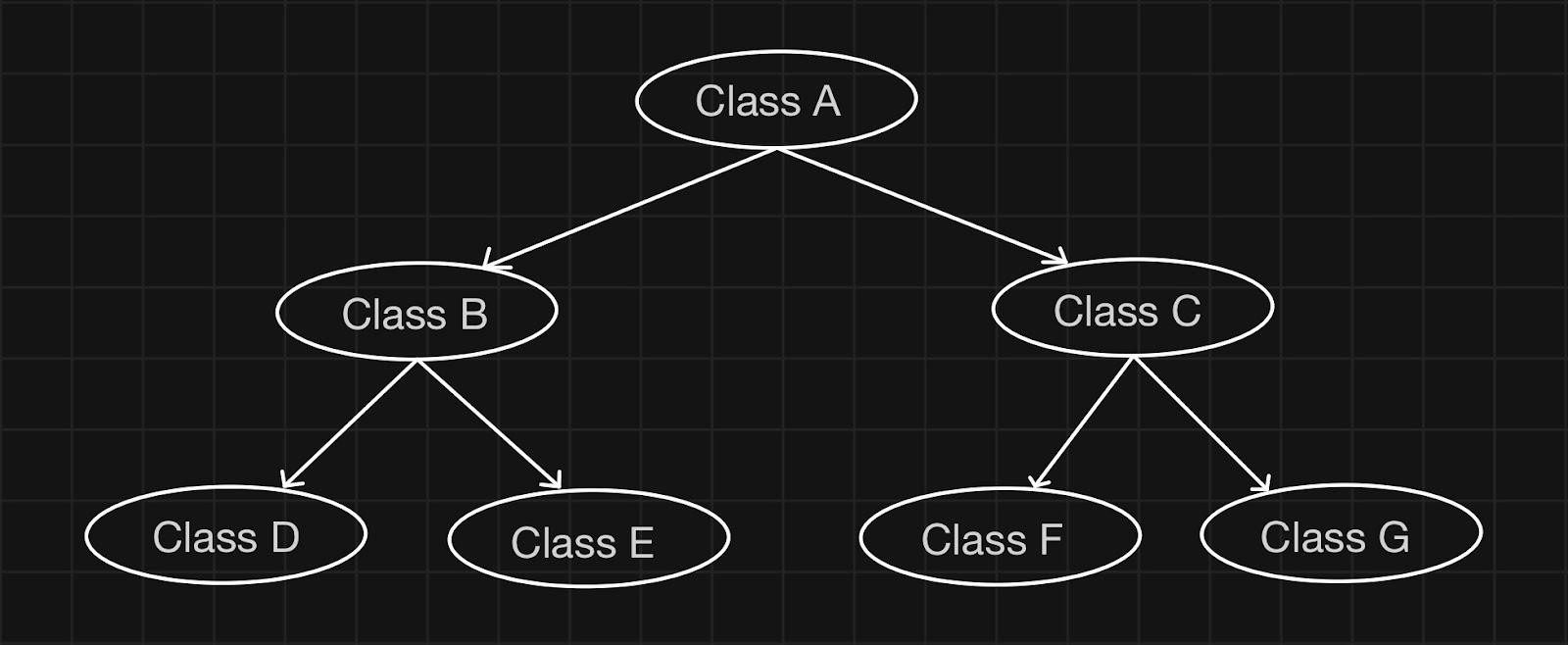
Syntax Of Hierarchical Inheritance In C++
Class Parent
{
//Data members and member functions of Parent Class
}
Class Derived-1 : access modifier Parent
{
//Data members and member functions of Derived-1 class
}
Class Derived-2 : access modifier Parent
{
//Data members and member functions of Derived-2 class
}
How Does Hierarchical Inheritance Works In C++?
In C++, hierarchical inheritance involves creating a class hierarchy where multiple derived classes inherit from a single base class. Each derived class inherits the properties and behaviors of the base class, forming a tree-like structure. For example, consider a base class "Vehicle" with derived classes "Car" and "Motorcycle." Both "Car" and "Motorcycle" inherit common attributes and methods from "Vehicle" but can also have their unique features. This allows for code reuse and promotes modularity, as changes made to the base class propagate to all derived classes. Hierarchical inheritance facilitates organizing classes based on their relationships and promotes a more structured and scalable codebase.
What Is The Use Of Hierarchical Inheritance In C++?
Hierarchical inheritance in C++ allows for the creation of class hierarchies where multiple derived classes inherit from a single base class. It promotes code reuse, as common properties and behaviors defined in the base class can be inherited by multiple derived classes. This reduces redundancy and improves maintainability by centralizing shared functionality in one place. Additionally, hierarchical inheritance facilitates polymorphism, enabling derived classes to override inherited methods to provide specialized behavior while still maintaining compatibility with the base class interface. Overall, hierarchical inheritance enhances code organization, modularity, and extensibility in C++ programs.
Visibility Modes in Hierarchical Inheritance in C++
In hierarchical inheritance, C++ supports three visibility modes: public, protected, and private. Public inheritance allows public and protected members of the base class to be inherited as public and protected members, respectively, in the derived class. Protected inheritance inherits public and protected members of the base class as protected members in the derived class, whereas private inheritance inherits them as private members. These visibility modes control the accessibility of base class members in derived classes, influencing the level of encapsulation and the relationship between base and derived classes.
Example of Hierarchical Inheritance in C++
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class X
{
public:
int x, y;
void getdata()
{
cout << "Enter value of x and y:\n"; cin >> x >> y;
}
};
class Y : public X
{
public:
void difference()
{
cout << "Difference= " << x - y<<endl;
}
};
class Z : public X
{
public:
void sum()
{
cout << "Sum= " << x + y<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Y obj_1;
Z obj_2;
obj_1.getdata();
obj_1.difference();
obj_2.getdata();
obj_2.sum();
return 0;
}

You can also try this code with Online C++ Compiler
Output
Enter value of x and y:
10 6
Difference= 4
Enter value of x and y:
12 5
Sum= 17
Explanation
In the given example, Class X is the base class from which 2 classes: Class Y and Class Z are derived. Class X has two data members and a member function that gets the value for its data members, this is used by Class Y and Class Z in order to get their respective operands so that they can perform their operations.
Know about Single Inheritance in Java in detail.
Frequently Asked Questions
When to use hierarchical inheritance?
Hierarchical inheritance is used when we need to represent or maintain a hierarchy.
What is the difference between hierarchical inheritance and multiple inheritance?
Hierarchical inheritance is when more than one class is derived from a base class, whereas, in multiple inheritance, a single class is derived from multiple base classes.
What is a Hierarchical Family Structure?
A hierarchical family structure refers to an organization where family members are arranged in a hierarchy, with roles and authority distributed in levels. Typically, parents hold the highest authority, followed by children and other relatives, creating a clear chain of command.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hierarchical inheritance in C++ provides an efficient way to share common functionality among multiple derived classes, promoting reusability and reducing code duplication. By allowing multiple classes to inherit from a single base class, it simplifies the design of systems with common attributes or behaviors.
Recommended Readings: