Introduction
Flask is a web framework in Python. It is called a microframework since it doesn’t require any particular tools or libraries to compile Flask files.
The url_for() function is used to build a URL to the specific function dynamically. The first argument is the name of the specified function, and then we can pass any number of keywords as arguments corresponding to the variable part of the URL.
This function is helpful because we can avoid hard-coding the URLs into the templates by dynamically building them.
Example with Code
Let us look at an example of URL building using Flask to understand this concept better,
from flask import *
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/ios')
def ios():
return '<h1>User Selected IOS<h1>'
@app.route('/windows')
def windows():
return '<h1>User Selected Windows<h1>'
@app.route('/android')
def android():
return '<h1>User Selected Android<h1>'
@app.route('/prod/<name>')
def user(name):
if name == 'ios':
return redirect(url_for('ios'))
if name == 'windows':
return redirect(url_for('windows'))
if name == 'android':
return redirect(url_for('android'))
if __name__ =='__main__':
app.run(debug = True) We have declared three URLs for IOS users, Windows users, and Android users in the above code. The prod function redirects the user to the respective URL mentioned in the route.
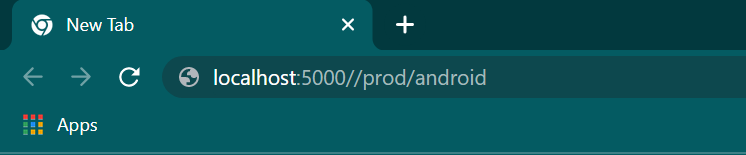
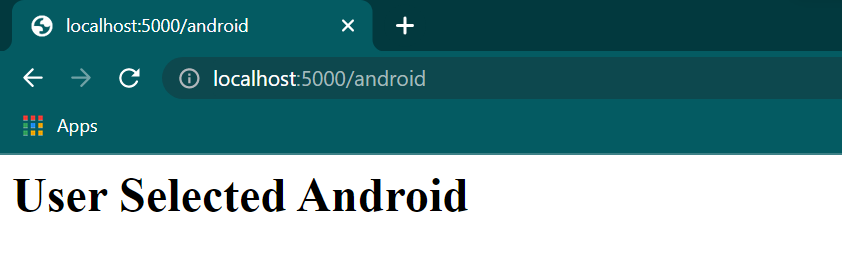
For example, the URL localhost:5000//prod/android is redirected to localhost:5000//android.
Also Read About, PHP For Loop




