Introduction
Before discussing deletion in the Red-Black Tree, let’s revisit the properties of the Red-Black Tree. A red-black tree is one type of binary search tree that satisfies the following properties:
- Every node is either red or black.
- The root is black.
- Every leaf (nil) is black.
- If a parent node is red, then both of its children are black.
- All simple paths from the node to descendant leaves contain the same number of black nodes for each node.
The deletion in the red-black tree is similar to the deletion operation in a binary search tree. But nodes have a colour property. After the deletion operation, we need to check all the properties of the red-black tree. If all the properties are not satisfied, we perform the following operation to make it a red-black tree.
- Recolour
- Rotation followed by recolouring.
Algorithm
- The first step is to perform the process of deletion in BST. This step is the same as any BST. While performing this type of deletion, we always end up deleting a node that either has only one child or is a leaf. So we only need to handle cases where the node is a leaf node or has only one child. Let v be the node to be deleted, and u be the child that replaces v.
2. If either v or u is red, we mark the replaced child as black (deletion causes no change in black height). Note that as v is the parent of u, and two consecutive reds are not allowed in the red-black tree, both u and v cannot be red.
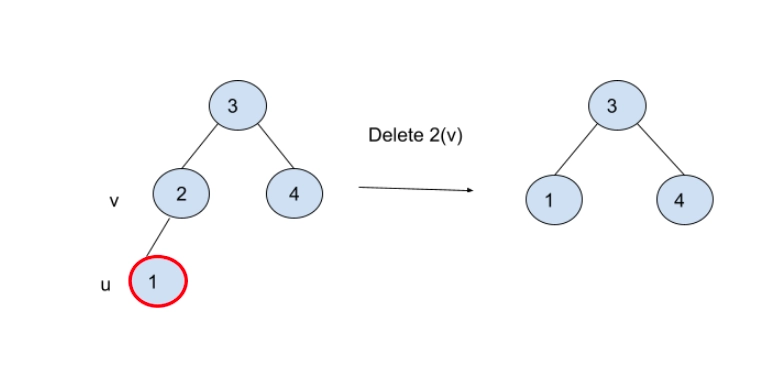
3. If Both u and v are Black
- colour u as double black (keeping a node double-black, we know exactly where the black shortage is). Now the task reduces to convert this double black to single black. Note that If v is a leaf, then u is NULL, and the colour of NULL is considered black. So the deletion of a black leaf causes a double black.
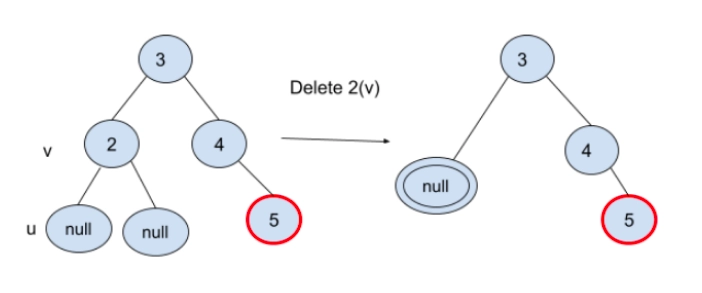
- For a sibling node s of current node u that is double black but not the root
Case 1:
If sibling node s is black and at least one of its children is red, perform rotation for rebalancing the red-black tree. This case can be divided into four subcases depending upon positions of s and r, red child of s .
1. right-right( where s is the right child of its parent and r is the right child of s, or both children of s are red). See the below diagram for a better understanding.

2. right-left( where s is the right child of its parent and r is the red left child of s). See the below diagram for a better understanding.

3. left-left( where s is left child of its parent and r is left child of s; it is mirror case of the right-right case)
4. left-right(where s is left child of its parent and r is right child of s; it is mirror case of the left-right case)
Case 2:
If the sibling s is black and both of its children are black,
perform recolouring of nodes, and recur for the parent if the parent is
Black. See the below diagram for a better understanding.

Case 3:
If sibling s is red, perform a rotation to move the old sibling node up,
recolor the old sibling and parent. The new sibling is always black (See
the below diagram). This converts the tree to the black sibling case (by
rotation) and leads to previous cases. This case is divided into two
subcases; left and right cases.
1. right case(s is right child of its parent): left rotate the parent p to move the node up. See the below diagram for a better understanding.

2. left case ( s is left child of its parent): this mirror of the previous case. Here we perform the right rotation.
4. If u is the root, make it single black




