Example
Let us have a graph with five vertices and seven edges. We have to calculate its minimum cut.
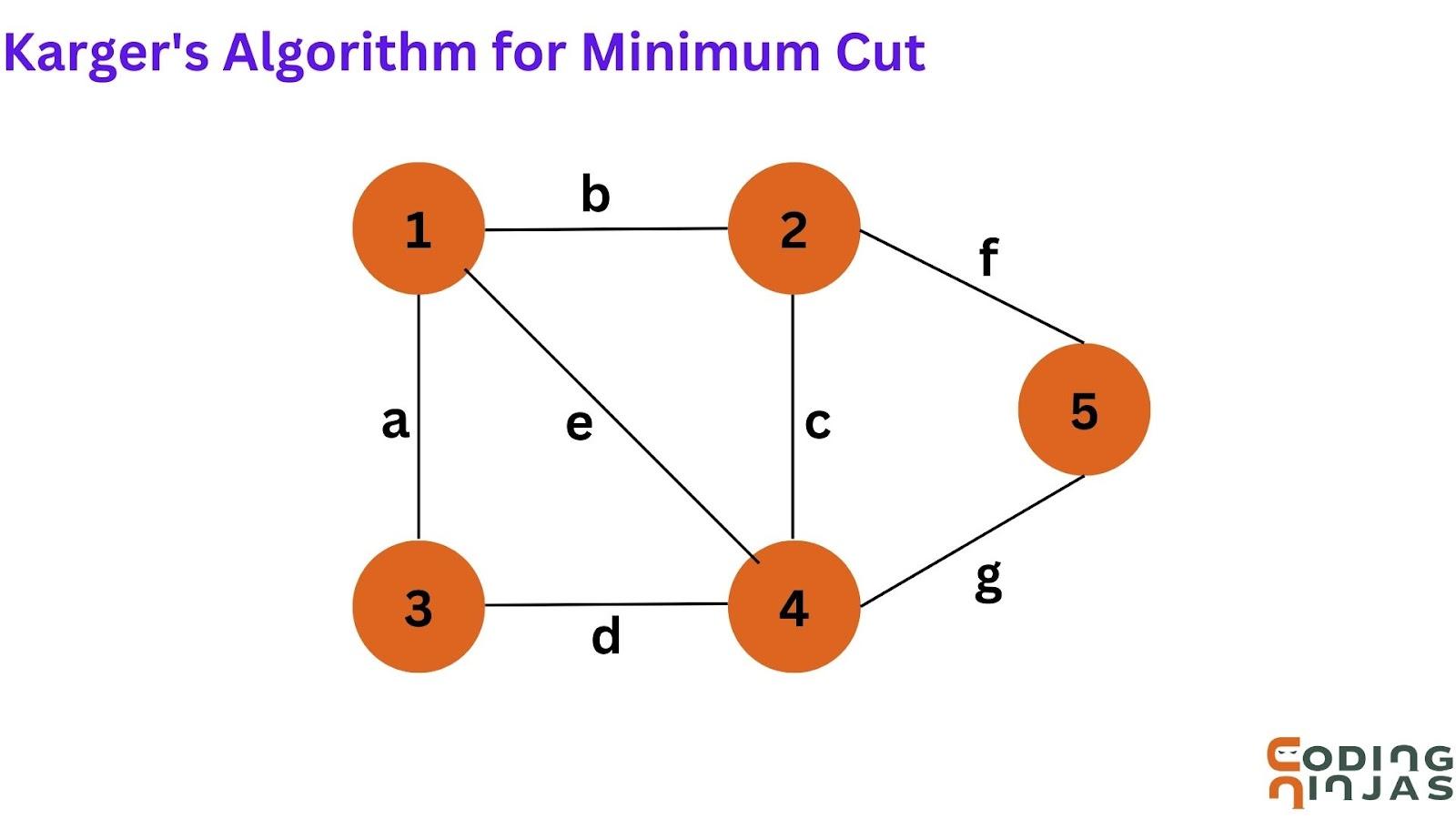
We choose a node a to contract. Then, Nodes 1 and 3 will be merged into a single node, as shown in the figure.

We choose to contract edge c. Here, nodes 2 and 4 will be merged into a single node, and all the edges are adjusted accordingly.

Now, we choose edge e to contract. Then both the above supernode, i.e., {1,3},{2,4}, will be merged in a single node, as shown in the figure below. Hence, we get a node {1,3,2,4}.

Now we get our resultant contracted graph containing only two vertices; hence, this is the minimum cut.
We can also remove the edges f and g from the graph to divide it into two components, as shown in the figure below.


Now, it's time to discuss the Algorithm used in Karger's Algorithm for Minimum Cut.
Algorithm
The first step is to make a copy of the graph (say CG)
While the CG (Contracted Graph) contains more than two vertices
- Select a random edge (say (u,v)).
- Contract the graph in one vertex.
- Remove self-loop.
Return the cut, which is represented by two vertices.
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: The time complexity of Karger's Algorithm for Minimum Cut is O(V^2).
For graph G with V vertices and E edges, when it is implemented by using the most optimized DSU approach is O(E∗α(V)) because, in every iteration, we are contracting the edges in the contracted graph.
Since O(E∗α(V)) = O(E) and since the maximum number of edges in a graph is an order of V^2. Therefore the time complexity is O(V^2) in terms of V.
Read More - Time Complexity of Sorting Algorithms
Let's discuss FAQs related to Karger's Algorithm for Minimum Cut.
Must Read Algorithm Types
Frequently Asked Questions
What do you mean by a randomized algorithm?
A Randomized Algorithm is an algorithm that uses random numbers to decide what to do next in its logic.
What are the two main types of randomized algorithms?
Las Vegas and Monte Carlo algorithms are the two main types of randomized algorithms.
Karger's Algorithm is which type of randomized algorithms?
It is a "Monte Carlo" algorithm, which may also produce the wrong output. But the probability is very low.
What are the different applications of Karger's Algorithm for Minimum Cut?
Karger's Algorithm for Minimum Cut can be used to get an idea about the reliability of a network and is also used in image segmentation.
What is the advantage of randomized min cut?
The main advantage is performance, as the randomized algorithms run faster than the deterministic algorithms for many problems. It is also easy to describe and implement.
Conclusion
We have discussed the Introduction to Karger's Algorithm for Minimum Cut, in which we have addressed the problem with an example. We also cover its time complexity and FAQs related to them.
After reading about the introduction to Karger’s Algorithm for Minimum Cut, are you not feeling excited to read/explore more articles on Data Structures and Algorithms? Don't worry; Coding Ninjas has you covered. See Graph, Binary Tree, BFS vs DFS, Check for Balanced Parentheses in an Expression, and Stack to learn.
Refer to our Guided Path on Coding Ninjas Studio to upskill yourself in Data Structures and Algorithms, Competitive Programming, JavaScript, System Design, and many more!
Do upvote our blogs if you find them helpful and engaging!
Happy Learning!












