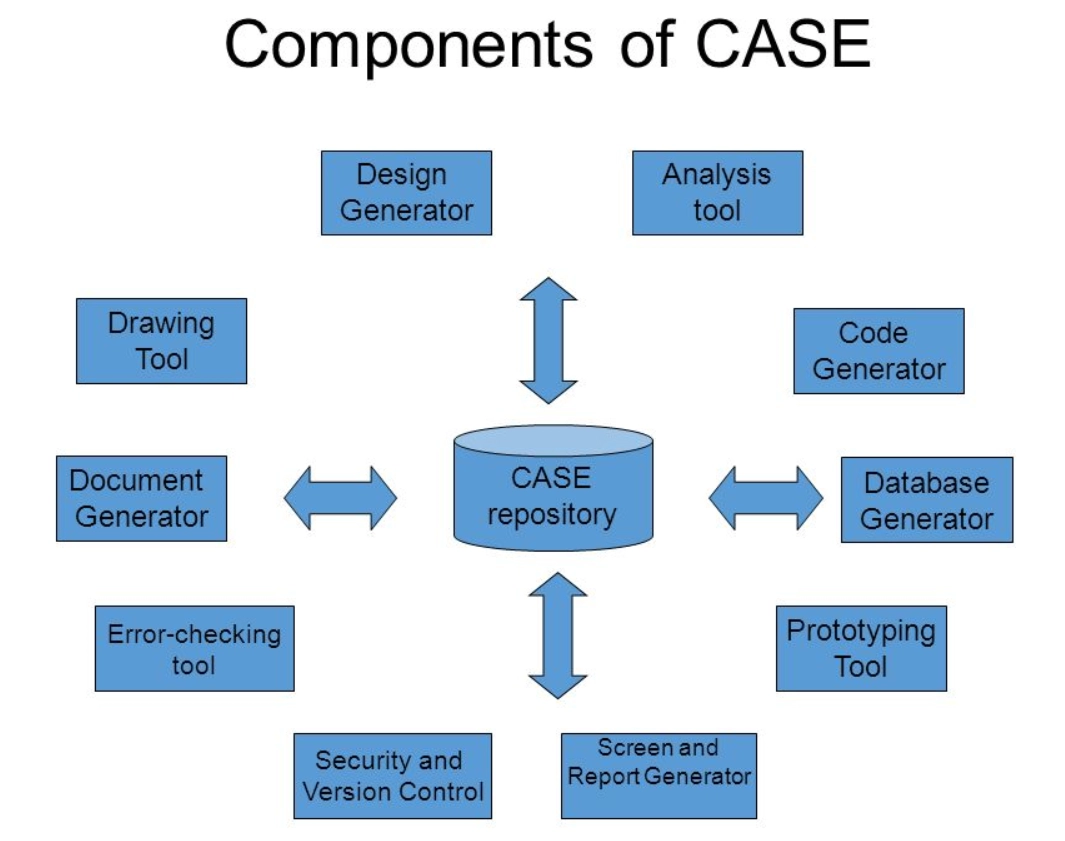
Important components of a modern CASE environment are
- User interface
- Toolset
- Object management system
-
CASE repository
-
User interface
The user interface provides a common framework for accessing different tools by simplifying and reducing the time of learning of the tools.
-
Toolset
It controls the behavior of the tool within the environment by performing multitask synchronization and composition and coordinating the flow of information repository to OMS into the tools. It provides a security function that collects feedback on tool usage.
-
Object management system
It performs the mapping of logical entities such as specification data, design data, project planning data, etc., into the storage management system. i.e., repository. It also has an object management language (OML) module to provide support for version control, change control, status control, and security control.
-
CASE repository
This is the case database containing an access control function to enable the OMS to interact with the database.