Introduction
Azure Files is a cloud storage service for file sharing, debugging tools, and applications that count on native file systems. Using the Azure CLI or PowerShell, you can create and manage your file shares using the built-in UI. You can use azure files to replace traditional on-premises file servers or NAS devices. Azure file shares can be directly mounted by popular operating systems such as Windows, macOS, and Linux. In this blog, we will learn about Azure files fundamentals. Let us dive deeper into the topic.
Azure Files Fundamentals
As we read in the previous paragraph, Azure Files are cloud storage services that offer entirely managed file shares in the cloud accessible through the industry-standard SMB protocol or NFS protocol. Azure Files file shares can be mounted concurrently by cloud or on-premises deployments. SMB Azure file shares are accessible from Windows, Linux, and macOS clients. NFS Azure Files shares are accessible from Linux or macOS clients. Additionally, you can cache SMB Azure file shares on Windows Servers with Azure File Sync for fast access.
Azure Files can be used in the following situations:
- File shares are used by many on-premises applications. Azure Files makes migrating those applications that share data to Azure easier. If the Azure file share is mounted to the same drive letter that the on-premises application uses, the part of your application accessing the file share can work with minimal changes.
- For storing configuration files on a file share and accessing them from multiple VMs. You can store tools and utilities used by various developers in a group on a file share, ensuring that everybody can find and use the same version.
- For writing data to a file share and analysing it later. For example, you might want to do this with diagnostic logs, metrics, and crash dumps.
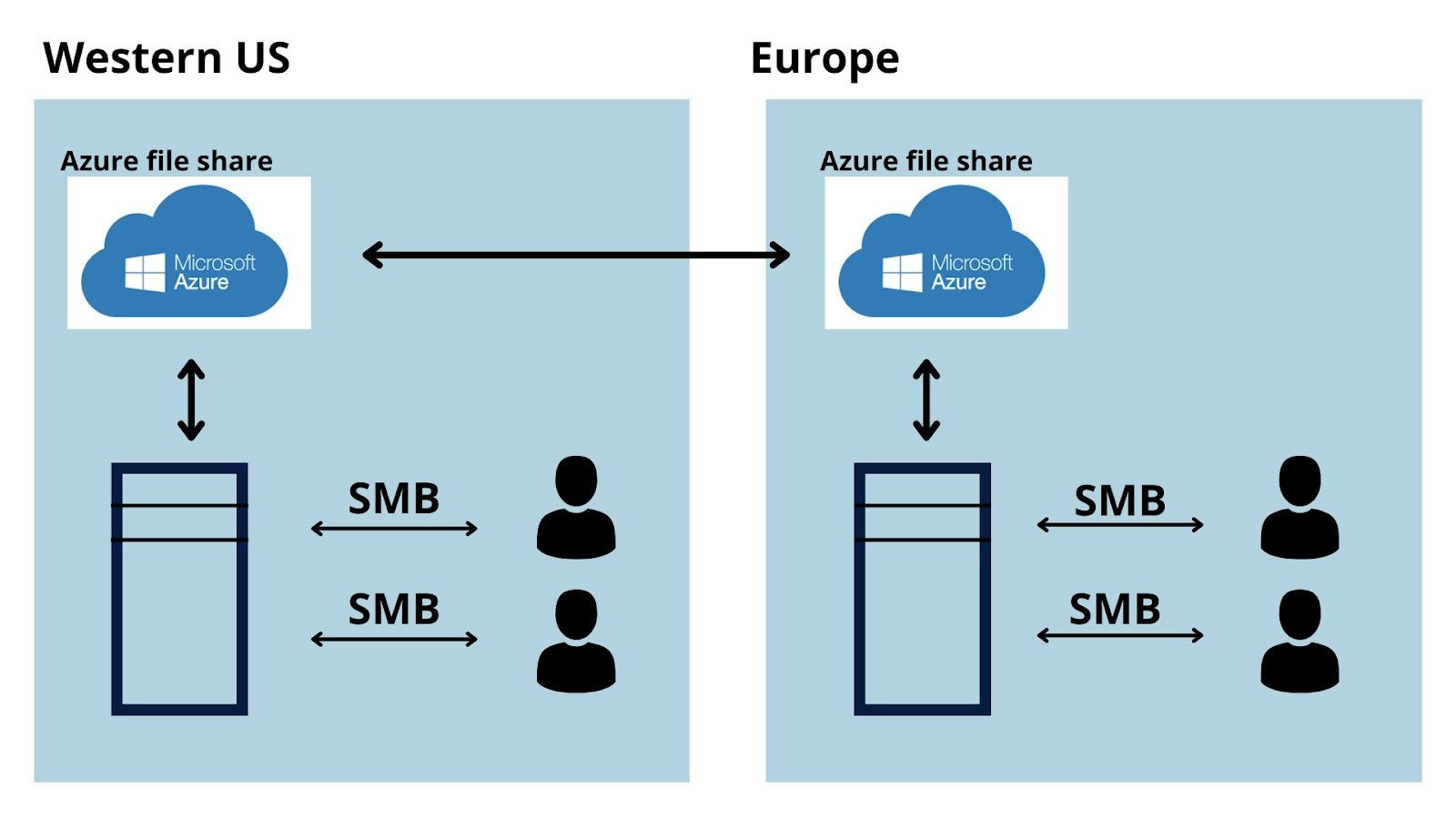
The above image illustrates Azure Files sharing data from one geographical location to another. Azure Files ensures the data is encrypted at rest, and the SMB protocol ensures the data is encrypted in transit.