Attributes of h:commandButton
Each tag comes with multiple attributes. Listed below are the attributes of the JSF h:commandButton tag.
- id: The tag’s identifier
- rendered: A boolean value where false would suppress the rendering
- styleClass: class name of Cascading stylesheet (CSS)
- value: The value binding
- valueChangeListener: A method binding that responds to changes in value
- required: A boolean; if set to true, marks the tag as needed
- coords: An element’s coordinates whose shape is a rectangle, circle, or polygon
- dir: Direction for text. ltr (left to right) and rtl (right to the left) are valid values.
- disabled: An Input element or button disabled state
- style: Inline style info
- tabindex: Numerical value to specify a tab index
- target: The name of a frame in which the document is opened
- title: We can use a title for accessibility. Browsers typically create tooltips for the value of the title
- width: An element’s Width
- onblur: Event handler for losing focus
- onchange: Event handler for changes in value
- onclick: Event handler for the click of the Mouse button over the element
- ondblclick: Event handler for double-click of the Mouse button
- onfocus: Event handler for element received focus
- onkeydown: Event handler for Keypress
- onkeypress: Event handler for Key press and release
- onkeyup: Event handler for Key release
- onmousedown: Event handler for Mouse button press
- onmousemove: Event handler for mouse movement
- onmouseout: Event handler for mouse moved left
- onmouseover: Event handler for mouse moved onto
- onmouseup: Event handler for mouse button released
- onreset: Event handler for form reset
- onselect: Event handler for selected Text
Example
Now that we have seen the attributes and the basic syntax of the h.commandButton tag, we can move forward with the implementation using an elementary example.
test.xhtml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html"
xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core"
xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets">
<h:head>
<title>JSF command button example.</title>
</h:head>
<h:body>
<h3>JSF command button example.</h3>
<h:form>
<h:commandButton value="Say Hello" action="welcome" />
</h:form>
</h:body>
</html>
welcome.xhtml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html"
xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core"
xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets">
<h:head>
<title>JSF command button example.</title>
</h:head>
<h:body>
<h3>Hello World.</h3>
</h:body>
</html>
faces-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1252"?>
<faces-config version="2.0"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XInclude"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-facesconfig_2_0.xsd">
<navigation-rule>
<from-view-id>test.xhtml</from-view-id>
<navigation-case>
<from-outcome>success</from-outcome>
<to-view-id>welcome.xhtml</to-view-id>
</navigation-case>
</navigation-rule>
</faces-config>
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="3.0"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>faces</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
javax.faces.webapp.FacesServlet
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>faces</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/faces/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Output

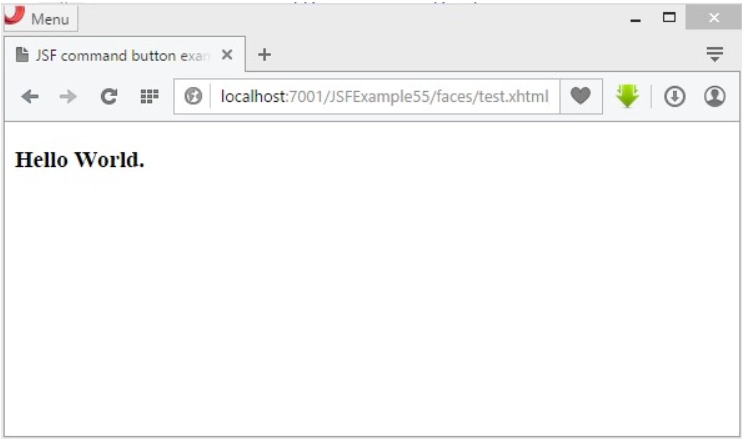
After clicking the Say Hello button, you should see the following page appear.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a Button and a Command Button?
- h:button: On clicking the h:button issues GET requests that we can bookmark.
- h:commandButton: Instead of a get request, issues a POST request which sends the form data back to the server.
What is a JSF tag?
JSF provides a standard HTML tag library. These tags render into corresponding html output. For these tags, we need to use some namespaces of URI in the html node.
What is the JSF form?
The <h:form> tag in JSF represents an input form with child components that may contain data presented to the user or submitted with the form. It might also include HTML markup laying out the components on the page.
What is a facet tag in JSF?
A facet tag in a project is a specific unit of functionality you can add to a project when you require that functionality. When you add a project facet to a project, it can add nature, classpath entries, builders, and resources to that project, depending on the nature and characteristics.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we have understood the functionalities, attributes, implementations, and needs of the commandButton Tag in JSF. We hope this article helped you in your journey towards mastering JSF.
Please see our Code studio guided routes to learn more about DSA, Competitive Programming, JavaScript, System Design, and other topics. Also, enroll in our courses and use the accessible sample tests and problems. For placement preparations, have a look at the interview experiences and interview bundle.
Happy Learning!






